Abstract
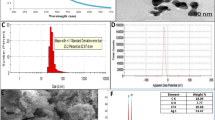
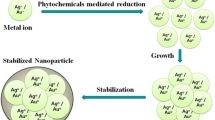
The present study describes green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and inulin hydrolyzing enzyme nanocomplexes (ENC) using Azadirachta indica (Ai) and Punica granatum (Pg) leaf extracts. Surface topology and physico-chemical characteristics of AgNPs were studied using surface plasmon resonance (SPR), FTIR, SEM, AFM and EDX analyses. Particle size analysis using dynamic light scattering and AFM studies revealed that Ai-AgNPs (76.4 nm) were spherical in shape having central bigger nano-regime with smaller surroundings while Pg-AgNPs (72.1 nm) and ENCs (Inulinase-Pg-AgNPs ~ 145 nm) were spherical particles having smooth surfaces. Pg-AgNPs exhibited significant photocatalysis of a thiazine dye, methylene blue. Both Ai- and Pg-AgNPs showed selective antibacterial action by inhibiting pathogenic Bacillus cereus, while the probiotic Lactobacillus strains remained unaffected. Ai-AgNPs showed potential anti-biofilm effect (30% viability) on B. cereus biofilms. Pg-AgNPs showed anti-cancer effect against human colon cancer cell lines (Caco-2) resulting in 40% cell death in 48 h. Enzymes (inulinase, L-asparaginase and glucose oxidase) were successfully immobilized onto nanoparticles together with the biogenic synthesis of AgNPs and recyclability of the Inulinase-Pg-AgNPs complex was demonstrated. The study elaborates characteristics of green synthesized nanoparticles and their potential applications as anti-cancer, antibacterial and antioxidant nano drugs that could be used in food and nutraceutical industries. Enzyme immobilization on AgNPs without any toxic cross-linker opens up newer possibilites in enzyme-nanocomplex research.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal S, Kango N (2019) Development and catalytic characterization of L-asparaginase nano-bioconjugates. Int J Biol Macromol 135:1142–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.154
Ahmad A, Syed F, Shah A, Khan Z, Tahir K, Khan AU, Yuan Q (2015) Silver and gold nanoparticles from Sargentodoxa cuneata: synthesis, characterization and anti leishmanial activity. RSC Adv 5:73793–73806. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA13206A
Ahmed Q, Gupta N, Kumar A, Nimesh S (2017) Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles synthesized employing Terminalia arjuna bark extract. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 45:1192–1200. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1215328
Anand Mariadoss AV, Vinayagam R, Vijayakumar S, Balupillai A, Herbert FJ, Kumar S, Ghidan AY, Al-Antary TM, David E (2019) Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles by Malus domestica and its cytotoxic effect on (MCF-7) cell line. Microb Pathog 135:103609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103609
Behravan M, Hossein Panahi A, Naghizadeh A, Ziaee M, Mahdavi R, Mirzapour A (2019) Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol 124:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.101
Bhatwalkar SB, Gound SS, Mondal R, Srivastava RK, Anupam R (2019) Anti-biofilm and antibacterial activity of Allium sativum against drug resistant shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolates from patient samples and food Sources. Indian J Microbiol 59:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00784-3
Cattò C, Garuglieri E, Borruso L, Erba D, Casiraghi MC, Cappitelli F, Villa F, Zecchin S, Zanchi R (2019) Impacts of dietary silver nanoparticles and probiotic administration on the microbiota of an in-vitro gut model. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.019
Chen X, Zheng Z, Ke X, Jaatinen E, Xie T, Wang D, Guo C, Zhao J, Zhu H (2010) Supported silver nanoparticles as photocatalysts under ultraviolet and visible light irradiation. Green Chem 12:414–419. https://doi.org/10.1039/B921696K
Ding S, Cargill AA, Medintz IL, Claussen JC (2015) Increasing the activity of immobilized enzymes with nanoparticle conjugation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 34:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2015.04.005
Erdogan O, Abbak M, Demirbolat M, Id FB (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via Cynara scolymus leaf extracts: the characterization, anticancer potential with photodynamic therapy in MCF7 cells. PLoS ONE 14:e0216496. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216496
Firdhouse MJ, Lalitha P (2013a) Fabrication of antimicrobial perspiration pads and cotton cloth using Amaranthus dubius mediated silver nanoparticles. J Chem 2013:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/741743
Firdhouse MJ, Lalitha P (2013b) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the extract of Alternanthera sessilis-anti proliferative effect against prostate cancer cells. Cancer Nano 4:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12645-013-0045-4
Garibo D, Borbón-Nuñez HA, de León JND, Mendoza EG, Estrada I, Toledano-Magaña Y, Tiznado H, Ovalle-Marroquin M, Soto-Ramos AG, Blanco A, Rodríguez JA, Romo OA, Chávez-Almazán LA, Susarrey-Arce A (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulcensis exhibit high-antimicrobial activity. Sci Rep 10:12805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69606-7
Gomaa EZ (2017) Antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Allium cepa extract: a green approach. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 15:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.12.002
Hsueh YH, Lin KS, Ke WJ, Te Hsieh C, Chiang CL, Tzou DY, Liu ST (2015) The antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles in Bacillus subtilis are mediated by released Ag+ ions. PLoS ONE 10:e0144306. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144306
Jain S, Mehata MS (2017) Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Sci Rep 7:15867. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15724-8
Karuppaiya P, Satheeshkumar E, Sheng H (2019) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using rhizome extract of Dysosma pleiantha and its anti proliferative effect against breast and human gastric cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 46:4725–4734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04917-1
Khan T, Yasmin A, Townley HE (2020) An evaluation of the activity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles against bacteria, fungi and mammalian cell lines. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111156
Khorrami S, Zarepour A, Zarrabi A (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles at low temperature in a fast pace with unique DPPH radical scavenging and selective cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and BT-20 tumor cell lines. Biotechnol Rep 24:e00393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00393
Masum MI, Siddiqa MM, Ali KA, Zhang Y, Abdallah Y, Ibrahim E, Qiu W, Yan C, Li B (2019) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract and its inhibitory action against the pathogen Acidovorax oryzae strain RS-2 of rice bacterial brown stripe. Front Microbiol 10:820. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00820
Misson M, Zhang H, Jin B (2015) Nanobiocatalyst advancements and bioprocessing applications. J R Soc Interface 12:20140891. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2014.0891
Mohseni MS, Khalilzadeh MA, Mohseni M, Hargalani FZ, Getso MI, Raissi V, Raiesi O (2020) Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles from pomegranate seeds extract and synthesis of Ag-Starch nanocomposite and characterization of mechanical properties of the films. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 25:101569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101569
Padinjarathil H, Joseph MM, Unnikrishnan BS, Preethi GU, Shiji R, Archana MG, Maya S, Syama HP, Sreelekha TT (2018) Galactomannan endowed biogenic silver nanoparticles exposed enhanced cancer cytotoxicity with excellent biocompatibility. Int J Biol Macromol 118:1174–1182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.194
Patil S, Singh N (2019) Antibacterial silk fibroin scaffolds with green synthesized silver nanoparticles for osteoblast proliferation and human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 176:150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.067
Patra JK, Baek KH (2017) Antibacterial activity and synergistic antibacterial potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles against food borne pathogenic bacteria along with its anti candidal and antioxidant effects. Front Microbiol 8:167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00167
Priyadarshini S, Sulava S, Bhol R, Jena S (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica and Ocimum sanctum leaf extract. Curr Sci 117:1300–1307. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v117/i8/1300-1307
Qing Y, Cheng L, Li R, Liu G, Zhang Y, Tang X, Wang J, Liu H, Qin Y (2018) Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int J Nanomedicine 13:3311–3327. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165125
Raj S, Mali SC, Trivedi R (2018) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Enicostemma axillare (Lam.) leaf extract. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2814–2819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.045
Ranoszek-Soliwoda K, Tomaszewska E, Małek K, Celichowski G, Orlowski P, Krzyzowska M, Grobelny J (2019) The synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles with plant extracts. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 177:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.037
Rasheed T, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN, Li C (2017) Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves extract of Artemisia vulgaris and their potential biomedical applications. Colloids Surf B 158:408–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.07.020
Rashid S, Azeem M, Khan SA, Shah MM, Ahmad R (2019) Characterization and synergistic antibacterial potential of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous root extracts of important medicinal plants of Pakistan. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 179:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.04.016
Rautela A, Rani J, Debnath M (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tectona grandis seeds extract: characterization and mechanism of antimicrobial action on different microorganisms. J Anal Sci Technol 10:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-018-0163-z
Rawat HK, Ganaie MA, Kango N (2015) Production of inulinase, fructosyltransferase and sucrase from fungi on low-value inulin-rich substrates and their use in generation of fructose and fructo-oligosaccharides. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:799–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0373-3
Roy P, Das B, Mohanty A, Mohapatra S (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and its antimicrobial study. Appl Nanosci 7:843–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0621-8
Roy A, Bulut O, Some S, Mandal AK, Yilmaz MD (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv 9:2673–2702. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra08982e
Sahayaraj K, Balasubramanyam G, Chavali M (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dry leaf aqueous extract of Pongamia glabra Vent (Fab.), characterization and phyto fungicidal activity. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100349
Sangaonkar GM, Pawar KD (2018) Garcinia indica mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 164:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.01.044
Sarkar S, Banerjee A, Halder U, Biswas R, Bandopadhyay R (2017) Degradation of synthetic azo dyes of textile industry: a sustainable approach using microbial enzymes. Water Conserv Sci Eng 2:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-017-0031-5
Sarkar S, Ponce NT, Banerjee A, Bandopadhyay R, Rajendran S, Lichtfouse E (2020) Green polymeric nanomaterials for the photocatalytic degradation of dyes: a review. Environ Chem Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01021-w
Sathiyaraj S, Suriyakala G, Gandhi AD, Saranya S, Santhoshkumar M, Kavitha P, Babujanarthanam R (2020) Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using vallarai chooranam and their potential biomedical applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01683-7
Sheikh IA, Yasir M, Khan I, Khan SB, Azum N, Jiffri EH, Kamal MA, Ashraf GM, Beg MA (2018) Lactoperoxidase immobilization on silver nanoparticles enhances its antimicrobial activity. J Dairy Res 85:460–464. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029918000730
Siddiqi KS, Husen A, Rao RAK (2018) A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J Nanobiotechnology 16:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0334-5
Singh J, Dhaliwal AS (2018) Plasmon-induced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as photocatalyst. Environ Technol (United Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1540663
Sivakumar M, Surendar S, Jayakumar M, Seedevi P, Sivasankar P, Ravikumar M, Anbazhagan M, Murugan T, Siddiqui SS, Loganathan S (2020) Parthenium hysterophorus mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its evaluation of antibacterial and antineoplastic activity to combat liver cancer cells. J Clust Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01775-x
Sreekumar S, Sithul H, Muraleedharan P, Azeez JM, Sreeharshan S (2014) Pomegranate fruit as a rich source of biologically active compounds. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/686921
Syed F, Ali K, Asad MJ, Fraz MG, Khan Z, Imran M, Taj R, Ahmad A (2016) Preparation and characterization of a green nano-support for the covalent immobilization of glucoamylase from Neurospora sitophila. J PhotochemPhotobiol B Biol 162:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.07.002
Torabizadeh H, Mahmoudi A (2018) Inulin hydrolysis by inulinase immobilized covalently on magnetic nanoparticles prepared with wheat gluten hydrolysates. Biotechnol Rep 17:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2018.02.004
Ulaeto SB, Mathew GM, Pancrecious JK, Nair JB, Rajan TPD, Maiti KK, Pai BC (2020) Biogenic Ag nanoparticles from Neem extract: their structural evaluation and antimicrobial effects against Pseudomonas nitroreducens and Aspergillus unguis (NII 08123). ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01257
Umapathi A, Nagaraju NP, Madhyastha H, Jain D, Srinivas SP, Rotello VM, Daima HK (2019) Highly efficient and selective antimicrobial isonicotinyl hydrazide-coated polyoxometalate-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 184:110522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110522
Vanaja M, Paulkumar K, Baburaja M, Rajeshkumar S, Gnanajobitha G, Malarkodi C, Sivakavinesan M, Annadurai G (2014) Degradation of methylene blue using biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/742346
Veenashri BR, Muralikrishna G (2011) In vitro anti-oxidant activity of xylo-oligosaccharides derived from cereal and millet brans: a comparative study. Food Chem 126:1475–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.163
Yu Z, Wang W, Dhital R, Kong F, Lin M, Mustapha A (2019a) Antimicrobial effect and toxicity of cellulose nanofibril/silver nanoparticle nanocomposites prepared by an ultraviolet irradiation method. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 180:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.04.054
Yu Z, Wang W, Kong F, Lin M, Mustapha A (2019b) Cellulose nanofibril/silver nanoparticle composite as an active food packaging system and its toxicity to human colon cells. Int J Biol Macromol 129:887–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.084
Zangeneh MM, Joshani Z, Zangeneh A, Miri E (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Stachys lavandulifolia flower, and their cytotoxicity, antioxidant, antibacterial and cutaneous wound-healing properties. Appl Organometal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.5016
Acknowledgements
Author RC acknowledges UGC, New Delhi for financial assistance as PhD scholarship. Authors acknowledge the instrumentation facilities (FTIR, SEM-EDX, Zetasizer, AFM, electrochemical workstation) available under Sophisticated Instrumentation Centre (SIC) and Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi PURSE (II) scheme at Dr. Harisingh Gour Vishwavidyalaya, Sagar, India.
Funding
There is no funding provided by any agency to drive this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RC and AJ performed characterization experiments. Photocatalytic degradation of MB has been performed by AJ. Rest of all application experiments were performed and data analyzed by RC. NK conceptualized and supervised the work. Writing, review and editing of the manuscript has been done by NK and RC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choukade, R., Jaiswal, A. & Kango, N. Characterization of biogenically synthesized silver nanoparticles for therapeutic applications and enzyme nanocomplex generation. 3 Biotech 10, 462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02450-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02450-8