Abstract
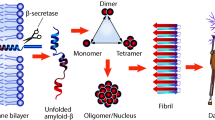
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a chronic and progressive neurological brain disorder. AD pathophysiology is mainly represented by formation of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Neuritic plaques are made up of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides, which play a central role in AD pathogenesis. In AD brain, Aβ peptide accumulates due to overproduction, insufficient clearance and defective proteolytic degradation. The degradation and cleavage mechanism of Aβ peptides by several human enzymes have been discussed previously. In the mean time, numerous experimental and bioinformatics reports indicated the significance of microbial enzymes having potential to degrade Aβ peptides. Thus, there is a need to shift the focus toward the substrate specificity and structure–function relationship of Aβ peptide-degrading microbial enzymes. Hence, in this review, we discussed in vitro and in silico studies of microbial enzymes viz. cysteine protease and zinc metallopeptidases having ability to degrade Aβ peptides. In silico study showed that cysteine protease can cleave Aβ peptide between Lys16–Cys17; similarly, several other enzymes also showed capability to degrade Aβ peptide at different sites. Thus, this review paves the way to explore the role of microbial enzymes in Aβ peptide degradation and to design new lead compounds for AD treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References:s
Aprahamian I, Stella F, Forlenza OV (2013) New treatment strategies for Alzheimer’s disease: is there a hope? Indian J Med Res 138:449–460
Backstrom JR, Lim GP, Cullen MJ, Tokes ZA (1996) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is synthesized in neurons of the human hippocampus and is capable of degrading the amyloid-beta peptide (1–40). J Neurosci 16:7910–7919
Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A, Brayne C, Aarsland D, Jones E (2011) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 377:1019–1031
Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:663–672
Barage SH, Sonawane KD (2015) Amyloid cascade hypothesis: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropeptides 52:1–18
Barale S, Parulekar R, Fandilolu P, Dhanavade M, Sonawane K (2019) Molecular insights into destabilization of Alzheimer’s Aβ protofibril by arginine containing short peptides: a molecular modeling approach. ACS Omega 4(1):892–903
Baranello R, Bharani K, Padmaraju V, Chopra N, Lahiri D, Greig N, Pappolla M, Sambamurti K (2015) Amyloid-beta protein clearance and degradation (ABCD) pathways and their role in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 12(1):32–46
Bateman R, Siemers E, Mawuenyega K, Wen G, Browning K, Sigurdson W, Yarasheski K, Friedrich S, Demattos R, May P, Paul S, Holtzman D (2009) A gamma secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-beta production in the central nervous system. Ann Neurol 66:48–54
Borghammera P, Berge N (2019) Brain-first versus gut-first Parkinson’s disease: a hypothesis. J Parkinson’s Dis 9:S281–S295
Briguglio M, Dell’Osso B, Panzica G, Malgaroli A, Banfi G, Zanaboni Dina C, Galentino R, Porta M (2018) Dietary neurotransmitters: a narrative review on current knowledge. Nutrients 10:591
Brunden K, Trojanowski J, Lee V (2009) Advances in taufocused drug discovery for Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:783–793
Cataldo A, Nixon R (1990) Enzymatically active lysosomal proteases are associated with amyloid deposits in Alzheimer brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3861–3865
Cataldo A, Barnett J, Pieroni C, Nixon R (1997) Increased neuronal endocytosis and protease delivery to early endosomes in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: neuropathologic evidence for a mechanism of increased β-amyloidogenesis. J Neurosci 17:6142–6151
Cimerman N, Prebanda M, Turk B, Popovic T, Dolenc I, Turk V (1999) Interaction of cystatin C variants with papain and human cathepsins B, H and L. J Enzyme Inhib 14:167–174
Cummings J, Lee G, Ritter A, Sabbagh M, Zhong K (2019) Alzheimer's disease drug development pipeline: 2019. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 5:272–293
De Chiara G, Marcocci M, Civitelli L, Argnani R, Piacentini R, Ripoli C et al (2010) APP processing induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) yields several APP fragments in human and rat neuronal cells. PLoS ONE 5:e13989
De la Torre J (2004) Is Alzheimer’s disease a neurodegenerative or a vascular disorder? Data, dogma, and dialectics. Lancet Neurol 3:184–190
Deb S, Gottschall PE (1996) Increased production of matrix metalloproteinases in enriched astrocyte and mixed hippocampal cultures treated with beta-amyloid peptides. J Neurochem 66:1641–1647
Dhanavade M, Sonawane K (2014) Insights into the molecular interactions between aminopeptidase and amyloid beta peptide using molecular modeling techniques. Amino Acids 46:1853–1866
Dhanavade M, Jalkute C, Barage S, Sonawane K (2013) Homology modeling, molecular docking and MD simulation studies to investigate role of cysteine protease from Xanthomonas campestris in degradation of Ab peptide. Comput Biol Med 43:2063–2070
Eckman E, Reed D, Eckman C (2001) Degradation of the Alzheimer’s amyloid beta peptide by endothelin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 276:24540–24548
Fede G, Catania M, Morbin M, Rossi G, Suardi S, Mazzoleni G, Merlin M, Giovagnoli A, Prioni S, Erbetta A, Falcone C, Gobbi M, Colombo L, Bastone A, Beeg M, Manzoni C, Francescucci B, Spagnoli A, Cantù L, Del Favero E, Levy E, Salmona M, Tagliavini F (2009) A recessive mutation in the APP gene with dominant-negative effect on amyloidogenesis. Science 323:1473–1477
Frautschy S, Horn D, Sigel J, Harris-White M, Mendoza J, Yang F, Saido T, Cole G (1998) Protease inhibitor coinfusion with amyloid beta-protein results in enhanced deposition and toxicity in rat brain. J Neurosci 18:8311–8321
Giau V, An S, Hulme J (2018a) Mitochondrial therapeutic interventions in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuro Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2018.09.033
Giau V, Wu S, Jamerlan A, An S, Kim S, Hulme J (2018b) Gut microbiota and their neuroinflammatory implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients 10:1765–1782
Glabe C (2001) Intracellular mechanisms of amyloid accumulation and pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 17:137–145
Glenner G, Wong C (1984) Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:885–890
Gottschall P (1996) beta-Amyloid induction of gelatinase B secretion in cultured microglia: inhibition by dexamethasone and indomethacin. NeuroReport 7:3077–3080
Gouras G, Xu H, Jovanovic J, Buxbaum J, Wang R, Greengard P, Relkin N, Gandy S (1998) Generation and regulation of beta-amyloid peptide variants by neurons. J Neurochem 71:1920–1925
Hamazaki H (1996) Cathepsin D is involved in the clearance of Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid protein. FEBS Lett 396:139–142
Haran J, Bhattarai S, Foley S, Dutta P, Ward D, Bucci V, McCormickb B (2019) Alzheimer’s disease microbiome is associated with dysregulation of the anti-inflammatory P-glycoprotein pathway. mbio 10:e00632–e719
Hardy J, Selkoe D (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Harris S, Harris E (2018) Molecular mechanisms for herpes simplex virus type 1 pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 10:48–72
Hawkes C, Hartig W, Kacza J, Schliebs R, Weller R, Nicoll J, Carare R (2011) Perivascular drainage of solutes is impaired in the ageing mouse brain and in the presence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathol 121:431–443
Henley D, May P, Dean R, Siemers E (2009) Development of semagacestat (LY450139), a functional gamma-secretase inhibitor, for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10:1657–1664
Honjo K, van Reekum R, Verhoeff N (2009) Alzheimer’s disease and infection: do infectious agents contribute to progression of Alzheimer’s disease? Alzheimers Dement 5:348–360
Hsu R, Lee K, Wang J, Lily Y, Lee L, Rita P, Chen Y (2009) Amyloid-degrading ability of Nattokinase from Bacillus subtilis Natto. J Agric Food Chem 57:503–508
Hu J, Igarashi A, Kamata M, Nakagawa H (2001) Angiotensin converting enzyme degrades Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide (A beta); retards A beta aggregation, deposition, fibril formation; and inhibits cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 276:47863–47868
Hui K (2007) Neuropeptidases. In: Lajtha A, Banik N (eds) Handbook of neurochemistry and molecular neurobiology: neural protein metabolism and function, vol 7, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Itzhaki R, Cosby S, Wozniak M (2008) Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: the autophagy connection. J Neurovirol 14:1–4
Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, Shirotani K, Lu B, Gerard NP, Gerard C, Hama E, Lee HJ, Saido TC (2001) Metabolic regulation of brain Aβ by neprilysin. Science 292:1550–1552
Jalkute C, Barage S, Dhanavade M, Sonawane K (2015) Insight into molecular interactions of Aβ peptide and gelatinase from Enterococcus faecalis: a molecular modeling approach. RSC Adv 5:10488–10496
Jung S, Zhang W, Van Nostrand W (2003) Pathogenic A beta induces the expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells. J Neurochem 85:1208–1215
Kurochkin I, Goto S (1994) Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide specifically interacts with and is degraded by insulin degrading enzyme. FEBS Lett 345:33–37
Kuruppua S, Rajapakseb N, Spicerd A, Parkingtonc H, Smith A (2016) Stimulating the activity of amyloid-beta degrading enzymes: a novel approach for the therapeutic manipulation of amyloid-beta levels. J Alzheimers Dis 54:891–895
Leissring M, Farris W, Chang A, Walsh D, Wu X, Sun X, Frosch M, Selkoe D (2003) Enhanced proteolysis of β-amyloid in APP transgenic mice prevents plaque formation, secondary pathology, and premature death. Neuron 40:1087–1093
Lendeckel U, Arndt M, Frank K, Spiess A, Reinhold D, Ansorge S (2000) Modulation of WNT-5A expression by actinonin: linkage of APN to the WNT-pathway? Adv Exp Med Biol 477:35–41
Loncarevic N, Mehmedika-Sulic E, Alajibegovic A (2005) The neurologist role in diagnostics and therapy of the Alzheimer’s disease. Med Arc 59(2):106–109
Love S, Miners S, Palmer J, Chalmers K, Kehoe P (2009) Insights into the pathogenesis and pathogenicity of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Front Biosci 14:4778–4792
Lyte M, Villageliú D, Crooker B, Brown D (2018) Symposium review: microbial endocrinology—why the integration of microbes, epithelial cells, and neurochemical signals in the digestive tract matters to ruminant health1. J Dairy Sci 101:5619–5628
Maheshwari P, Eslick G (2015) Bacterial infection and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 43:957–966
Maruyama M, Higuchi M, Takaki Y, Matsuba Y, Tanji H, Nemoto M, Tomita N, Matsui T, Iwata N, Mizukami H, Muramatsu S, Ozawa K, Saido TC, Arai H, Sasaki H (2005) Cerebrospinal fluid neprilysin is reduced in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 57:832–842
Masters C, Simms G, Weinman N, Multhaup G, McDonald B, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4245–4249
McDermott J, Gibson A (1997) Degradation of Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid protein by human and rat brain peptidases: involvement of insulin-degrading enzyme. Neurochem Res 22:49–56
Medeiros R, Baglietto-Vargas D, LaFerla F (2011) The Role of tau in Alzheimer's Disease and related disorders. CNS Neurosci Ther 17(5):514–524
Miklossy J (2011a) Alzheimer’s disease_a neurospirochetosis. Analysis of the evidence following Koch’s and Hill’s criteria. J Neuroinflammation 8:90
Miklossy J (2011b) Emerging roles of pathogens in Alzheimer disease. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e30
Miners J, Baig S, Palmer J, Palmer L, Kehoe P, Love S (2008) A beta-degrading enzymes in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol 18:240–252
Morris G, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner M, Belew R, Goodsell D, Olson A (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30(16):2785–2791
Mort J, Buttle D (1997) Cathepsin B. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29:715–720
Mueller-Steiner S, Zhou Y, Arai H, Roberson E, Sun B, Chen J, Wang X, Yu G, Esposito L, Mucke L, Gan L (2006) Antiamyloidogenic and neuroprotective functions of cathepsinB: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 51:703–714
Nalivaeva N, Fisk L, Belyaev N, Turner A (2008) Amyloid-degrading enzymes as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 5:212–224
Ningthoujama D, Mukherjeea S, Devia L, Singha E, Tamreihaoa K, Khunjamayuma R, Banerjeeb S, Mukhopadhyay D (2019) In vitro degradation of β-amyloid fibrils by microbial keratinase. Alzheimer’s Dementia Transl Res Clin Interv 5:154–163
Nishino R, Mikami K, Takahashi H, Tomonaga S, Furuse M, Hiramoto T, Aiba Y, Koga Y, Sudo N (2013) Commensal microbiota modulate murine behaviors in a strictly contamination-free environment confirmed by culture-based methods. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:521–528
Parsons C, Danysz W, Dekundy A, Pulte I (2013) Memantine and cholinesterase inhibitors: complementary mechanisms in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res 24:358–369
Poole S, Singhrao S, Kesavalu L, Curtis M, Crean S (2013) Determining the presence of periodontopathic virulence factors in short-term postmortem Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue. J Alzheimers Dis 36:665–677
Qiu W, Borth W, Ye Z, Haass C, Teplow D, Selkoe D (1996) Degradation of amyloid beta-protein by a serine proteasealpha2-macroglobulin complex. J Biol Chem 271:8443–8451
Qiu W, Walsh D, Ye Z, Vekrellis K, Zhang J, Podlisny M, Rosner M, Safavi A, Hersh L, Selkoe D (1998) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates extra-cellular levels of amyloid β-protein by degradation. J Biol Chem 273:32730–32738
Rangan S, Liu R, Brune D, Planque S, Paul S, Sierks M (2003) Degradation of beta-amyloid by proteolytic antibody light chains. J Biochem 42:14328–14334
Reitz C (2012) Alzheimer’s Disease and the amyloid cascade hypothesis: a critical review. Int J Alzheimer’s Dis. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/369808
Ribaric S (2018) Peptides as potential therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 23:283–313
Riviere G, Riviere K, Smith K (2002) Molecular and immunological evidence of oral Treponema in the human brain and their association with Alzheimer’s disease. Oral Microbiol Immunol 17:113–118
Roher A, Kasunic T, Woods A, Cotter R, Ball M, Fridman R (1994) Proteolysis of A beta peptide from Alzheimer disease brain by gelatinase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 205:1755–1761
Rowsell S, Hawtin P, Minshull C, Jepson H, Brockbank S, Barratt D, Slater A, McPheat W, Waterson D, Henney A, Pauptit R (2002) Crystal structure of human MMP9 in complex with a reverse hydroxamate inhibitor. J Mol Biol 319(1):173–181
Russo C, Saido T, DeBusk L, Tabaton M, Gambetti P, Teller J (1997) Heterogeneity of water-soluble b-peptide in Alzheimer’s disease and Down’s syndrome brains. FEBS Lett 409:411–416
Saido T, Yamao-Harigaya W, Iwatsubo T, Kawashima S (1996) Amino-and carboxy-terminal heterogeneity of b-amyloid peptides deposited in human brain. Neurosci Lett 215:173–176
Sánchez-López E, Ettcheto M, Egea M, Espina M, Cano A, Calpena A, Camins A, Carmona N, Silva A, Souto E, García M (2018) Memantine loaded PLGA PEGylated nanoparticles for Alzheimer's disease: in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Nanobiotechnol 16(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0356-z
Sasaki H, Saito Y, Hayashi M, Otsuka K, Niwa M (1988) Nucleotide sequence of the tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA from human fetal lung cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16(12):5692
Schneider L, Insel P, Weiner M (2011) Treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine of patients in the Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative treatment with ChEIs and Memantine in ADNI. Arch Neurol 68:58–66
Sevalle J, Amoyel A, Robert P, Fournié-Zaluski M, Roques B, Checler F (2009) Aminopeptidase A contributes to the N-terminal truncation of amyloid b-peptide. J Neurochem 109:248–256
Shima K, Kuhlenbäumer G, Rupp J (2010) Chlamydia pneumonia infection and Alzheimer’s disease: a connection to remember? Med Microbiol Immunol 199:283–289
Sikanyika N, Parkington H, Smith A, Kuruppu S (2019) Powering amyloid beta degrading enzymes: a possible therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02756-x
Sochocka M, Donskow-Łysoniewska K, Diniz B, Kurpas D, Brzozowska E, Leszek J (2019) The gut microbiome alterations and inflammation-driven pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease—a critical review. Mol Neurobiol 56(3):1841–1851
Stakos D, Stamatelopoulos K, Bampatsias D, Sachse M, Zormpas E, Vlachogiannis N, Tual-Chalot S, Stellos K (2020) The Alzheimer’s Disease amyloid-beta hypothesis in cardiovascular aging and disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 75(8):952–967
Stoltze L, Schirle M, Schwarz G, Schroter C, Thompson M, Hersh L, Kalbacher H, Stevanovic S, Rammensee H, Schild H (2000) Two new proteases in the MHC class I processing pathway. Nat Immunol 1:413–418
Tanzi R, Bertram L (2005) Twenty years of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid hypothesis: a genetic perspective. Cell 120:545–555
Taylor A (1993a) Aminopeptidases: structure and function. FASEB J 7:290–298
Taylor A (1993b) Aminopeptidases: towards a mechanism of action. Trends Biochem Sci 18:167–171
Thomas C, Hong T, van Pijkeren J, Hemarajata P, Trinh D, Hu W, Britton R, Kalkum M, Versalovic J (2012) Histamine derived from probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri suppresses TNF via modulation of PKA and ERK signaling. PLoS ONE 7:e31951
Tucker H, Kihiko M, Caldwell J, Wright S, Kawarabayashi T, Price D, Walker D, Scheff S, McGillis J, Rydel R, Estus S (2000) The plasmin system is induced by and degrades amyloid-β aggregates. J Neurosci 20:3937–3946
Turk B, Bieth J, Bjork I, Dolenc I, Turk D, Cimerman N, Kos J, Colic A, Stoka V, Turk V (1995) Regulation of the activity of lysosomal cysteine proteinases by pH-induced inactivation and/or endogenous protein inhibitors, cystatins. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 376:225–230
Verde P, Boast S, Franze A, Robbiati F, Blasi F (1988) An upstream enhancer and a negative element in the 5_flanking region of the human urokinase plasminogen activator gene. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10699–10716
Wall R, Cryan J, Ross R, Fitzgerald G, Dinan T, Stanton C (2014) Bacterial neuroactive compounds produced by psychobiotics. Adv Exp Med Biol 817:221–239
Wang D, Dickson D, Malter J (2006) Beta-Amyloid degradation and Alzheimer's disease. J Biomed Biotechnol 2006:58406
Wang Y, Garg S, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow E (2010) Proteolytic processing of tau. Biochem Soc Trans 38:955–961
Weller R, Yow H, Preston S, Mazanti I, Nicoll J (2002) Cerebrovascular disease is a major factor in the failure of elimination of Ab from the aging human brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 977:162–168
Yamada T, Kluve-Beckerman B, Liepnieks J, Benson M (1995a) In vitro degradation of serum amyloid A by cathepsin D and other acid proteases: possible protection against amyloid fibril formation. Scand J Immunol 41:570–574
Yamada T, Miyazaki K, Koshikawa N, Takahashi M, Akatsu H, Yamamoto T (1995b) Selective localization of gelatinase A, an enzyme degrading beta-amyloid protein, in white matter microglia and in Schwann cells. Acta Neuropathologica (Berl) 89:199–203
Yan P, Hu X, Song H, Yin K, Bateman R, Cirrito J, Xiao Q, Hsu F, Turk J, Xu J, Hsu C, Holtzman D, Lee J (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 degrades amyloid-β fibrils in vitro and compact plaques in situ. J Biol Chem 281:24566–24574
Yao T, Cohen R (1999) Giant proteases: beyond the proteasome. Curr Biol 9:R551–R553
Yin K, Cirrito J, Yan P, Hu X, Xiao Q, Pan X, Bateman R, Song H, Hsu F, Turk J (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases expressed by astrocytes mediate extracellular amyloid-beta peptide catabolism. J Neurosci 26:10939–10948
Yoo C, Ahn K, Park J, Kim M, Jo S (2010) An aminopeptidase from Streptomyces sp. KK565 degrades beta amyloid monomers, oligomers and fibrils. FEBS Lett 584:4157–4162
Yuedea C, Donga H, Csernansky J (2007) Anti-dementia drugs and hippocampal-dependent memory in rodents. Behav Pharmacol 18(5–6):347–363
Zou K, Yamaguchi H, Akatsu H, Sakamoto T, Ko M, Mizoguchi K, Gong J, Yu W, Yamamoto T, Kosaka K (2007) Angiotensin converting enzyme converts amyloid beta-protein1–42 (Aβ1–42) toAβ1–40, and its inhibition enhances brain Abeta deposition. J Neurosci 27:8628–8635
Acknowledgements
KDS is thankful to University Grants Commission, New Delhi for providing financial support under UGC SAP DRS Phase-II programme sanctioned to Department of Biochemistry, Shivaji University, Kolhapur. Authors are thankful to Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for providing fellowship as research assistance under DST-PURSE scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanavade, M.J., Sonawane, K.D. Amyloid beta peptide-degrading microbial enzymes and its implication in drug design. 3 Biotech 10, 247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02240-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02240-2