Abstract
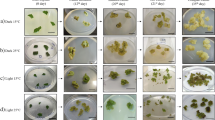
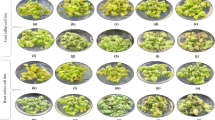
Anthocyanins are major water-soluble and dynamic colouring plant pigment present in plant tissues with the high antioxidant properties. The role of ammonium and potassium nitrate in the culture medium on anthocyanin augmentation is probed thoroughly, but the mechanism of its biosynthesis continues to be unclear. Hence, the present study was undertaken to optimise nitrate ratio in the culture medium for anthocyanin augmentation and examination of its biosynthesis pathway in callus culture of Daucus carota. MS basal medium fortified with various ratio of NH4NO3:KNO3 was employed to find their impact on biomass, anthocyanin augmentation and the expression profile of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in the callus culture. The data indicated that the highest anthocyanin content (9.30 ± 0.25 mg/100 g FW) was seen in callus grown on the medium supplemented with 20.0 mM NH4NO3:37.6 mM KNO3 and the least was seen in the medium which contained 40.0 mM NH4NO3:18.8 mM KNO3 (2.74 ± 0.27 mg/100 g FW). This indicates an optimal concentration of NH4NO3:KNO3 ratio is essential to produce a higher amount of anthocyanin in in vitro culture. Meanwhile, anthocyanin biosynthesis genes were differentially expressed as confirmed by qRT-PCR in the time interval of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 days. The transcript levels of nine anthocyanin biosynthesis genes were increased in the response of varying NH4NO3:KNO3 ratio in the medium. The transcript level of early genes PAL, 4CL, CHS and CHI increased by 19.5, 21.0, 16.2 and 9.98-fold, respectively, compared with control. In addition, late biosynthesis genes LDOX and UFGT resulted in the transcript level of 11.3 and 13.6-fold, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- 4CL:
-
4-Coumaroyl:CoA-ligase
- C4H:
-
Cinnamate 4-hydroxylase
- CHI:
-
Chalcone isomerase
- CHS:
-
Chalcone synthase
- DFR:
-
Dihydroflavonol reductase
- F3H:
-
Flavanone 3-hydroxylase
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- Kin:
-
Kinetin
- LDOX:
-
Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonia lyase
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction
- UFGT:
-
UDP glucose:flavonoid-3-O-glucosyltransferase
References
Abe Y, Sawada A, Momose T, Sasaki N, Kawahara N, Kamakura H, Ozeki Y (2008) Structure of an anthocyanin–anthocyanin dimer molecule in anthocyanin-producing cells of a carrot suspension culture. Tetrahedron Lett 49(51):7330–7333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.10.041
Acquaviva R, Russo A, Galvano F, Galvano G, Barcellona ML, Volti GL, Vanella A (2003) Cyanidin and cyanidin 3-O-β-d-glucoside as DNA cleavage protectors and antioxidants. Cell Biol Toxicol 19(4):243–252. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CBTO.0000003974.27349.4e
Ali M, Abbasi BH, Ahmad N, Khan H, Ali GS (2017) Strategies to enhance biologically active-secondary metabolites in cell cultures of Artemisia—current trends. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37(7):833–851. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2016.1261082
Al-Ibresam OT, Al-Meer UN (2008) Effect of ammonium and potassium nitrate in some characteristics of callus and somatic embryos of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) by in vitro. Basrah J Date Palm Res 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2014.116.125
Al-Turki S, Shahba MA, Stushnoff C (2010) Diversity of antioxidant properties and phenolic content of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits as affected by cultivar and location. J Food Agric Environ 8:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1234/4.2010.1495
Chan LK, Koay SS, Boey PL, Bhatt A (2010) Effects of abiotic stress on biomass and anthocyanin production in cell cultures of Melastoma malabathricum. Biol Res 43(1):127–135. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0716-97602010000100014
Christie PJ, Alfenito MR, Walbot V (1994) Impact of low-temperature stress on general phenylpropanoid and anthocyanin pathways: enhancement of transcript abundance and anthocyanin pigmentation in maize seedlings. Planta 194(4):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00714468
Hennayake CK, Takagi S, Nishimura K, Kanechi M, Uno Y, Inagaki N (2006) Differential expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in suspension culture cells of Rosa hybrida cv. Charleston. Plant Biotechnol 23(4):379–385. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.23.379
Hirasuna TJ, Shuler ML, Lackney VK, Spanswick RM (1991) Enhanced anthocyanin production in grape cell cultures. Plant Sci 78(1):107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9452(91)90167-7
Hiratsuka S, Onodera H, Kawai Y, Kubo T, Itoh H, Wada R (2001) ABA and sugar effects on anthocyanin formation in grape berry cultured in vitro. Sci Hortic 90(1–2):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(00)00264-8
Hussain MS, Fareed S, Saba Ansari M, Rahman A, Ahmad IZ, Saeed M (2012) Current approaches toward production of secondary plant metabolites. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 4(1):10. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.92725
Irshad M, Debnath B, Mitra S, Arafat Y, Li M, Sun Y, Qiu D (2018) Augmentation of anthocyanin in callus cultures of red-pod okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Hongjiao] in response to light and nitrogen levels. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 134:29–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1397-6
Jamwal K, Bhattacharya S, Puri S (2018) Plant growth regulator mediated consequences of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2017.12.003
Kang SY, Seeram NP, Nair MG, Bourquin LD (2003) Tart cherry anthocyanins inhibit tumour development in ApcMin mice and reduce proliferation of human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett 194(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(02)00583-9
Lee Y, Lee DE, Lee HS, Kim SK, Lee WS, Kim SH, Kim MW (2011) Influence of auxins, cytokinins, and nitrogen on production of rutin from callus and adventitious roots of the white mulberry tree (Morus alba L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105(1):9–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9832-3
Li L, Ban ZJ, Li XH, Wu MY, Wang AL, Jiang YQ, Jiang YH (2012) Differential expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes and transcription factor PcMYB10 in pears (Pyrus communis L.). PLos One 7(9):e46070. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046070
Liu W, Zhu DW, Liu DH, Geng MJ, Zhou WB, Mi WJ, Hamilton D (2010) Influence of nitrogen on the primary and secondary metabolism and synthesis of flavonoids in Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. J Plant Nutr 33(2):240–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160903434287
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \({2^{ - \Delta \Delta {C_{\text{T}}}}}\) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loreti E, Povero G, Novi G, Solfanelli C, Alpi A, Perata P (2008) Gibberellins, jasmonate and abscisic acid modulate the sucrose-induced expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 179(4):1004–1016. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02511.x
Lovdal T, Olsen KM, Slimestad R, Verheul M, Lillo C (2010) Synergetic effects of nitrogen depletion, temperature, and light on the content of phenolic compounds and gene expression in leaves of tomato. Phytochemistry 71(5–6):605–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.12.014
Lu Q, Yang Q, Zou H (2006) Effects of cerium on augmentation of anthocyanins and expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in potato cell tissue cultures. J Rare Earth 24(4):479–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(06)60147-6
Madhavi DL, Juthangkoon S, Lewen K, Berber-Jimenez MD, Smith MAL (1996) Characterization of anthocyanins from Ajuga pyramidalis Metallica Crispa cell cultures. J Agric Food Chem 44(4):1170–1176. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf950504u
Madrigal-Santillan E, Madrigal-Bujaidar E, Alvarez-Gonzalez I, Sumaya-Martinez MT, Gutierrez-Salinas J, Bautista M, Morales-Gonzalez JA (2014) Review of natural products with hepatoprotective effects. World J Gastroenterol 20(40):14787. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14787
Maharik N, Elgengaihi S, Taha H (2009) Anthocyanin production in callus cultures of Crataegus sinaica Boiss. Int J Acad Res 1(1):30–34. https://doi.org/10.7813/2075-4124.2009/1-1/A.3
Manuhara YSW, Kristanti AN, Utami ESW, Yachya A (2015) Effect of sucrose and potassium nitrate on biomass and saponin content of Talinum paniculatum Gaertn. hairy root in balloon-type bubble bioreactor. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 5(12):1027–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.09.009
Meyer HJ, Van Staden J (1995) The in vitro production of an anthocyanin from callus cultures of Oxalis linearis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 40(1):55–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041119
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Nabavi SF, Habtemariam S, Daglia M, Shafighi N, Barber AJ, Nabavi SM (2015) Anthocyanins as a potential therapy for diabetic retinopathy. Curr Med Chem 22(1):51–58. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666140815123852
Peng M, Hudson D, Schofield A, Tsao R, Yang R, Gu H, Rothstein SJ (2008) Adaptation of Arabidopsis to nitrogen limitation involves induction of anthocyanin synthesis which is controlled by the NLA gene. J Exp Bot 59(11):2933–2944. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern148
Ramirez-Tortosa C, Andersen OM, Gardner PT, Morrice PC, Wood SG, Duthie SJ, Duthie GG (2001) Anthocyanin-rich extract decreases indices of lipid peroxidation and DNA damage in vitamin E-depleted rats. Free Radic Biol Med 31(9):1033–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00618-9
Saad KR, Parvatam G, Shetty NP (2018) Medium composition potentially regulates the anthocyanin production from suspension culture of Daucus carota. 3 Biotech 8(3):134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1146-x
Salmona J, Dussert S, Descroix F, De Kochko A, Bertrand B, Joet T (2008) Deciphering transcriptional networks that govern Coffea arabica seed development using combined cDNA array and real-time RT-PCR approaches. Plant Mol Biol 66(1–2):105–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9256-6
Samanta A, Das G, Das SK (2011) Roles of flavonoids in plants. Int J Pharm Sci Technol 6(1):12–35
Shan X, Zhang Y, Peng W, Wang Z, Xie D (2009) Molecular mechanism for jasmonate-induction of anthocyanin augmentation in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 60(13):3849–3860. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp223
Shehata WF, Aldaej MI, Alturki SM, Ghazzawy HS (2014) Effect of ammonium nitrate on antioxidants production of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) in vitro. Biotechnology 13(3):116–125. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2014.116.125
Shi MZ, Xie DY (2010) Features of anthocyanin biosynthesis in pap1-D and wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana plants grown in different light intensity and culture media conditions. Planta 231(6):1385–1400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1142-9
Solfanelli C, Poggi A, Loreti E, Alpi A, Perata P (2006) Sucrose-specific induction of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140(2):637–646. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.066688
Tanaka N, Shimomura K, Ishimaru K (1995) Tannin production in callus cultures of Quercus acutissima. Phytochemistry 40(4):1151–1154. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(95)00378-K
Valenti L, Riso P, Mazzocchi A, Porrini M, Fargion S, Agostoni C (2013) Dietary anthocyanins as nutritional therapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/145421
Wan H, Zhang J, Song T, Tian J, Yao Y (2015) Promotion of flavonoid biosynthesis in leaves and calli of ornamental crabapple (Malus sp.) by high carbon to nitrogen ratios. Front Plant Sci 6:673. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00673
Wang N, Zhang Z, Jiang S, Xu H, Wang Y, Feng S, Chen X (2016) Synergistic effects of light and temperature on anthocyanin biosynthesis in callus cultures of red-fleshed apple (Malus sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 127(1):217–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1044-z
Wrolstad RE, Durst RW, Lee J (2005) Tracking color and pigment changes in anthocyanin products. Trends Food Sci Technol 16:423–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.03.019
Zahedzadeh F, Kakavand F, Mahna N (2015) Effects of carbohydrate, light, nitrogen and magnesium on in vitro production of anthocyanin in apple. Int J Biosci 6(5):250–260. https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/6.5.250-5
Zhang W, Curtin C, Franco C (2002) Towards manipulation of post-biosynthetic events in secondary metabolism of plant cell cultures. Enzym Microb Technol 30(6):688–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00041-8
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Central Food Technological Research Institute (CFTRI). We thank to our Director CSIR-CFTRI who provided insight and expertise that greatly assisted the research. We would also like to thank Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saad, K.R., Kumar, G., Giridhar, P. et al. Differential expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in Daucus carota callus culture in response to ammonium and potassium nitrate ratio in the culture medium. 3 Biotech 8, 431 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1447-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1447-0