Abstract
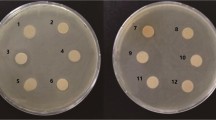
The antimicrobial compound produced by Bacillus paralicheniformis UBBLi30 showed UV spectra absorption at 208 nm. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) revealed characteristic bands for aliphatic chain related to hydrophobic amino acids (l-isoleucine/l-leucine) (3068, 2965 and 2871 cm−1) and peptide bonds (1538, 1667 and 3312 cm−1). The proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) showed signals for aromatic amino acid (6.5–9.5 ppm) and alkyl amines (3–4 ppm). The results of carbon (13C) NMR showed signals for aromatic, nitro and amide compounds. Besides this, the mass fragments (1422.576 [M+H]+, 711.912 [M+2H]2+ and 475.174 [M+3H]3+ m/z) observed in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) were coordinated well to the fragments of polypeptide antibiotic bacitracin. The presence of bacA gene further confirmed the production of bacitracin. Bacitracin inhibited the growth of a range of Gram-positive bacteria such as Micrococcus luteus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), S. aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Propionibacterium acnes, and biofilm formation of M. luteus and MRSA. Moreover, this polypeptide reduced the zeta potential of M. luteus and MRSA, indicating the electrostatic sorption on bacterial surface and concentration-dependent cell membrane damages. Besides this, polypeptide showed stability in the presence of proteases (proteinase K, trypsin and pepsin), pH (1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11) and temperature up to 100 °C. B. paralicheniformis UBBLi30 therefore has the potential to be utilized as a bio-preservative to control the growth of spoilage and pathogenic bacteria.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abriouel H, Franz CM, Omar NB, Gálvez A (2011) Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35(1):201–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00244.x
Achinas S, Charalampogiannis N, Euverink GJW (2019) A brief recap of microbial adhesion and biofilms. Appl Sci 9:2801. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9142801
Ahire JJ, Dicks LM (2014) 2, 3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid-containing nanofiber wound dressings inhibit biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(4):2098–2104. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02397-13
Ahire JJ, Dicks LM (2015) Nisin incorporated with 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoic acid in nanofibers inhibits biofilm formation by a methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Probiotics Antimicrob Prot 7(1):52–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-014-9171-5
Ahire JJ, Neveling DP, Hattingh M, Dicks LM (2015) Ciprofloxacin-eluting nanofibers inhibits biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE ONE 10(4):e0123648. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123648
Ahire JJ, Robertson DD, Van Reenen AJ, Dicks LM (2017) Surfactin-loaded polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers alters adhesion of Listeria monocytogenes to polystyrene. Mater Sci Eng C 77:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.248
Aitken A, Learmonth MP (2009) Protein determination by UV absorption. In: Walker J (ed) The protein protocols handbook. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 3–6
Al-Amoudi S, Essack M, Simões MF, Bougouffa S, Soloviev I, Archer JA, Lafi FF, Bajic VB (2016) Bioprospecting red sea coastal ecosystems for culturable microorganisms and their antimicrobial potential. Mar Drugs 14(9):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090165
Andrews JM (2001) Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J Antimicrob Chemother 48(S1):5–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/48.suppl_1.5
Arbsuwan N, Payoungkiattikun W, Sirithorn P, Daduang S, Jangpromma N, Dhiravisit A, Hahm YT, Neubert LK, Klaynongsruang S (2018) Purification and characterization of macrolactins and amicoumacins from Bacillus licheniformis BFP011: a new source of food antimicrobial substances. CyTA J Food 16(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476337.2017.1337047
Bechard J, Eastwell KC, Sholberg PL, Mazza G, Skura B (1998) Isolation and partial chemical characterization of an antimicrobial peptide produced by a strain of Bacillus subtilis. J Agri Food Chem 46(12):5355–5361. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9803987
Bera S, Mondal D (2019) Natural cyclic peptides as clinical and future therapeutics. Curr Org Chem 23(1):38–75. https://doi.org/10.2174/1385272823666190110103558
Boto A, Pérez de la Lastra J, González C (2018) The road from host-defense peptides to a new generation of antimicrobial drugs. Molecules 23(2):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020311
Choi YH, Cho SS, Simkhada JR, Rahman MS, Choi YS, Kim CS, Yoo JC (2017) A novel multifunctional peptide oligomer of bacitracin with possible bioindustrial and therapeutic applications from a Korean food-source Bacillus strain. PLoS ONE ONE 12(5):e0176971. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176971
Collins FW, O’Connor PM, O'Sullivan O, Rea MC, Hill C, Ross RP (2016) Formicin–a novel broad-spectrum two-component lantibiotic produced by Bacillus paralicheniformis APC 1576. Microbiol 162(9):1662–1671. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000340
de Boer AS, Priest F, Diderichsen B (1994) On the industrial use of Bacillus licheniformis: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40(5):595–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173313
Deng W, Dong XF, Tong JM, Zhang Q (2012) The probiotic Bacillus licheniformis ameliorates heat stress-induced impairment of egg production, gut morphology, and intestinal mucosal immunity in laying hens. Poult Sci 91(3):575–582. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2010-01293
Dicks LM, Dreyer L, Smith C, Van Staden AD (2018) A review: the fate of bacteriocins in the human gastro-intestinal tract: do they cross the gut–blood barrier? Front Microbiol 9:2297. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02297
Du Y, Ma J, Yin Z, Liu K, Yao G, Xu W, Fan L, Du B, Ding Y, Wang C (2019) Comparative genomic analysis of Bacillus paralicheniformis MDJK30 with its closely related species reveals an evolutionary relationship between B. paralicheniformis and B. licheniformis. BMC Genomics 20(1):283. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5646-9
Dunlap CA, Kwon SW, Rooney AP, Kim SJ (2015) Bacillus paralicheniformis sp. nov., isolated from fermented soybean paste. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65(10):3487–3492. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000441
Economou NJ, Cocklin S, Loll PJ (2013) High-resolution crystal structure reveals molecular details of target recognition by bacitracin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(35):14207–14212. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1308268110
Elshaghabee FM, Rokana N, Gulhane RD, Sharma C, Panwar H (2017) Bacillus as potential probiotics: status, concerns, and future perspectives. Front Microbiol 8:1490. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01490
Field LD, Sternhell S, Kalman JR (2007) Organic structures from spectra, 4th edn. Wiley, New York
Halder S, Yadav KK, Sarkar R, Mukherjee S, Saha P, Haldar S, Karmakar S, Sen T (2015) Alteration of zeta potential and membrane permeability in bacteria: a study with cationic agents. SpringerPlus 4:672. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-1476-7
Hartmann M, Berditsch M, Hawecker J, Ardakani MF, Gerthsen D, Ulrich AS (2010) Damage of the bacterial cell envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLa as revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(8):3132–3142. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00124-10
Harwood CR, Mouillon JM, Pohl S, Arnau J (2018) Secondary metabolite production and the safety of industrially important members of the Bacillus subtilis group. FEMS Microbiol Rev 42(6):721–738. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuy028
Hetem DJ, Rooijakkers HM, Ekkelenkamp MB (2017) Staphylococcus and micrococci. In: Versalovic J, Carroll KC, Funke G, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Warnock DW (eds) ). Infectious diseases, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1509–1522.e2
Jia P, Cui K, Ma T, Wan F, Wang W, Yang D, Wang Y, Guo B, Zhao L, Diao Q (2018) Influence of dietary supplementation with Bacillus licheniformis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae as alternatives to monensin on growth performance, antioxidant, immunity, ruminal fermentation and microbial diversity of fattening lambs. Sci Rep 8(1):16712. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35081-4
Johnson BA, Anker H, Meleney FL (1945) Bacitracin: a new antibiotic produced by a member of the Bacillus subtilis group. Science 102(2650):376–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.102.2650.376
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Li Y, Wang Z, Li X, Yin T, Bian K, Gao F, Gao D (2017) Facile synthesis of bacitracin-templated palladium nanoparticles with superior electrocatalytic activity. J Power Sources 341:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.12.006
Makled SO, Hamdan AM, El-Sayed AF (2019) Effects of dietary supplementation of a marine thermotolerant bacterium, Bacillus paralicheniformis SO-1, on growth performance and immune responses of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquacult Nutr 24(4):817–827. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12899
Mingmongkolchai S, Panbangred W (2018) Bacillus probiotics: an alternative to antibiotics for livestock production. J Appl Microbiol 124(6):1334–1346. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13690
Morikawa M, Hirata Y, Imanaka T (2000) A study on the structure–function relationship of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1488(3):211–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-1981(00)00124-4
Odonnell JA, Gelone SP, Safdar A (2015) Topical antibacterials. In: Dixon N (ed) Mandell, Douglas, and Bennetts principles and practice of infectious diseases. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Oh E, Bae J, Kumar A, Choi HJ, Jeon B (2018) Antioxidant-based synergistic eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) biofilms with bacitracin. Int J Antimicrob Agents 52(1):96–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.03.006
Schägger H (2006) Tricine–sds-page. Nat Protoc 1(1):16–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.4
Sumi CD, Yang BW, Yeo IC, Hahm YT (2014) Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: a new era for antibiotics. Can J Microbiol 61(2):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2014-0613
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040023
van Staden AD (2015) In vitro and in vivo characterization of amyloliquecidin, a novel two-component lantibiotic produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Doctoral dissertation, Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch University).
Xu S, Lin Y, Zeng D, Zhou M, Zeng Y, Wang H, Zhou Y, Zhu H, Pan K, Jing B, Ni X (2018) Bacillus licheniformis normalize the ileum microbiota of chickens infected with necrotic enteritis. Sci Rep 8(1):1744. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20059-z
Zhao X, Kuipers OP (2016) Identification and classification of known and putative antimicrobial compounds produced by a wide variety of Bacillales species. BMC Genomics 17(1):882. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3224-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJA, LSG and RSM contributed to the study conception. JJA designed the experiments. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by JJA and MSK. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JJA and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose that financial support for the research described in the manuscript was provided by Unique Biotech Limited, Hyderabad, India. Dr. Ratna Sudha Madempudi is the Managing Director of Unique Biotech Limited. This does not alter our adherence to journal policies on sharing data and materials.
Human participants and animal studies
The research conducted for this article did not involve studies on humans or animals.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahire, J.J., Kashikar, M.S., Lakshmi, S.G. et al. Identification and characterization of antimicrobial peptide produced by indigenously isolated Bacillus paralicheniformis UBBLi30 strain. 3 Biotech 10, 112 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2109-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2109-6