Abstract
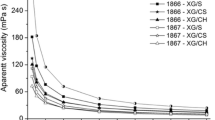
Xanthan gum is an exo-polysaccharide industrially produced by fermentation using simple sugars. In this study, broomcorn stem was introduced as a low-cost- and widely available carbon source for xanthan gum fermentation. Broomcorn stem was hydrolyzed using sulphuric acid to liberate reducing sugar which was then used as a carbon source for biosynthesis of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campesteris. Effects of hydrolysis time (15, 30, 45 and 60 min), sulphuric acid concentration (2, 4, 6 and 8% v/v) and solid loading (3, 4, 5 and 6% w/v) on the yield of reducing sugar and consequent xanthan production were investigated. Maximum reducing sugar yield (55.2%) and xanthan concentration (8.9 g/L) were obtained from hydrolysis of 4% (w/v) broomcorn stem with 6% (v/v) sulphuric acid for 45 min. The fermentation product was identified and confirmed as xanthan gum using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis. Thermogrvimetric analysis showed that thermal stability of synthesized xanthan gum was similar to those reported in previous studies. The molecular weight of the produced xanthan (2.23 × 106 g/mol) was determined from the intrinsic viscosity. The pyruvate and acetyl contents in xanthan gum were 4.21 and 5.04%, respectively. The chemical composition results indicated that this biopolymer contained glucose, mannose and glucoronic acid with molecular ratio of 1.8:1.5:1.0. The kinetics of batch fermentation was also investigated. The kinetic parameters of the model were determined by fermentation results and evaluated. The results of this study are noteworthy for the sustainable xanthan gum production from low-value agricultural waste.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatia SK, Kumar N, Bhatia RK (2015) Stepwise bioprocess for exopolysaccharide production using potato starch as carbon source. 3 Biotech 5(5):735–739
Bhatia SK, Lee BR, Sathiyanarayanan G, Song HS, Kim J, Jeon JM, Kim JH, Park SH, Yu JH, Park K, Yang YH (2016) Medium engineering for enhanced production of undecylprodigiosin antibiotic in Streptomyces coelicolor using oil palm biomass hydrolysate as a carbon source. Bioresour Technol 217:141–149
Bhatia SK, Kim J, Song HS, Kim HJ, Jeon JM, Sathiyanarayanan G, Yoon JJ, Park K, Kim YG, Yang YH (2017) Microbial biodiesel production from oil palm biomass hydrolysate using marine Rhodococcus sp. YHY01. Bioresour Technol 233:99–109
Casas J, Santos V, Garcıa-Ochoa F (2000) Xanthan gum production under several operational conditions: molecular structure and rheological properties. Enzyme Microb Technol 26(2):282–291
Chen M, Zhao J, Xia L (2009) Comparison of four different chemical pretreatments of corn stover for enhancing enzymatic digestibility. Biomass Bioenergy 33(10):1381–1385
de Sousa Costa LA, Inomata Campos M, Izabel Druzian J, de Oliveira AM, de Oliveira Junior EN (2014) Biosynthesis of xanthan gum from fermenting shrimp shell: yield and apparent viscosity. Int J Polym Sci 2014:1–8
Demirci AS, Arici M, Gumus T (2012) Xanthan gum production from hydrolyzed rice bran as a carbon source by Xanthomonas spp. Korean J Microbiol Biotechnol 40:356–363
Farahi A, Najafpour G, Ghoreyshi A, Mohammadi M, Esfahanian M (2012) Enzymatic production of reducing sugars from broomcorn seed (Sorghum vulgare): process optimization and kinetic studies. World Appl Sci J 18(4):568–574
Faria S, Vieira P, Resende M, França F, Cardoso V (2009) A comparison between shaker and bioreactor performance based on the kinetic parameters of xanthan gum production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 156(1–3):45–58
Faria S, Vieira PA, Resende MM, Ribeiro EJ, Cardoso VL (2010) Application of a model using the phenomenological approach for prediction of growth and xanthan gum production with sugar cane broth in a batch process. LWT Food Sci Technol 43(3):498–506
Faria S, de Oliveira Petkowicz CL, de Morais SAL, Terrones MGH, de Resende MM, de França FP, Cardoso VL (2011) Characterization of xanthan gum produced from sugar cane broth. Carbohyd Polym 86(2):469–476
Garcia-Ochoa F, Santos VE, Alcon A (2004) Chemical structured kinetic model for xanthan production. Enzyme Microb Technol 35(4):284–292
Ghashghaei T, Soudi MR, Hoseinkhani S (2016) Optimization of xanthan gum production from grape juice concentrate using Plackett–Burman design and response surface methodology. Appl Food Biotechnol 3(1):15–23
Gilani S, Najafpour G, Heydarzadeh H, Zare H (2011) Kinetic models for xanthan gum production using Xanthomonas campestris from molasses. Chem Ind Chem Eng 17(2):179–187
Gunasekar V, Reshma K, Treesa G, Gowdhaman D, Ponnusami V (2014) Xanthan from sulphuric acid treated tapioca pulp: influence of acid concentration on xanthan fermentation. Carbohyd Polym 102:669–673
Jazini M, Fereydouni E, Karimi K (2017) Microbial xanthan gum production from alkali-pretreated rice straw. RSC Adv 7(6):3507–3514
Kalogiannis S, Iakovidou G, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M, Kyriakidis DA, Skaracis GN (2003) Optimization of xanthan gum production by Xanthomonas campestris grown in molasses. Process Biochem 39(2):249–256
Kerdsup P, Tantratian S, Sanguandeekul R, Imjongjirak C (2011) Xanthan production by mutant strain of Xanthomonas campestris TISTR 840 in raw cassava starch medium. Food Bioprocess Technol 4(8):1459–1462
Khosravi-Darani K, Reyhani FS, Nejad B, Farhadi GBN (2011) Bench scale production of xanthan from date extract by Xanthomonas campestris in submerged fermentation using central composite design. Afr J Biotechnol 10(62):13520–13527
Kim S-J, Dwiatmoko AA, Choi JW, Suh Y-W, Suh DJ, Oh M (2010) Cellulose pretreatment with 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride for solid acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8273–8279
Kumar D, Murthy GS (2011) Impact of pretreatment and downstream processing technologies on economics and energy in cellulosic ethanol production. Biotechnol Biofuels 4(1):27
Li R, Feke DL (2015) Rheological and kinetic study of the ultrasonic degradation of xanthan gum in aqueous solution: effects of pyruvate group. Carbohyd polym 124:216–221
Li P, Li T, Zeng Y, Li X, Jiang X, Wang Y, Xie T, Zhang Y (2016) Biosynthesis of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campestris LRELP-1 using kitchen waste as the sole substrate. Carbohyd Polym 151:684–691
Mccomb EA, Mccready RM, Chem A (1957) Determination of acetyl in pectin and in acetylated carbohydrate polymers. Anal Chem 29(5):819–821
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Mirahmadi K, Kabir MM, Jeihanipour A, Karimi K, Taherzadeh M (2010) Alkaline pretreatment of spruce and birch to improve bioethanol and biogas production. BioResources 5(2):928–938
Niknezhad SV, Asadollahi MA, Zamani A, Biria D, Doostmohammadi M (2015) Optimization of xanthan gum production using cheese whey and response surface methodology. Food Sci Biotechnol 24(2):453–460
Nikzad M, Movagharnejad K, Talebnia F, Najafpour G, Ghorban Farahi AH (2014) A study on alkali pretreatment conditions of sorghum stem for maximum sugar recovery using statistical approach. Chem Ind Chem Eng 20(2):261–271
Palaniraj A, Jayaraman V (2011) Production, recovery and applications of xanthan gum by Xanthomonas campestris. J Food Eng 106(1):1–12
Papagianni M, Psomas S, Batsilas L, Paras S, Kyriakidis D, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M (2001) Xanthan production by Xanthomonas campestris in batch cultures. Process Biochem 37(1):73–80
Pooja D, Panyaram S, Kulhari H, Rachamalla SS, Sistla R (2014) Xanthan gum stabilized gold nanoparticles: characterization, biocompatibility, stability and cytotoxicity. Carbohyd Polym 110:1–9
Riazi S, Rahimnejad M, Najafpour G (2015) Hydrolysis of sorghum (broomcorn) in diluted hydrochloric acid. Int J Eng 28(11):1543
Rosalam S, England R (2006) Review of xanthan gum production from unmodified starches by Xanthomonas comprestris sp. Enzyme Microb Technol 39(2):197–207
Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2011) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory Technical Report NREL
Salah RB, Chaari K, Besbes S, Ktari N, Blecker C, Deroanne C, Attia H (2010) Optimisation of xanthan gum production by palm date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) juice by-products using response surface methodology. Food Chem 121(2):627–633
Silva MF, Fornari RCG, Mazutti MA, Oliveira D, Padilha FF, Cichoski AJ, Cansian RL, Luccio MD, Treichel H (2009) Production and characterization of xantham gum by Xanthomonas campestris using cheese whey as sole carbon source. J Food Eng 90:119–123
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2005) Determination of ash in biomass standard biomass analytical procedures. National Renewable Energy Laboratory Technical Report NREL
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2008) Determination of ash in biomass (NREL/TP-510-42622). National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden 2005
Taherzadeh MJ, Gustafsson L, Niklasson C, Liden G (2000) Physiological effects of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:701–708
Talebnia F, Bafrani MP, Lundin M, Taherzadeh M (2007) Optimization study of citrus wastes saccharification by dilute acid hydrolysis. BioResources 3(1):108–122
Talebnia F, Karakashev D, Angelidaki I (2010) Production of bioethanol from wheat straw: an overview on pretreatment, hydrolysis and fermentation. Bioresour Technol 101(13):4744–4753
Wang M, Zhou D, Wang Y, Wei S, Yang W, Kuang M, Ma L, Fang D, Xu S, Du S-K (2016a) Bioethanol production from cotton stalk: a comparative study of various pretreatments. Fuel 184:527–532
Wang Z, Wu J, Zhu L, Zhan X (2016b) Activation of glycerol metabolism in Xanthomonas campestris by adaptive evolution to produce a high-transparency and low-viscosity xanthan gum from glycerol. Bioresour Technol 211(2016):390–397
Wang z, Wu J, Gao MJ, Zhu L, Zhan XB (2017) High production of xanthan gum by a glycerol tolerant strain Xanthomonas campestris WXLB-006. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(5):468–472
West TP, Nemmers B (2008) Curdlan production by Agrobacterium sp. ATCC 31749 on an ethanol fermentation coproduct. J Basic Microbiol 48(1):65–68
Wu S-J, Wu J-H, Xia L-Z, Chu C, Liu D, Gong M (2013) Preparation of xanthan-derived oligosaccharides and their hydroxyl radical scavenging activity. Carbohyd Polym 92(2):1612–1614
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soleymanpour, Z., Nikzad, M., Talebnia, F. et al. Xanthan gum production from acid hydrolyzed broomcorn stem as a sole carbon source by Xanthomonas campestris. 3 Biotech 8, 296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1322-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1322-z