Abstract
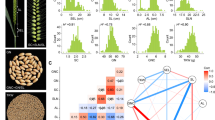
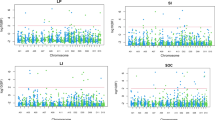
A core set of 190 rice landraces were used to decipher the genetic structure and to discover the chromosomal regions containing QTLs, affecting the grain micro-nutrients, fatty acids, and yield-related traits by using 148 molecular markers in this study. Landraces were categorized into three sub-groups based on population stratification study and followed by neighbor-joining tree and principal component analysis. Analysis of variance revealed abundant variations among the landraces for studied traits with less influence of environmental factors. Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS) revealed 22 significant and consistent QTLs through marker trait association (MTAs) for 12 traits based on 2 years and pooled analysis. Out of 22 QTLs, three have been reported earlier while 19 QTLs are novel. Interestingly, 13 QTLs out of 22 were explained more than 10% phenotypic variance. Association of RM1148 and RM205 with Days to 50% flowering was comparable with flowering control genes Ghd8/qDTH8 and qDTH9, respectively. Similarly, Zn content was associated with RM44, which is situated within the QTL qZn8-1. Moreover, significant association of RM25 with oleic acid content was closely positioned with QTL qOle8. Association of RM7434 with grain yield/plant; RM184 with spikelet fertility %; R3M10, R9M42 with hundred seed weight; RM536, RM17467, RM484, RM26063 with Fe content; RM44, RM6839 with Zn content are the major outcomes of this study. In addition, association of R11M23 with days to 50% flowering, panicle length and total spikelets per panicle are explained the possible occurrence of pleiotropism among these traits. Prominent rice landraces viz., Anjani (early maturity); Sihar (extra dwarf); Gangabaru (highest grain yield/plant); Karhani (highest iron content); Byalo-2 (highest zinc content) and Kadamphool (highest oleic acid) were identified through this study. The present study will open many avenues towards utilization of these QTLs and superior landraces in rice breeding for developing nutrition-rich high yielding varieties.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrama H, Eizenga G, Yan W (2007) Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol Breed 19(4):341–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9066-6
Babu RV, Neeraja CN, Sanjeeva Rao D, Sundaram RM, Longvah T, Usharani G, Padmavathi G, Balachandran SM, Nirmala Devi G, Bhadana VP, Suneetha K, Rao KV, Surekha K, Sarla N, Brajendra P, Raghuveer Rao P, Girish C, Shashidhar HE, Bijan A. and Viraktamath BC (2014) Bioforotification in Rice. DRR Technical Bulletin No. 81/2014. Hyderabad: Directorate of Rice Research. p 86
Borba C, Oliveria D, Brondani RPV, Breseghello F, Coelho ASG, Mendonca JA, Rangel PHN, Brondani C (2010) Association mapping for yield and grain quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genet Mol Biol 33:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572010005000065
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
DelCruz N, Khush GS (2000) Rice grain quality evaluation procedures. In: Singh RK, Singh US, Khush GS (eds) Aromatic rices. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, pp 16–28
Descalsota GIL, Swamy BPM, Zaw H, Asilo MAI, Amparado A, Mauleon R, Mohanty PC, Arocena EC, Raghavan C, Leung H, Hernandez JE, Lalusin AB, Mendioro MS, Diaz MGQ, Reinke R (2018) Genome-wide association mapping in rice MAGIC plus population detects QTLs and genes useful for biofortification. Front Plant Sci 9(1347):1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01347
Donde R, Mohapatra S, Baksh SKY, Padhy B, Mukherjee M, Roy S, Chattopadhyay K, Anandan A, Swain P, Sahoo KK, Singh ON, Behera L, Dash SK (2020) Identification of QTLs for high grain yield and component traits in new plant types of rice. PLoS ONE 15(7):e0227785. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227785
Earl DA (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
FAOSTAT (2020) https://www.fao.org/state-of-food-security-nutrition/en/. Accessed 12 May 2020
Federer WT (1956) Augmented (or Hoonuiaku) Designs. Hawaii Plr Rec 55:191–208
Feng Y, Zhai RR, Li ZC, Cao LY, Wei XH, Cheng SH (2015) Quantitative trait locus analysis for rice yield traits under two nitrogen levels. Rice Sci 22(3):108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2015.05.014
Garcia-Oliveira AL, Tan L, Fu Y, Sun C (2009) Genetic identification of quantitative trait loci for contents of mineral nutrients in rice grain. J Integr Plant Biol 51(1):84–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00730.x
Hammer Q, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9
Haritha B, Yadav AK, Vinod KK, Gopala Krishnan S, Bhowmick PK, Nagarajan M, Neeraja CN, Ellur RK, Singh AK (2020) Genome-wide association study reveals novel marker-trait associations (MTAs) governing the localization of Fe and Zn in the rice grain. Front Genet 11:213. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00213
Hua JP, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Sun XL, Yu SB, Zhang Q (2002) Genetic dissection of an elite rice hybrid revealed that heterozygotes are not always advantageous for performance. Genet 162(4):1885–1895
Huang Y, Sun C, Min J, Chen Y, Tong C, Bao J (2015) Association mapping of quantitative trait loci for mineral element contents in whole grain rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 63(50):10885–10892. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04932
Juan LR, Marques L, Talon M, Domingo C (2018) Genome-wide association study of agronomic traits in rice cultivated in temperate regions. BMC Plant Biol 19:706. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5086-y
Kadam NN, Struik PC, Rebolledo CM, Yin X, Jagadish SVK (2018) Genome-wide association reveals novel genomic loci controlling rice grain yield and its component traits under water-deficit stress during the reproductive stage. J Exp Bot 69(16):4017–4032. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery186
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) Power Marker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Lu Q, Zhang M, Niu X, Wang S, Xu Q, Feng Y, Wang C, Deng H, Yuan X, Yuan H, Wang Y, Wei X (2015) Genetic variation and association mapping for 12 agronomic traits in indica rice. BMC Genom 16:1067. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2245-2
Mondal BJ, Singh A, Yadav A, Tomar RSS, SinghPrakash VGSKV (2017) QTL mapping for early ground cover in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under drought stress. Current Sci 112(6):1266–1271. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v112/i06/1266-1271
Mondal S, Nazareth J, Bhad PG, Badigannavar AM (2018) Isolation of high oleate recombinants in peanut by near infra-red spectroscopy and confirmation with allele specific polymerase chain reaction marker. J American Oil Chem Soc 95:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/aocs.12012
Moran MD (2003) Arguments for rejecting the sequential Bonferroni in ecological studies. Oikos 100:403–405. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0706.2003.12010.x
Norton GJ, Douglas A, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Guerinot ML, Pinson SRM, Tarpley L, Eizenga GC, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Rafiqul Islam M, Islam S, Duan G, Zhu Y, Salt DE, Meharg AA, Price AH (2014) Genome wide association mapping of grain arsenic, copper, molybdenum and zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at Four International Field Sites. PLoS ONE 9(2):e89685. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089685
Norton GJ, Travis AJ, Douglas A, Fairley S, De Paiva AE, Ruang-areerate P, Naredo MEB, McNally KL, Hossain M, Islam MR, Price AH (2018) Genome wide association mapping of grain and straw biomass traits in the rice Bengal and Assam Aus Panel (BAAP) Grown Under Alternate Wetting and Drying and Permanently Flooded Irrigation. Front Plant Sci 9:1223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01223
Pradhan SK, Pandit E, Pawar S, Bharati B, Chatopadhyay K, Singh S, Dash P, Reddy JN (2019) Association mapping reveals multiple QTLs for grain protein content in rice useful for biofortification. Mol Geneti Genom MGG. 294(4):963–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01556-w
Pradhan SK, Pandit E, Pawar S, Naveenkumar R, Barik SR, Mohanty SP, Nayak DK, Ghritlahre SK, Sanjiba Rao D, Reddy JN, Patnaik SSC (2020) Linkage disequilibrium mapping for grain Fe and Zn enhancing QTLs useful for nutrient dense rice breeding. BMC Plant Biol 20:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-2262-4
Prasanth VV, Babu MS, Basava RK, Tripura Venkata VGN, Mangrauthia SK, Voleti SR, Neelamraju S (2017) Trait and marker associations in Oryza nivara and O. rufipogon derived rice lines under two different heat stress conditions. Front Plant Sci. 26:1819. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01819
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genet 155(2):945–959
Rabson R, Bhatia C, Mitra RK (1978) Crop productivity, grain protein and energy. In: Joint FAO/IAEA (ed) Seed protein improvement by nuclear techniques. (Proc. Meet. Bader, 1977). lnternational Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria, pp 3–20
Rahman S, Sharma MP, Sahai S (2006) Nutritional and medicinal values of some indigenous rice varieties. Indian J Tradit Knowl 5:454–458
Rao SD, Babu PM, Swarnalatha P, Kota S, Bhadana VP, Surekha K, Neerja CN, Babu RV (2014) Assessment of grain zinc and iron variability in rice germplasm using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer (ED-XRF). J Rice Res 7:45–52
Rathna Priya TS, Nelson ARLE, Ravichandran K, Antony U (2019) Nutritional and functional properties of coloured rice varieties of South India: a review. J Ethn Foods 6:1–11
Richharia RH, Misro B, Butany WT, Seetharaman R (1960) Linkage studies in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 9(1):122–126
Sahu PK, Mondal S, Sharma D, Vishwakarma G, Kumar V, Das BK (2017) InDel marker based genetic differentiation and genetic diversity in traditional rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces of Chhattisgarh, India. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0188864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188864
Sanjeeva Rao D, Neeraja CN, Madhu Babu P, Nirmala B, Suman K, Rao L, Surekha K, Raghu P, Longvah T, Surendra P, Kumar R, Babu VR, Voleti SR (2020) Zinc biofortified rice varieties: challenges, possibilities, and progress in India. Front Nutr 7:26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00026
Sarawgi AK, Gauraha D, Nair SK, Sao A, Bhandarkar S, Verma R, Sharma B, Chandel G, Sharma D, Kar S (2019) Development of improved varieties of rice- 1987 to 2019 (Dhan ki unnat kishmo ka vikas-1987 to 2019). IGKV publications, Raipur, India, pp 1–32
SES, IRRI (2013) Standard evaluation system for rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila
Shen YJ, Jiang H, Jin JP, Zhang ZB, Xi B, He YY, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu QB, Liu HJ, Chen DH, Gao JH, Huang H, Shi TL, Yang ZN (2004) Development of genome-wide DNA polymorphism database for mapbased cloning of rice genes. Plant Physiol 135:1198–1205. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.038463
Smouse PE, Whitehead MR, Peakall R (2015) An informational diversity framework, illustrated with sexually deceptive orchids in early stages of speciation. Mol Ecol Resour 15(6):1375–1386. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12422
Suh JP, Ahn SN, Cho YC, Kang KH, Choi IS, Kim YG, Suh HS, Hong HC (2005) Mapping of QTLs for yield traits using an advanced backcross population from a cross between Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima. Korean J Breed. 37(4):214–220
Suman K, Madhubabu P, Rathod R, Sanjeeva Rao D, Rojarani A, Prashant S, Subbarao LV, Ravindrababu V, Neeraja CN (2020) Variation of grain quality characters and marker-trait association in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Genet 99:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1164-4
Swamy BPM, Shamsudin NAA, Rahman SNA, Mauleon R, Ratnam W, Cruz MTS, Kumar A (2017) Association mapping of yield and yield related traits under reproductive stage drought stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 10(21):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-017-0161-6
Wei X, Xu J, Guo H, Jiang L, Chen S, Yu C, Zhou J, Hu P, Zhai H, Wan J (2010) DTH8 suppresses flowering in rice, influencing plant height and yield potential simultaneously. Plant Physiol 153:1747–1758. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.156943
Xiang-dong L, Jun Z, Liang-fang D, Fan-tao Z, Yi Z, Yong W, Jina-kun X (2016) Linkage map construction and QTL mapping for cold tolerance in Oryza rufipogon Griff. at early seedling stage. J Integr Agric 15:60345–60347
Xing YZ, Xu CG, Hua JP, Tan YF (2001) Analysis of QTL x environment interaction for rice panicle characteristics. Acta Genet Sin 28:439–446
Xing J, Jia MH, Correll JC, Yuan LP, Deng H, Jia Y (2015) Confirming and identifying new loci for rice blast disease resistance using Magnaporthe oryzae field isolates in the US. Crop Sci. 55:2620–2627. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2015.02.0077
Xu F, Jin L, Huang Y, Tong C, Chen YL, Bao JS (2016) Association mapping of quantitative trait loci for yield-related agronomic traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Integr Agric 15(10):2192–2202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61244-8
Ying JZ, Shan JX, Gao JP, Zhu MZ, Shi M, Lin HX (2012) Identification of quantitative trait loci for lipid metabolism in rice seeds. Mol Plant 5(4):865–875. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr100
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB (2006) A unified mixed model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38(2):203–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1702
Zhang M, Pinson SRM, Tarpley L, Huang XY, Lahner B, Yakubova E et al (2014) Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain. Theor Appl Genet 127:137–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2207-5
Zhang P, Zhong K, Zhong Z, Tong H (2019) Genome-wide association study of important agronomic traits within a core collection of rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 19:259. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1842-7
Zhao K, Tung CW, Eizenga GC, Wright MH, Ali ML, Price AH, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Rynolds A, Mezey J, McClung AM, Bustamante CD, McCouch SR (2011) Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa L. Nat Commun 2(467):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1467
Acknowledgements
Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India is sincerely acknowledged for providing financial support as INSPIRE fellowship to PKS. Indian Institute of Rice Research, Hyderabad is duly acknowledged for technical and scientific cooperation. Authors are also thankful to Head, NA&BTD; Associate Director, BSG, BARC, Mumbai and Head, Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, IGKV, Raipur for technical support and cooperation during the experiment.
Funding
Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Grant number [IF150523].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization of work: DS, SM, BKD; Data curation: PKS, SM, GV, RS, VK; Data analysis: PKS, SM; Funding acquisition: DS, BKD; Investigation: PKS, SM; Methodology: PKS, SM, GV, VK; Resources: DS, SM, BKD, VK; Supervision: DS, BKD; Writing ± original draft: PKS, SM, RS; Review and editing: SM, DS, BKD, VK, GV. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, P.K., Mondal, S., Sao, R. et al. Genome-wide association mapping revealed numerous novel genomic loci for grain nutritional and yield-related traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces. 3 Biotech 10, 487 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02467-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02467-z