Abstract
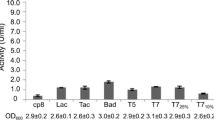
Long-chain fatty acids are widely used in food and chemical industries, and the enzymatic preparation of fatty acids is considered an environmentally friendly process. In the present study, long-chain fatty acids were prepared by the enzymatic hydrolysis of rapeseed oil with a genetically engineered lipase. Because thermophilic lipase has strong stability at higher temperatures, it was more suitable for the industrial production of long-chain fatty acids. Therefore, the thermophilic lipase BTL2 from Geobacillus thermocatenulatus was efficiently expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) cells with an enzyme activity of 39.50 U/mg followed by gene codon optimisation. Experimental results showed that the recombinant lipase BTL2 exhibited excellent resistance to certain organic solvents (n-hexane, benzene, ethanol, and butanol). The metal cation Ca2+ and the non-ionic surfactant Triton-100X enhanced enzyme activity by 7.36% and 56.21% respectively. Moreover, the acid value of the liberated long-chain fatty acids by hydrolysing rapeseed oil was approximately 161.64 mg KOH/g at 50 °C in 24 h, the hydrolytic conversion rate was 91.45%, and the productivity was approximately 6.735 mg KOH/g h. These results suggested that the recombinant lipase BTL2 has excellent hydrolytic performance for rapeseed oil and showed great potential for the enzymatic preparation of long-chain fatty acids.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlercreutz P (2013) Immobilisation and application of lipases in organic media. Chem Soc Rev 42(15):6406–6436. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35446f
Al-Jawadi A, Moussa H, Ramalingam L, Dharmawardhane S, Gollahon L, Gunaratne P, Rahman RL, Moustaid-Moussa N (2018) Protective properties of n-3 fatty acids and implications in obesity-associated breast cancer. J Nutr Biochem 53:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.09.018
Amada K, Kwon HJ, Haruki M, Morikawa M, Kanaya S (2001) Ca2+-induced folding of a family 1.3 lipase with repetitive Ca2+ binding motifs at the C-terminus. Febs Lett 509(1):17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03108-8
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340(4):783–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028
Brzozowski AM, Savage H, Verma CS, Turkenburg JP, Lawson DM, Svendsen A, Patkar S (2000) Structural origins of the interfacial activation in Thermomyces (Humicola) lanuginosa lipase. Biochemistry-Us 39(49):15071–15082. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0013905
Chor Leow T, Noor Zaliha Raja Abd Rahman R, Basri M, Salleh AB (2007) A thermoalkaliphilic lipase of Geobacillus sp T1. Extremophiles 11 (3):527–535. 10.1007/s00792-007-0069-y
Cordeiro Y, Kraineva J, Ravindra R, Lima L, Gomes MPB, Foguel D, Winter R, Silva JL (2004) Hydration and packing effects on prion folding and beta-sheet conversion—High pressure spectroscopy and pressure perturbation calorimetry studies. J Biol Chem 279(31):32354–32359. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M404295200
Cui Y, Thomas-Hall SR, Schenk PM (2019) Phaeodactylum tricornutum microalgae as a rich source of omega-3 oil: progress in lipid induction techniques towards industry adoption. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.06.004
Delorme V, Dhouib R, Canaan S, Fotiadu F, Carriere F, Cavalier JF (2011) Effects of surfactants on lipase structure, activity, and inhibition. Pharm Res-Dordr 28(8):1831–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0362-9
El Khattabi M, Van Gelder P, Bitter W, Tommassen J (2003) Role of the calcium ion and the disulfide bond in the Burkholderia glumae lipase. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 22(5–6):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1381-1177(03)00047-x
Fernandes MLM, Krieger N, Baron AM, Zamora PP, Ramos LP, Mitchell DA (2004) Hydrolysis and synthesis reactions catalysed by Thermomyces lanuginosa lipase in the AOT/Isooctane reversed micellar system. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 30(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2004.03.004
Godoy CA, Klett J, Di Geronimo B, Hermoso JA, Guisan JM, Carrasco-Lopez C (2019) Disulfide engineered lipase to enhance the catalytic activity: a structure-based approach on BTL2. Int J Mol Sci 20 (21). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215245
Gomes I, Gomes J, Steiner W (2003) Highly thermostable amylase and pullulanase of the extreme thermophilic eubacterium Rhodothermus marinus: production and partial characterization. Bioresour Technol 90(2):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(03)00110-x
Goncalves KM, Barbosa LRS, Lima LMTR, Cortines JR, Kalume DE, Leal ICR, Mariz e Miranda LS, de Souza ROM, Cordeiro Y (2014) Conformational dissection of Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase in solution. Biophys Chem 185:88–97. 10.1016/j.bpc.2013.12.001
He HM, Han HB, Shi H, Tian YY, Sun FX, Song Y, Li QS, Zhu GS (2016) Construction of thermophilic lipase-embedded metal organic frameworks via biomimetic mineralization: a biocatalyst for ester hydrolysis and kinetic resolution. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 8(37):24517–24524. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b05538
Hide WA, Chan L, Li WH (1992) Structure and evolution of the lipase superfamily. J Lipid Res 33(2):167–178
Hu YL, Dai LM, Liu DH, Du W, Wang YJ (2018) Progress & prospect of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for enzyme immobilization (enzyme/MOFs). Renew Sustain Energy Rev 91:793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.103
Ibarra-Molero B, Loladze VV, Makhatadze GI, Sanchez-Ruiz JM (1999) Thermal versus guanidine-induced unfolding of ubiquitin. An analysis in terms of the contributions from charge-charge interactions to protein stability. Biochemistry-Us 38(25):8138–8149. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9905819
Kajiwara S, Yamada R, Matsumoto T, Ogino H (2020) N-linked glycosylation of thermostable lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus to improve organic solvent stability. Enzyme Microb Tech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109416
Lessard LP, Hill CG (2000) Effect of pH on the production of lipolyzed butter oil by a calf pregastric esterase immobilized in a hollow-fiber reactor: II Multiresponse kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng 70(3):332–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0290(20001105)70:3%3c332::Aid-bit10%3e3.0.Co;2-g
Li M, Yang LR, Xu G, Wu JP (2016) Cloning and characterization of a novel lipase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia GS11: the first member of a new bacterial lipase family XVI. J Biotechnol 228:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.04.034
Li GH, Chen JZ, Ma X, Zhang Z, Liu N, Wang Y (2018) Enzymatic preparation and facile purification of medium-chain, and medium- and long-chain fatty acid diacylglycerols. LWT-Food Sci Technol 92:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.02.032
Malhotra R, Noorwez SM, Satyanarayana T (2000) Production and partial characterization of thermostable and calcium-independent alpha-amylase of an extreme thermophile Bacillus thermooleovorans NP54. Lett Appl Microbiol 31(5):378–384. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765x.2000.00830.x
Murakami MT, Arni RK, Vieira DS, Degreve L, Ruller R, Ward RJ (2005) Correlation of temperature induced conformation change with optimum catalytic activity in the recombinant G/11 xylanase A from Bacillus subtilis strain 168 (1A1). Febs Lett 579(28):6505–6510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2005.10.039
Paetzel M, Dalbey RE, Strynadka NCJ (1998) Crystal structure of a bacterial signal peptidase in complex with a beta-lactam inhibitor. Nature 396(6707):186–190
Quyen DT, Schmidt-Dannert C, Schmid RD (2003) High-level expression of a lipase from Bacillus thermocatenulatus BTL2 in Pichia pastoris and some properties of the recombinant lipase. Protein Express Purif 28(1):102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1046-5928(02)00679-4
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5:17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Rua ML, SchmidtDannert C, Wahl S, Sprauer A, Schmid RD (1997) Thermoalkalophilic lipase of Bacillus thermocatenulatus large-scale production, purification and properties: aggregation behaviour and its effect on activity. J Biotechnol 56(2):89–102
Sarmah N, Revathi D, Sheelu G, Rani KY, Sridhar S, Mehtab V, Sumana C (2018) Recent advances on sources and industrial applications of lipases. Biotechnol Progr 34(1):5–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2581
Singh A, Van Hamme JD, Ward OP (2007) Surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology: Part 2 Application aspects. Biotechnol Adv 25(1):99–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.10.004
Velez AM, Iemma MR, Silva AJ, Horta ACL, Giordano RC, Giordano RL (2009) Influence of operational conditions in the expression of Bacillus thermocatenulatus lipase BTL2 in Escherichia coli. New Biotechnol 25:S219–S220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2009.06.180
Wang JR, Wu ZZ, Zhang TY, Wang YH, Yang B (2019) High-level expression of Thermomyces dupontii thermophilic lipase in Pichia pastoris via combined strategies. 3 Biotech 9(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1597-8
Won K, Kim S, Kima KJ, Park HW, Moon SJ (2005) Optimization of lipase entrapment in Ca-alginate gel heads. Process Biochem 40(6):2149–2154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.08.014
Wu XY, Jaaskelainen S, Linko YY (1996) An investigation of crude lipases for hydrolysis, esterification, and transesterification. Enzyme Microb Tech 19(3):226–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(95)00239-1
Wu YP, Guo WB, Zhao JB, Ding LS, Chen XH (2018) Isolation and identification of a novel LCI like antibacterial protein from Bacillus sp MD-5 reveals its potential application in controlling Staphylococcus aureus in food industry. Food Control 89:142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.01.026
Yamada R, Kimoto Y, Ogino H (2016) Combinatorial library strategy for strong overexpression of the lipase from Geobacillus thermocatenulatus on the cell surface of yeast Pichia pastoris. Biochem Eng J 113:7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.05.005
Yenenler A, Venturini A, Burduroglu HC, Sezerman OU (2018) Investigating the structural properties of the active conformation BTL2 of a lipase from Geobacillus thermocatenulatus in toluene using molecular dynamic simulations and engineering BTL2 via in-silico mutation. J Mol Model 24(9):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-018-3753-1
Zhang Y, Ge J, Liu Z (2015) Enhanced activity of immobilized or chemically modified enzymes. Acs Catal 5(8):4503–4513. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b00996
Zhu X, Ye A, Verrier T, Singh H (2013) Free fatty acid profiles of emulsified lipids during in vitro digestion with pancreatic lipase. Food Chem 139(1–4):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.12.060
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangdong Special Support Program (No. 2017TX04Z109), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51606201), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2016A010104008), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2017A010104010), the National Key research and development program of China (No. 2019YFB1504003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51903236) and the Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC (No. 51861145103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Writing—original draft: ZJ; Validation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Software: TM; Supervision, Data curation: LW and WZY; Resources, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Data curation: LPM, XJL and WZM.
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Tian, M., Lv, P. et al. High-efficiency expression of the thermophilic lipase from Geobacillus thermocatenulatus in Escherichia coli and its application in the enzymatic hydrolysis of rapeseed oil. 3 Biotech 10, 523 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02517-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02517-6