Abstract
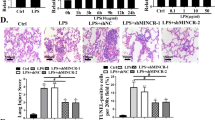
Limb ischemia reperfusion (I/R) triggers local or systemic injury, and whether the process is mediated by pyroptosis remains unclear, we aimed to explore whether pyroptosis was involved in the process of rapamycin alleviating lung injury induced by I/R and investigate the molecular mechanisms. The histopathology of lung injury induced by I/R was confirmed by hematoxylin–eosin (HE) staining, and malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and the expression of pyroptosis related molecules were detected. RNA sequencing was used to mine key long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). The model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced L2 cell damage was also used to explore the effect and mechanism of rapamycin on lncRNA. Rapamycin treatment alleviated I/R—induced lung histopathologically injury and increased the concentration of MDA while decreased activity of SOD and expression of NLRP3, Caspase-1, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and IL-18 in rat. A total of 63 differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) were identified from IR + Rap group compared with IR group, and these DElncRNAs were mainly involved in cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) and endocytosis pathway. The lncRNA LOC102553434 and its target gene MMP9 were most significantly up-regulated in I/R-injured rat. In vitro experiments showed that LPS induction caused a significant increase in LOC102553434, MMP9, IL-1β, and IL-18 in L2 cells, but rapamycin treatment significantly reversed the effects. After interfering with the expression of LOC102553434 in the LPS-injured cells pretreated with rapamycin, cell proliferation significantly increased, and the expression of MMP, NLRP3 and caspase-1 were significantly decreased. Rapamycin protects the lung from limb I/R injury by regulating LOC102553434 expression and inhibiting pyroptosis pathway. LOC102553434 plays a role in promoting pyroptosis and thus provides a target for clinical treatment of I/R-induced lung injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The RNA-seq data generated in this study is available from NCBI under accession numbers PRJNA682855. Other data used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Chen L et al (2017) The antioxidant procyanidin reduces reactive oxygen species signaling in macrophages and ameliorates experimental colitis in mice. Front Immunol 8:1910. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01910
Fang X, Tao D, Shen J, Wang Y, Dong X, Ji X (2015) Neuroprotective effects and dynamic expressions of MMP9 and TIMP1 associated with atorvastatin pretreatment in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Neurosci Lett 603:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.07.013
Fei L et al (2020) Preconditioning with rHMGB1 ameliorates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophage pyroptosis via the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Transl Med 18:301. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02467-w
Francis A, Baynosa R (2017) Ischaemia-reperfusion injury and hyperbaric oxygen pathways: a review of cellular mechanisms Diving and hyperbaric medicine 47:110–117. https://doi.org/10.28920/dhm47.2.110-117
Gibb et al (2011) The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol Cancer 12:87
Harkin DW, Barros D’Sa AA, McCallion K, Hoper M, Campbell FC (2002) Ischemic preconditioning before lower limb ischemia–reperfusion protects against acute lung injury. J Vasc Surg 35:1264–1273. https://doi.org/10.1067/mva.2002.121981
Hori K et al (2013) Protective effect of edaravone for tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle in murine hindlimb. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14:113. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-14-113
Hoss F, Rodriguez-Alcazar JF, Latz E (2017) Assembly and regulation of ASC specks. CMLS 74:1211–1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2396-6
Hsu C, Huang C, Chien L, Lin M, Chang C, Lin H, Chio C (2020) Ischemia/reperfusion injured intestinal epithelial cells cause cortical neuron death by releasing exosomal microRNAs associated with apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. Sci Reports 10:14409. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71310-5
Li D, Ren W, Jiang Z, Zhu L (2018) Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Mol Med Reports 18:4399–4409. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9427
Liao Y, Lin X, Li J, Tan R, Zhong X, Wang L (2020) Nodakenin alleviates renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting reactive oxygen species-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nephrology. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.13781
Liu X, Pan Z, Su D, Yang Z, Zheng B, Wang X, Tian J (2015) Remifentanil ameliorates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of interleukin-18 signaling. Transplantation 99:2109–2117. https://doi.org/10.1097/tp.0000000000000737
Mansour Z et al (2014) Remote effects of lower limb ischemia-reperfusion: impaired lung, unchanged liver, and stimulated kidney oxidative capacities. BioMed Res Int 2014:392390. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/392390
McMillan S et al (2004) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 deficiency results in enhanced allergen-induced airway inflammation. J Immunol 172:2586–2594. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.172.4.2586
Rashad S et al (2018) Early BBB breakdown and subacute inflammasome activation and pyroptosis as a result of cerebral venous thrombosis. Brain Res 1699:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.06.029
Sun T, Cheng Y, Yan L, Krittanawong C, Qian W, Zhang H (2019) LncRNA MALAT1 knockdown alleviates myocardial apoptosis in rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:10523–10531. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201912_19693
Vizza D et al (2018) Rapamycin-induced autophagy protects proximal tubular renal cells against proteinuric damage through the transcriptional activation of the nerve growth factor receptor NGFR. Autophagy 14:1028–1042. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1448740
Volanska M, Zavacky P, Bober J (2006) Ischaemic-reperfusion damage of tissue and critical limb ischaemia. Bratislavske lekarske listy 107:264–268
Wang YC et al (2019) Dihydromyricetin alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis in mice model. Inflammation 42:1301–1310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-00990-7
Wei L, Li J, Han Z, Chen Z, Zhang Q (2019) Silencing of lncRNA MALAT1 prevents inflammatory injury after lung transplant ischemia-reperfusion by downregulation of IL-8 via p300 molecular therapy. Nucleic Acids 18:285–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.009
Wen H, Zhang H, Wang W, Li Y (2020) Tetrahydropalmatine protects against acute lung injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion through restoring PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy in rats. Pulmon Pharmacol Ther 64:101947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pupt.2020.101947
Wu XB, Sun HY, Luo ZL, Cheng L, Duan XM, Ren JD (2020) Plasma-derived exosomes contribute to pancreatitis-associated lung injury by triggering NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis in alveolar macrophages. Biochimica et biophysica acta Molecular basis of Disease 1866:165685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165685
Xu Y et al (2020) PINK1-mediated mitophagy protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by restraining NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radical Biol Med 160:871–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.09.015
Yao F et al (2019) Imatinib prevents elastase-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm progression by regulating macrophage-derived MMP9. Eur J Pharmacol 860:172559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172559
Yassin MM, Harkin DW, Barros D’Sa AA, Halliday MI, Rowlands BJ (2002) Lower limb ischemia-reperfusion injury triggers a systemic inflammatory response and multiple organ dysfunction. World J Surg 26:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-001-0169-2
Ye Y, Shan Y, Bao C, Hu Y, Wang L (2018) Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against hind-limb ischemia reperfusion induced lung injury via NF-kappaB/COX-2 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 60:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.040
Yu W, Qin X, Zhang Y, Qiu P, Wang L, Zha W, Ren J (2020) Curcumin suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via a PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent manner. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 10:752–769. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt-19-707
Yuhua et al (2019) Rapamycin improves the neuroprotection effect of inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation after TBI. Brain Res 25:789
Zhao Y, Lv W, Zhou J (2017) Role of carbonyl sulfide in acute lung injury following limb ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Eur J Med Res 22:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-017-0255-z
Zheng C et al (2018) Long noncoding RNA AK12348 is involved in the regulation of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury by targeting PARP and caspase-3. Heart Lung Circ 27:e51–e58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2017.04.011
Zhuo L et al (2020) βRapamycin inhibited pyroptosis and reduced the release of IL-1 and IL-18 in the septic response. BioMed Research International 2020:5960375. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5960375
Funding
This study was supported by Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. 160156); Science and Technology Plan of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province (No. 20204366); Science and Technology Plan of Health and Family Planning Commission of Jiangxi Province (20181079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Funding acquisition: BT and SCY. Data curation: JZ, ZZL, and DH. Formal analysis: LZ, BZ and JZ. Experimental studies: DH and LZ. Software: DH and ZZL. Writing—original draft and review and editing: DH, BT, and SCY. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This project was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University.
Consent for publication
All authors declared their agreement to this manuscript published on 3 Biotech.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, D., Zhang, Ll., Zhou, B. et al. Rapamycin inhibits LOC102553434-mediated pyroptosis to improve lung injury induced by limb ischemia–reperfusion. 3 Biotech 11, 335 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02708-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02708-9