Abstract
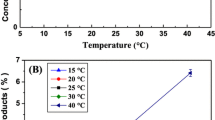
In the present study, fungal biotransformation of synthetic levodopa to stable dopamine in an l-ascorbate-mediated thermophilic-aerobic biochemical reaction was investigated. A mutant strain of Aspergillus oryzae EMS-6 was used for the preparation of mycelial biomass. The mutant was previously developed through EMS-induced mutagenesis and repressed against l-cysteine HCl. Growth parameters such as rate of cultivation (48 h), initial pH (6) and incubation temperature (30 °C) supported 18.84 g/l biomass with 23 g/l glucose consumption. Thermophilic behaviour of culture was observed at 25–40 °C. Kinetic variables notably µ = 0.385 /h and Qs, exhibited consistent growth pattern. Biochemical reactions were performed aerobically using mycelial biomass as the source of enzyme ‘tyrosinase’ in a digital hotplate equipped with magnetic stirrers. The reaction conditions included 5 mg/ml biomass and 2.5 mg/ml levodopa as basal substrate in a thermophilic reaction of 25 min duration acidified with l-ascorbic acid. TLC and HPLC analysis of reaction mixture confirmed the presence of levodopa and dopamine using a CN-9dth (R) column. Activation enthalpy and entropy of dopa decarboxylase (DDC) and its thermal inactivation showed an improved biotransformation of levodopa to dopamine at the optimal temperature (30 °C) as compared to other temperatures being employed. Overall, 3.68 mg/ml dopamine (4.55 mg/ml proteins) synthesis from 2.38 mg/ml levodopa was accomplished. The enhancement in metabolic activity of the mutant strain is ~ 2.75-fold improved when compared to the unoptimized reaction conditions, which is highly significant (HS) indicating an eco-commercially viable (LSD ~ 0.412) bioprocess.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba S, Humphrey AE, Millis NF (1973) Biochemical engineering, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 92–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm
Ali S, Haq I, Qadeer MA, Rajoka MI (2005) Double mutant of Aspergillus oryzae for improved production of 3,4-dihydroxy phenyl-l-alanine from l-tyrosine. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 42:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1042/BA20040180
Arnow LE (1973) Colorimetric determination of the components of l-3,4-dihydroxy phenylalanine in tyrosine mixtures. J Biochem 88:531
Bertoldi M, Voltattorni CB (2000) Reaction of dopa decarboxylase with l-aromatic amino acids under aerobic and anaerobic condition. Biochem J 352:533–538
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid method for the quantification of program quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Charteris A, John RA (1975) An investigation of the assay of dopamine using trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid. Anal Biochem 66:365–371
Christensen G (1972) Effects of metal cations and other chemicals upon the in vitro activity of two enzymesin the blood plasma of the white sucker Catostomus commersoni. Chem Biol Interact 4:351–361
Converti A, Dominguez JM (2001) Influence of temperature and pH on xylitol production from xylose by Debarryomyces hansenii. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:39–45
Felger JC, Miller AH (2012) Cytokine effects on the basal ganglia and dopamine function: the subcortical source of inflammatory malaise. Front Neuroendocrinol 33:315–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2012.09.003
Felger JC, Hernandez CR, Miller AH (2015) Levodopa reverses cytokine-induced reductions in striatal dopamine release. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyu084
Haneda Y, Tsuji FI, Sugiyama N (1969) Luminescent systems in apogonid fishes from the Philippines. Science 165(3889):188–190
Haneda K, Watanabe S, Takeda P (1973) l-DOPA by microorganisms. J Ferment Technol 51:398–406
Haq I, Ali S, Qadeer MA (2002) Biosynthesis of l-Dopa by Aspergillus oryzae. Bioresour Technol 85:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00060-3
Hodgetts RB, O’Keefe SL (2006) Dopa decarboxylase: a model gene-enzyme system for studying development, behaviour and systematics. Annu Rev Entomol 51:259–284. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151143
Hyland K, Surtees RAH, Rodeck C, Clayton PT (1992) Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, diagnosis and treatmentof a new born error of neurotransmitter amine synthesis. Neurol 42:1980–1988
Kaljunen H, Gasparetti C, Kruus K, Rouvinen J, Hakulinen N (2011) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of Aspergillus oryzae catechol oxidase. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67:672–674. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309107060721
Kanteev M, Goldfeder M, Fishman A (2015) Structure-function correlations in tyrosinases. Protein Sci 24:1360–1369. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2734
Li J, Christensen BM (1993) Identification of products and intermediates during l-dopa oxidation to dopachrome using pressure liquid chromatography. J LIq Chromatogr 16:1117–1133
Minelli A, Charteris AT, Voltattorni CB, John RA (1979) Reactions of Dopa (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) decarboxylase with Dopa. Biochem J 183:2843–2851
Nakamura M, Nakajima T, Ohba Y, Yamauchi S, Lee BR, Ichishima E (2000) Identification of copper ligands in Aspergillus oryzae tyrosinase by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J 350:537–545
Piccini P, Brooks DJ, Bjorklund A, Gunn RN, Grasby PM, Rimoldi O, Brundin P, Hagell P, Rehnrona S, Widner H, Lindwall O (1999) Dopamine release from nigral transplants visualized in vivo in a Parkinson’s patient. Nat Neurosci 2:1137–1140
Pirt SJ (1975) Principles of cell cultivation. Blackwells Scientific Corporation, London
Pontecarvo J, Roper JA, Hemmous LM, Buftan W (1969) Basic techniques of UV-irradiation and chemical mutation. Adv Genet 5:141–183
Raju BG, Rao GH, Ayyanna C (1993) Bioconversion of tyrosine to melanin using mycelia of Aspergillus spp. CBS Publishers, Visakhapatnam
Salinas AG, Davis MI, Lovinger DM, Mateo Y (2016) Dopamine dynamics and cocaine sensitivity differ between striosome and matrix compartments of the striatum. Neuropharmacol 108:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.049
Sherald AF, Sparrow JC, Wright TRF (1973) A spectrophotometric assay for Drosophila dopa decarboxylase. Anal Biochem 56:300–305
Sirivelu MP, Mohankumar SMJ, Wagner JG, Harkema JR, Mohankumar PS (2006) Activation of the stress axis and neurochemical alterations in specific brain areas by concentrated ambient particle exposure with concomitant allergic airway disease. Environ Health Perspect 114:870–874
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods, 7th edn. Ames, Iowa state University Press, Iowa.
Tang MC, Zou Y, Watanabe K, Walsh CT, Tang Y (2017) Oxidative cyclization in natural product biosynthesis. Chem Rev 117:5226–5333. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00478
Vaillancourt DE, Schonfeld D, Kwak Y, Bohnen NI, Seidler R (2013) Dopamine overdose hypothesis: evidence and clinical implications. Mov Disord 28:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25687
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S. Fungal biotransformation of synthetic levodopa to stable dopamine in l-ascorbate-mediated aerobic-thermophilic biochemical process. 3 Biotech 8, 370 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1398-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1398-5