Abstract
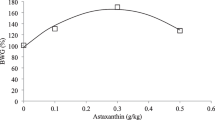
This study was aimed to investigate the facilitation of anthraquinone extract on growth performance, immunity, and antioxidant capacity of the oriental river prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense), and whether it could ameliorate the hyperthermia stress. A 12-week rearing experiment was conducted with 0, 125, 250, 500, and 1000 mg kg−1 anthraquinone extract from Rheum officinale Bail-supplemented diets (AE0, AE125, AE250, AE500, and AE1000), and followed a 48-h thermal stress with 32℃ incubation. Results indicate AE250 and AE500 significantly improved the growth performance and feed utilization, the optimum level was estimated to be 251.22 mg kg−1 based on the regression analysis of special growth ratio (SGR). Meanwhile, AE250 and AE500 improved antioxidant enzyme activity and immune-related protein concentration of iNOS-NO signaling. Under thermal stress, AE250 and AE500 improved the heat tolerance, and Toll–Relish signaling was active to the resistance. These results indicate anthraquinone extract could be used as an effective immunostimulant to improve growth performance, physiological balance and protect organism form environmental hyperthermia stress. This may provide insights for immunostimulant development in aquaculture production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JB, Audhya T, McDonough-Means S et al (2011) Nutritional and metabolic status of children with autism vs. neurotypical children, and the association with autism severity. Nutr Metab 8:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-8-34
Agarwal SK, Singh SS, Verma S, Kumar S (2000) Antifungal activity of anthraquinone derivatives from Rheum emodin. J Ethnopharmacol 72:43–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00195-1
Ameri K, Harris AL (2008) Activating transcription factor. Int J Biochem Cell B 40(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.01.020
Anavi S, Tirosh O (2020) iNOS as a metabolic enzyme under stress conditions. Free Radic Biol Med 146:16–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.10.411
Arts JAJ, Cornelissen FHJ, Cijsouw T et al (2007) Molecular cloning and expression of a Toll receptor in the giant tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23:504–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2006.08.018
Asaduzzaman M, Wahab MA, Verdegem MCJ et al (2009) Effects of stocking density of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii and addition of different levels of tilapia Oreochromis niloticus on production in C/N controlled periphyton based system. Aquaculture 286:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUACULTURE.2008.09.006
Bachère E, Gueguen Y, Gonzalez M et al (2004) Insights into the anti-microbial defense of marine invertebrates: the penaeid shrimps and the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Immunol Rev 198:149–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00115.x
Belenky P, Bogan KL, Brenner C (2007) NAD+ metabolism in health and disease. Trends Biochem Sci 32:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2006.11.006
Blais JD, Filipenko V, Bi M et al (2004) Activating transcription factor 4 is translationally regulated by hypoxic stress. Mol Cell Biol 24(17):7469–7482. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.24.17.7469-7482.2004
Bone K, Mills S (2012) Principles and practice of phytotherapy: modern herbal medicine, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-48725-7
Chang CC, Jiang JR, Cheng W (2015) A first insight into temperature stress-induced neuroendocrine and immunological changes in giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Fish Shellfish Immunol 47:528–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.09.041
Chen T, Wong NK, Jiang X et al (2015) Nitric oxide as an antimicrobial molecule against Vibrio harveyi infection in the hepatopancreas of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol 42:114–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.042
Cheng W, Chen JC (2000) Effects of pH, temperature and salinity on immune parameters of the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Fish Shellfish Immunol 10:387–391. https://doi.org/10.1006/fsim.2000.0264
Chukwujekwu JC, Coombes PH, Mulholland DA, van Staden J (2006) Emodin, an antibacterial anthraquinone from the roots of Cassia occidentalis. South African J Bot 72:295–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2005.08.003
Currie E, Schulze A, Zechner R et al (2013) Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer. Cell Metab 18:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.017
Devi G, Harikrishnan R, Paray BA et al (2019) Effects of aloe-emodin on innate immunity, antioxidant and immune cytokines mechanisms in the head kidney leucocytes of Labeo rohita against Aphanomyces invadans. Fish Shellfish Immunol 87:669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.02.006
Ding Z, Zhang Y, Ye J et al (2015) An evaluation of replacing fish meal with fermented soybean meal in the diet of Macrobrachium nipponense: growth, nonspecific immunity, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 44:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.02.024
Ding ZL, Kong YQ, Li JF et al (2017) Growth and metabolic responses of juvenile Macrobrachium nipponense to different dietary carbohydrate levels. Aquac Nutr 23:1136–1144. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12482
Flegel TW, Lightner DV, Lo CHUF, Owens L (2008) Shrimp disease control: past, present and future. Dis Asian Aquac VI:355–378
Gonzalez-Rivas PA, Chauhan SS, Ha M et al (2020) Effects of heat stress on animal physiology, metabolism, and meat quality: a review. Meat Sci 162:108025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.108025
Hai T, Hartman MG (2001) The molecular biology and nomenclature of the activating transcription factor/cAMP responsive element binding family of transcription factors: activating transcription factor proteins and homeostasis. Gene 273(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00551-0
Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway CA, Ezekowitz RAB (1999) Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 284:1313–1318. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5418.1313
Huang XD, Yin ZX, Liao JX et al (2009) Identification and functional study of a shrimp Relish homologue. Fish Shellfish Immunol 27:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.05.003
Huang XD, Yin ZX, Jia X, Ting X et al (2010) Identification and functional study of a shrimp Dorsal homologue. Dev Comp Immunol 34:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2009.08.009
Jiang G, Yu R, Zhou M (2006) Studies on nitric oxide synthase activity in haemocytes of shrimps Fenneropenaeus chinensis and Marsupenaeus japonicus after white spot syndrome virus infection. Nitric Oxide - Biol Chem 14:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2005.11.005
Kong Y, Ding Z, Zhang Y et al (2017) Dietary selenium requirement of juvenile oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquaculture 476:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.04.010
Li F, Xiang J (2013) Signaling pathways regulating innate immune responses in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol 34:973–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.08.023
Li F, Yan H, Wang D et al (2009) Identification of a novel relish homolog in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis and its function in regulating the transcription of antimicrobial peptides. Dev Comp Immunol 33:1093–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2009.06.001
Li F, Wang D, Li S et al (2010) A Dorsal homolog (FcDorsal) in the Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis is responsive to both bacteria and WSSV challenge. Dev Comp Immunol 34:874–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2010.03.008
Liang T, Li X, Du J et al (2011) Identification and isolation of a spiroplasma pathogen from diseased freshwater prawns, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, in China: a new freshwater crustacean host. Aquaculture 318:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.03.018
Lin H-Z, Li Z-J, Chen Y-Q et al (2006) Effect of dietary traditional Chinese medicines on apparent digestibility coefficients of nutrients for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone. Aquaculture 253:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.11.048
Liu B, Xie J, Ge X et al (2010) Effects of anthraquinone extract from Rheum officinale Bail on the growth performance and physiological responses of Macrobrachium rosenbergii under high temperature stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2010.02.018
Liu B, Xu P, Brown PB et al (2016) The effect of hyperthermia on liver histology, oxidative stress and disease resistance of the Wuchang bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol 52:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.03.018
Martin GG, Graves BL (1985) Fine structure and classification of shrimp hemocytes. J Morphol 185:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmor.1051850306
Ndong D, Chen YY, Lin YH et al (2007) The immune response of tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus and its susceptibility to Streptococcus iniae under stress in low and high temperatures. Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2006.08.015
Paul V, Ekambaram P (2011) Involvement of nitric oxide in learning & memory processes. Indian J Med Res 133:471–478
Ramyaa P, Krishnaswamy R, Padma VV (2014) Quercetin modulates OTA-induced oxidative stress and redox signalling in HepG2 cells—up regulation of Nrf2 expression and down regulation of NF-κB and COX-2. Biochim Biophys Acta - Gen Subj 1840:681–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.024
Roberts CK, Barnard RJ, Sindhu RK et al (2006) Oxidative stress and dysregulation of NAD(P)H oxidase and antioxidant enzymes in diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 55:928–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2006.02.022
Song C, Liu B, Xie J et al (2017) Comparative proteomic analysis of liver antioxidant mechanisms in Megalobrama amblycephala stimulated with dietary emodin. Sci Rep 7:40356. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40356
Song C, Cui Y, Liu B et al (2018a) HSP60 and HSP90β from blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala: molecular cloning, characterization, and comparative response to intermittent thermal stress and Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.046
Song C, Liu B, Xu P et al (2018b) Oxidized fish oil injury stress in Megalobrama amblycephala: evaluated by growth, intestinal physiology, and transcriptome-based PI3K-Akt/NF-κB/TCR inflammatory signaling. Fish Shellfish Immunol 81:446–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.07.049
Song C, Liu B, Xu P et al (2019) Emodin ameliorates metabolic and antioxidant capacity inhibited by dietary oxidized fish oil through PPARs and Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish Immunol 94:842–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.10.001
Sritunyalucksana K, Soderhall K (2000) The proPO and clotting system in crustaceans. Aquaculture 191:53–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00411-7
Tadese DA, Sun CX, Liu B et al (2020) Combined effects of emodin and Clostridium butyricum on growth and non-specific immunity of giant freshwater prawns, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture 525:735281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735281
Tanji T, Yun EY, Ip YT (2010) Heterodimers of NF-κB transcription factors DIF and Relish regulate antimicrobial peptide genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14715–14720. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009473107
Wang WN, Wang AL, Zhang YJ et al (2004) Effects of nitrite on lethal and immune response of Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquaculture 232:679–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2003.08.018
Wang PH, Liang JP, Gu ZH et al (2012) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of two novel Tolls (LvToll2 and LvToll3) and three putative Spätzle-like Toll ligands (LvSpz1-3) from Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev Comp Immunol 36:359–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2011.07.007
Wong JTY, McAndrew BJ (1994) Allozyme variation in riverine and lacustrine populations of Macrobrachium nipponense (de Haan). Aquac Res 25:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.1994.tb00704.x
Xie J, Liu B, Zhou Q et al (2008) Effects of anthraquinone extract from rhubarb Rheum officinale Bail on the crowding stress response and growth of common carp Cyprinus carpio var. Jian Aquaculture 281:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.03.038
Yang YZ, Zhao Y, Yang L et al (2018) Characterization of 2-Cys peroxiredoxin 3 and 4 in common carp and the immune response against bacterial infection. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem Mol Biol 217:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2017.12.012
Yearbook CFS (2019) China fishery statistics yearbook. Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing, China
Zhao GN, Jiang DS, Li H (2015) Interferon regulatory factors: at the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1852:365–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.04.030
Zhu YZ, Huang SH, Tan BKH et al (2004) Antioxidants in Chinese herbal medicines: a biochemical perspective. Nat Prod Rep 21:478–489. https://doi.org/10.1039/B304821G
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (2018HY-ZD0501); the earmarked fund for Jiangsu Agricultural Industry Technology System (JFTS(2019)474); the China Agriculture Research System-48 (CARS-48); the Project of National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD09002); the Project of Six Talent Peaks in Jiangsu Province (NY-174) and Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars in Wuxi City (201708).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC and LB contributed to the design of the experiment; JS and XY provided the rearing ponds; JZ conducted the rearing experiment; ZQ, BL, and ZH analyzed the parameters; SC and SC analyzed the data; SC wrote the paper; SC and LB revised the paper; all the authors approved the final version of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanjing Agricultural University (Nanjing, China). All animal procedures were performed according to the Guideline for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals in China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, C., Liu, B., Jiang, S. et al. Anthraquinone extract from Rheum officinale Bail improves growth performance and Toll–Relish signaling-regulated immunity and hyperthermia tolerance in freshwater prawn Macrobrachium nipponense. 3 Biotech 10, 526 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02519-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02519-4