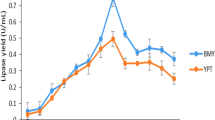
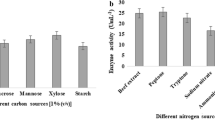
Abstract
Extremophilic microbial derived lipases have been widely applied in different biotechnological processes due to their resistance to harsh conditions such as high salt concentration, elevated temperature, and extreme acidic or alkaline pH. The present study was designed to overproduce the halophilic, thermoalkalophilic lipase of Bacillus atrophaeus FSHM2 through chemically induced random mutagenesis and optimization of cultural medium components assisted by statistical experimental design. At first, improvement of lipase production ability of B. atrophaeus FSHM2 was performed through exposure of the wild bacterial strain to ethidium bromide for 5–90 min to obtain a suitable mutant of lipase producer (designated as EB-5, 4301.1 U/l). Afterwards, Plackett–Burman experimental design augmented to D-optimal design was employed to optimize medium components (olive oil, maltose, glucose, sucrose, tryptone, urea, (NH4)2SO4, NaCl, CaCl2, and ZnSO4) for lipase production by the EB-5 mutant. A maximum lipase production of 14,824.3 U/l was predicted in the optimum medium containing 5% of olive oil, 0.5% of glucose, 0.5% of sucrose, 2% of maltose, 2.5 g/l of yeast extract, 1.75 g/l of urea, 1.75 g/l of (NH4)2SO4, 2.5 g/l of tryptone, 2 g/l of NaCl, 1 g/l of CaCl2, and 1 g/l of ZnSO4. A mean value of 14,773 ± 576.9 U/l of lipase was acquired from real experiments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlercreutz P (2013) Immobilisation and application of lipases in organic media. Chem Soc Rev 42:6406–6436. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35446f
Ameri A, Shakibaie M, Faramarzi MA, Ameri A, Amirpour-Rostami S, Rahimi HR, Forootanfar H (2017) Thermoalkalophilic lipase from an extremely halophilic bacterial strain Bacillus atrophaeus FSHM2: purification, biochemical characterization and application. Biocatal Biotransform 35:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/10242422.2017.1308494
Aravindan R, Anbumathi P, Viruthagiri T (2007) Lipase applications in food industry. Indian J Biotechnol 6:141–158
Barbosa O, Ortiz C, Berenguer-Murcia Á, Torres R, Rodrigues RC, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2015) Strategies for the one-step immobilization–purification of enzymes as industrial biocatalysts. Biotechnol Adv 33:435–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.03.006
Bisht D, Yadav SK, Darmwal NS (2012) Enhanced production of extracellular alkaline lipase by an improved strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 10,055. Am J Appl Sci 9:158–167. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajassp.2012.158.167
Bora L, Bora M (2012) Optimization of extracellular thermophilic highly alkaline lipase from thermophilic Bacillus sp. isolated from hotspring of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Braz J Microbiol 43:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822012000100004
Cantone S, Ferrario V, Corici L, Ebert C, Fattor D, Spizzo P, Gardossi L (2013) Efficient immobilisation of industrial biocatalysts: criteria and constraints for the selection of organic polymeric carriers and immobilisation methods. Chem Soc Rev 42:6262–6276. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35464d
Chang SW, Shaw JF (2009) Biocatalysis for the production of carbohydrate esters. New Biotechnol 26:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2009.07.003
Colla LM, Primaz AL, Benedetti S, Loss RA, Lima Md, Reinehr CO, Bertolin TE, Costa JAV (2016) Surface response methodology for the optimization of lipase production under submerged fermentation by filamentous fungi. Braz J Microbiol 47:461–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.01.028
Dandavate V, Jinjala J, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2009) Production, partial purification and characterization of organic solvent tolerant lipase from Burkholderia multivorans V2 and its application for ester synthesis. Bioresour Technol 100:3374–3381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.02.011
Darvishi F, Destain J, Nahvi I, Thonart P, Zarkesh-Esfahani H (2011) High-level production of extracellular lipase by Yarrowia lipolytica mutants from methyl oleate. New Biotechnol 28:756–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.02.002
Das A, Shivakumar S, Bhattacharya S, Shakya S, Swathi SS (2016) Purification and characterization of a surfactant-compatible lipase from Aspergillus tamarii JGIF06 exhibiting energy-efficient removal of oil stains from polycotton fabric. 3 Biotech 6:131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0449-z
Devi SC, Mohanasrinivasan V, Naine JS, Yamini B, Chitra M, Nandhini G (2015) Strain improvement of Pseudomonas sp. VITSDVM1 for optimization of lipase production by chemical mutagens. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 6:782–787
Faisal PA, Hareesh ES, Priji P, Unni KN, Sajith S, Sreedevi S, Josh MS, Benjamin S (2014) Optimization of parameters for the production of lipase from Pseudomonas sp. BUP6 by solid state fermentation. Adv Enzyme Res 2:125–134. https://doi.org/10.4236/aer.2014.24013
Forootanfar H, Amirpour-Rostami S, Jafari M, Forootanfar A, Yousefizadeh Z, Shakibaie M (2015) Microbial-assisted synthesis and evaluation the cytotoxic effect of tellurium nanorods. Mater Sci Eng C 49:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.12.078
Galvão WS, Pinheiro BB, Golçalves LRB, de Mattos MC, Fonseca TS, Regis T, Zampieri D, dos Santos JCS, Costa LS, Correa MA, Bohn F, Fechine PBA (2018) Novel nanohybrid biocatalyst: application in the kinetic resolution of secondary alcohos. J Mater Sci 53:14121–14137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2641-2645
Haider Ali C, Mbadinga SM, Liu J-F, Yang S-Z, Gu J-D, Mu B-Z (2015) Significant enhancement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa FW_SH-1 lipase production using response surface methodology and analysis of its hydrolysis capability. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 52:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.02.001
Hanefeld U, Cao L, Magner E (2013) Enzyme immobilisation: fundamentals and application. Chem Soc Rev 42:6211–6212. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS90042H
Hasan-Beikdashti M, Forootanfar H, Safiarian M, Ameri A, Ghahremani M, Khoshayand M, Faramarzi M (2012) Optimization of culture conditions for production of lipase by a newly isolated bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43:670–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.03.005
Iftikhar T, Niaz M, Abbas SQ, Zia MA, Ashraf I, Lee KJ, Haq I (2010) Mutation induced enhanced biosynthesis of lipases by Rhizopus oligosporus var. microsporus. Pak J Bot 42:1235–1249
Jaeger K-E, Eggert T (2002) Lipases for biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:390–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(02)00341-5
Khoobi M, Motevalizadeh SF, Asadgol Z, Forootanfar H, Shafiee A, Faramarzi MA (2014) Synthesis of functionalized polyethylenimine-grafted mesoporous silica spheres and the effect of side arms on lipase immobilization and application. Biochem Eng J 88:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.04.009
Khoobi M, Khalilvand-Sedagheh M, Ramazani A, Asadgol Z, Forootanfar H, Faramarzi MA (2016) Synthesis of polyethyleneimine (PEI) and β-cyclodextrin grafted PEI nanocomposites with magnetic cores for lipase immobilization and esterification. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4579
Kumar R, Mahajan S, Kumar A, Singh D (2011) Identification of variables and value optimization for optimum lipase production by Bacillus pumilus RK31 using statistical methodology. New Biotechnol 28:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2010.06.007
Li J, Shen W, Fan G, Li X (2018) Screening, purification and characterization of lipase from Burkholderia pyrrocinia B1213. 3 Biotech 8:387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1414-9
Liu J, Zhang Y (2011) Optimisation of lipase production by a mutant of Candida antarctica DSM-3855 using response surface methodology. Int J Food Sci Technol 46:695–701. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2011.02548.x
Liu C-H, Chen C-Y, Wang Y-W, Chang J-S (2011) Fermentation strategies for the production of lipase by an indigenous isolate Burkholderia sp. C20. Biochem Eng J 58:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2011.09.001
Lo CF, Yu CY, Kuan IC, Lee SL (2012) Optimization of lipase production by Burkholderia sp. using response surface methodology. Int J Mol Med Sci 13:14889–14897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131114889
Mahanta N, Gupta A, Khare S (2008) Production of protease and lipase by solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PseA in solid-state fermentation using Jatropha curcas seed cake as substrate. Bioresour Technol 99:1729–1735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.03.046
Manoel EA, Ribeiro MF, Dos Santos JC, Coelho MAZ, Simas AB, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Freire DM (2015) Accurel MP 1000 as a support for the immobilization of lipase from Burkholderia cepacia: application to the kinetic resolution of myo-inositol derivatives. Process Biochem 50:1557–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.06.023
Moshafi MH, Forootanfar H, Ameri A, Shakibaie M, Dehghan-Noudeh G, Razavi M (2011) Antimicrobial activity of Bacillus sp. strain FAS1 isolated from soil. Pak J Pharm Sci 24:269–275
Arana-Peña S, Lokha Y, Fernández-Lafuente R (2018) Immobilization of eversa lipase on octyl agarose beads and preliminary characterization of stability and activity features. Catalysts 8:511. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8110511
Pinheiro MP, Rios NS, Fonseca TdS, Bezerra FdA, Rodríguez-Castellón E, Fernandez-Lafuente R, Carlos de Mattos M, dos Santos JC, Gonçalves LR (2018) Kinetic resolution of drug intermediates catalyzed by lipase B from Candida antarctica immobilized on immobead-350. Biotechnol Prog 34:878–889. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2630
Raju EVN, Divakar G (2013) Non recombinant mutagenesis of Bacillus cereus for fibrinolytic protease production. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 2:6189–6201
Rios NS, Pinheiro BB, Pinheiro MP, Bezerra RM, dos Santos JCS, Gonçalves LRB (2018) Biotechnological potential of lipases from Pseudomonas: sources, properties and applications. Process Biochem 75:99–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.09.003
Riyadi FA, Alam MZ, Salleh MN, Salleh HM (2017) Optimization of thermostable organic solvent-tolerant lipase production by thermotolerant Rhizopus sp. using solid-state fermentation of palm kernel cake. 3 Biotech 7:300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0932-1
Salihu A, Alam MZ, AbdulKarim MI, Salleh HM (2011) Optimization of lipase production by Candida cylindracea in palm oil mill effluent based medium using statistical experimental design. J Mol Catal B Enzym 69:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.12.012
Samaei-Nouroozi A, Rezaei S, Khoshnevis N, Doosti M, Hajihoseini R, Khoshayand MR, Faramarzi MA (2015) Medium-based optimization of an organic solvent-tolerant extracellular lipase from the isolated halophilic Alkalibacillus salilacus. Extremophiles 19:933–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0769-7
Sangeetha R, Geetha A, Arulpandi I (2008) Optimization of protease and lipase production by Bacillus pumilus SG 2 isolated from an industrial effluent. Internet J Microbiol 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.5580/2126
Sathishkumar R, Ananthan G, Iyappan K, Stalin C (2015) A statistical approach for optimization of alkaline lipase production by ascidian associated—Halobacillus trueperi RSK CAS9. Biotechnol Rep 8:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2015.09.002
Sheldon RA, Pelt SV (2013) Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: why, what and how. Chem Soc Rev 42:6223–6235. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60075k
Toscano L, Gochev V, Montero G, Stoytcheva M (2011) Enhanced production of extracellular lipase by novel mutant strain of Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 25:2243–2247. https://doi.org/10.5504/BBEQ.2011.0019
Vasiee A, Behbahani BA, Yazdi FT, Moradi S (2016) Optimization of the production conditions of the lipase produced by Bacillus cereus from rice flour through Plackett-Burman design (PBD) and response surface methodology (RSM). Microb Pathog 101:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.10.020
Veerapagu M, Narayanan AS, Ponmurugan K, Jeya K (2013) Screening selection identification production and optimization of bacterial lipase from oil spilled soil. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 6:62–67
Verma S, Saxena J, Prasanna R, Sharma V, Nain L (2012) Medium optimization for a novel crude-oil degrading lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa SL-72 using statistical approaches for bioremediation of crude-oil. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 1:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2012.07.002
Yao C, Cao Y, Wu S, Li S, He B (2013) An organic solvent and thermally stable lipase from Burkholderia ambifaria YCJ01: purification, characteristics and application for chiral resolution of mandelic acid. J Mol Catal B Enzym 85:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2012.08.016
Yele VU, Desai K (2015) A new thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Staphylococcus warneri; optimization of media and production conditions using statistical methods. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:855–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1331-2
Zhang J, Shi H, Wu D, Xing Z, Zhang A, Yang Y, Li Q (2014) Recent developments in lipase-catalyzed synthesis of polymeric materials. Process Biochem 49:797–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.02.006
Zhang J-D, Zhao J-W, Gao L-L, Chang H-H, Wei W-L, Xu J-H (2019) Enantioselective synthesis of enantiopure β-amino alcohols via kinetic resolution and asymmetric reductive amination by a robust transaminase from Mycobacterium vanbaalenii. J Biotechnol 290:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.12.003
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute for Medical Research Development of Iran (NIMAD, 977008). Furthermore, we thank the Pharmaceutics Research Center, Institute of Neuropharmacology, Kerman University of Medical Sciences (Kerman, Iran) for their admirable participation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ameri, A., Shakibaie, M., Sahami, Z. et al. Statistical optimization of cultural medium composition of thermoalkalophilic lipase produced by a chemically induced mutant strain of Bacillus atrophaeus FSHM2. 3 Biotech 9, 268 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1789-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1789-2