Abstract
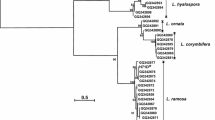
A Bacillus strain X2 that produced extracellular endo-xylanase (GH 11) (EC: 3.2.1.8) was isolated from the soil of the Northeast India region. This aerobic culture was Gram positive and endospore forming. Chemotaxonomic characterization showed variance with the fatty acid profile of related species in the Bacillus subtilis group. In Bacillus strain X2, distinct occurrence of iso-C14:0 lipids is absent in other related species. The 16S rRNA gene sequence homology showed 99% similarity with Bacillus subtilis subsp. inaquosorum. The phylogenetic analysis by the multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) of the nucleotide sequence of six concatenated genes (16S rRNA, groEL, gyrA, polC, purH and rpoB) resolved the taxonomic position of the Bacillus strain X2 in the Bacillus subtilis subsp. group. The MLSA showed that it is a member of a clade that includes Bacillus subtilis subsp. stercoris. In in silico DNA–DNA hybridization (DDH), the highest matching score was obtained with Bacillus subtilis subsp. stercoris (87%). The in silico DDH of the genome (G + C 43.7 mol %) shared 48.5%, with Bacillus subtilis subsp. inaquosorum. The MLSA phylogenetic tree and the highest degree of DNA hybridization, indicating that it belongs to the Bacillus subtilis subspecies stercoris.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 September 2020
Unfortunately, the funding information of the article has been missed in the publication of the article.
Abbreviations
- MALDI-ToF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight
- XOS:
-
Xylooligosaccharides
- MLSA:
-
Multilocus sequence analysis
- FAMEs:
-
Fatty acid methyl esters
References
Adelskov J, Patel BKC (2017) Erratum to: A molecular phylogenetic framework for Bacillus subtilis using genome sequences and its application to Bacillus subtilis subspecies stecoris strain D7XPN1, an isolate from a commercial food-waste degrading bioreactor. 3 Biotech 6:1
Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA (2011) BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-402
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Anil Kumar P, Aravind R, Francis K et al (2012) Shivajiella indica gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine bacterium of the family “ Cyclobacteriaceae” with nitrate reducing activity. Syst Appl Microbiol 35:320–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2012.04.004
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A et al (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw387
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best A et al (2008) The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23:257–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1656(92)90074-J
Bhalla A, Bischoff KM, Sani RK (2014) Highly thermostable GH39 β-xylosidase from a Geobacillus sp. strain WSUCF1. BMC Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-014-0106-8
Calderaro A, Arcangeletti M-C, Rodighiero I et al (2014) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry applied to virus identification. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06803
Carattoli A, Zankari E, Garciá-Fernández A et al (2014) In Silico detection and typing of plasmids using plasmidfinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02412-14
Christakopoulos P, Katapodis P, Kalogeris E et al (2003) Antimicrobial activity of acidic xylo-oligosaccharides produced by family 10 and 11 endoxylanases. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-8130(02)00079-X
Chun J, Bae KS (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis and related taxa based on partial gyrA gene sequences. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026555830014
Chun J, Lee J-H, Jung Y et al (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64915-0
Cohan FM (2002) What are bacterial species? Annu Rev Microbiol 56:457–487. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160634
Cohan FM (2006) Towards a conceptual and operational union of bacterial systematics, ecology, and evolution. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 361:1985–1996. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2006.1918
Cohan FM, Kane M (2001) Bacterial species and speciation. Syst Biol 50:513–524. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150118398
Colston SM, Fullmer MS, Beka L et al (2014) Bioinformatic genome comparisons for taxonomic and phylogenetic assignments using aeromonas as a test case. MBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02136-14
Dunlap CA, Bowman MJ, Schisler DA, Rooney AP (2016a) Genome analysis shows Bacillus axarquiensis is not a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus mojavensis; reclassification of Bacillus malacitensis and Brevibacterium halotolerans as heterotypic synonyms of Bacillus axarquiensis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:2438–2443. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001048
Dunlap CA, Kim SJ, Kwon SW, Rooney AP (2016b) Bacillus velezensis is not a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens; Bacillus methylotrophicus, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. Plantarum and ‘Bacillus oryzicola’ are later heterotypic synonyms of Bacillus velezensis based on phylogenom. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000858
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Gagné D, Narayanan C, Nguyen-Thi N et al (2016) Ligand binding enhances millisecond conformational exchange in xylanase B2 from Streptomyces lividans. Biochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00130
Gatson JW, Benz BF, Chandrasekaran C et al (2006) Bacillus tequilensis sp. nov., isolated from a 2000-year-old Mexican shaft-tomb, is closely related to Bacillus subtilis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1475–1484. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63946-0
Gevers D, Cohan FM, Lawrence JG et al (2005) Re-evaluating prokaryotic species. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:733–739
Gowdhaman D, Ponnusami V (2015) Production and optimization of xylooligosaccharides from corncob by Bacillus aerophilus KGJ2 xylanase and its antioxidant potential. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.05.046
Gullón B, Yáñez R, Alonso JL, Parajó JC (2010) Production of oligosaccharides and sugars from rye straw: a kinetic approach. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.080
Haddar A, Driss D, Frikha F et al (2012) Alkaline xylanases from Bacillus mojavensis A21: production and generation of xylooligosaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.06.036
Hakulinen N, Turunen O, Jänis J et al (2003) Three-dimensional structures of thermophilic β-1,4-xylanases from Chaetomium thermophilum and Nonomuraea flexuosa: Comparison of twelve xylanases in relation to their thermal stability. Eur J Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03496.x
Huang D, Liu J, Qi Y et al (2017) Synergistic hydrolysis of xylan using novel xylanases, β-xylosidases, and an α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:6023–6037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8341-2
Huerta-Cepas J, Forslund K, Coelho LP et al (2017) Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx148
Kerepesi C, Bánky D, Grolmusz V (2014) AmphoraNet: the webserver implementation of the AMPHORA2 metagenomic workflow suite. Gene 533:538–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.015
Kubo Y, Rooney AP, Tsukakoshi Y et al (2011) Phylogenetic analysis of Bacillus subtilis strains applicable to natto (fermented soybean) production. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00448-11
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA et al (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. Nucleic Acid Tech Bact Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2133-0
Lányi B (1988) Classical and rapid identification methods for medically important bacteria. Methods Microbiol 19:1–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70407-0
Logan NA, De Vos P (2009) Genus I. Bacillus Cohn 1872, 174AL. In: Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology Volume Three The Firmicutes. pp 21–130
Logan NA, Berge O, Bishop AH et al (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2114–2121. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.013649-0
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1996) TRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from micro-organisms. J Mol Biol 3:IN1–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(61)80047-8
Maughan H, Van der Auwera G (2011) Bacillus taxonomy in the genomic era finds phenotypes to be essential though often misleading. Infect Genet Evol 11:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2011.02.001
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Moaledj K (1986) Comparison of Gram-staining and alternate methods, KOH test and aminopeptidase activity in aquatic bacteria: their application to numerical taxonomy. J Microbiol Methods 5:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(86)90056-4
Nakamura LK (1989) Taxonomic relationship of black-pigmented Bacillus subtilis strains and a proposal for Bacillus atrophaeus sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-39-3-295
Nakamura LK, Roberts MS, Cohan FM (1999) Relationship of Bacillus subtilis clades associated with strains 168 and W23: a proposal for Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis subsp. nov. and Bacillus subtilis subsp. spizizenii subsp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-49-3-1211
Oakley AJ, Heinrich T, Thompson CA, Wilce MCJ (2003) Characterization of a family 11 xylanase from Bacillus subtillis B230 used for paper bleaching. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444903001227
Oraei M, Razavi SH, Khodaiyan F (2018) Optimization of effective minerals on riboflavin production by Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis ATCC 6051 using statistical designs. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol 10(1):49–55
Paës G, Berrin JG, Beaugrand J (2012) GH11 xylanases: Structure/function/properties relationships and applications. Biotechnol Adv 30(3):564–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.10.003
Palmisano MM, Nakamura LK, Duncan KE et al (2001) Bacillus sonorensis sp. nov., a close relative of Bacillus licheniformis, isolated from soil in the Sonoran Desert Arizona. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1671–1679. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-5-1671
Perry EB, Koeppel A, Krizanc D et al (2006) Identifying the fundamental units of diversity among Bacillus isolates from "Evolution Canyon" III. Isr J Ecol Evol 52:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1560/IJEE_52_3-4_543
Petersen TN, Brunak S, Von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Price NPJ, Rooney AP, Swezey JL et al (2007) Mass spectrometric analysis of lipopeptides from Bacillus strains isolated from diverse geographical locations. FEMS Microbiol Lett 271:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00702.x
Reddy SS, Krishnan C (2016a) Production of xylooligosaccharides in SSF by Bacillus subtilis KCX006 producing β-xylosidase-free endo-xylanase and multiple xylan debranching enzymes. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2014.970694
Reddy SS, Krishnan C (2016b) Production of high-pure xylooligosaccharides from sugarcane bagasse using crude β-xylosidase-free xylanase of Bacillus subtilis KCX006 and their bifidogenic function. LWT Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.08.013
Rhee MS, Wei L, Sawhney N et al (2014) Engineering the xylan utilization system in Bacillus subtilis for production of acidic xylooligosaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03246-13
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2015) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv681
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku316
Roberts MS, Cohan FM (1995) Recombination and migration rates in natural populations of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus mojavensis. Evolution. https://doi.org/10.2307/2410433
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK, Cohan FM (1994) Bacillus mojavensis sp. nov., distinguishable from Bacillus subtilis by sexual isolation, divergence in DNA sequence, and differences in fatty acid composition. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-44-2-256
Roberts MS, Nakamura LK, Cohan FM (1996) Bacillus vallismortis sp. nov., a close relative of Bacillus subtilis, isolated from soil in Death Valley. California Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:470–475. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-46-2-470
Rooney AP, Price NPJ, Ehrhardt C et al (2009) Phylogeny and molecular taxonomy of the Bacillus subtilis species complex and description of Bacillus subtilis subsp. inaquosorum subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2429–2436. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.009126-0
Ruiz-García C, Béjar V, Martínez-Checa F et al (2005) Bacillus velezensis sp. nov, a surfactant-producing bacterium isolated from the river Vélez in Málaga, southern Spain. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63310-0
Sabini E, Sulzenbacher G, Dauter M et al (1999) Catalysis and specificity in enzymatic glycoside hydrolysis: a 2,5 B conformation for the glycosyl-enzyme intermediate revealed by the structure of the Bacillus agaradhaerens family 11 xylanase. Chem Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(99)80066-0
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2006) Purification of nucleic acids by extraction with phenol:chloroform. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2006:pdb.prot4455. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot4455
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 607–654
Srinivas TNR, Nageswara Rao SSS, Vishnu Vardhan Reddy P et al (2009) Bacterial diversity and bioprospecting for cold-active lipases, amylases and proteases, from culturable bacteria of Kongsfjorden and Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard, Arctic. Curr Microbiol 59:537–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9473-0
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM et al (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02360-0
Takita T, Nakatani K, Katano Y et al (2019) Increase in the thermostability of GH11 xylanase XynJ from Bacillus sp. strain 41M–1 using site saturation mutagenesis. Enzyme Microb Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109363
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl149
Teng C, Yan Q, Jiang Z et al (2010) Production of xylooligosaccharides from the steam explosion liquor of corncobs coupled with enzymatic hydrolysis using a thermostable xylanase. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.004
Tindall BJ, Rosselló-Móra R, Busse HJ et al (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.016949-0
van Heel AJ, de Jong A, Montalbán-López M et al (2013) BAGEL3: Automated identification of genes encoding bacteriocins and (non-)bactericidal posttranslationally modified peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt391
Vázquez MJ, Alonso JL, Domínguez H, Parajó JC (2001) Xylooligosaccharides: manufacture and applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 11:387–393
Wang LT, Lee FL, Tai CJ et al (2007) Reclassification of Bacillus axarquiensis Ruiz-García et al. 2005 and Bacillus malacitensis Ruiz-García et al. 2005 as later heterotypic synonyms of Bacillus mojavensis Roberts et al. 1994. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1663–1667. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64808-0
Wang LT, Lee FL, Tai CJ, Kuo HP (2008) Bacillus velezensis is a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65191-0
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK et al (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. Nov., a novel member of the family “Oxalobacteraceae” isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63407-0
Yagi H, Takehara R, Tamaki A et al (2019) Functional characterization of the GH10 and GH11 xylanases from Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86 provide insights into the advantage of GH11 xylanase in catalyzing biomass degradation. J Appl Glycosci. https://doi.org/10.5458/jag.jag.jag-2018_0008
Yi H, Chun J, Cha CJ (2014) Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the three subspecies of Bacillus subtilis. Syst Appl Microbiol 37:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2013.09.006
Zankari E, Hasman H, Cosentino S et al (2012) Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J Antimicrob Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dks261
Zwick ME, Joseph SJ, Didelot X et al (2012) Genomic characterization of the Bacillus cereus sensu lato species: backdrop to the evolution of Bacillus anthracis. Genome Res 22:1512–1524. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.134437.111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhruw, C., Husain, K., Kumar, V. et al. Novel xylanase producing Bacillus strain X2: molecular phylogenetic analysis and its application for production of xylooligosaccharides. 3 Biotech 10, 328 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02322-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02322-1