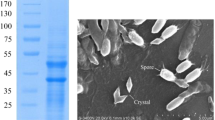
Abstract
Mosquitocidal Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strain S2160-1 was proposed to be an alternative to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis (Bti). Discovering and validating a toxic gene by experimentation was a complex and time-consuming task, which can benefit from high-throughput sequencing analysis. In this research, we predicted and identified toxic proteins in the strain S2160-1 based on the draft whole genome sequence data. Through a local BLASP, 46 putative toxins were identified in S2160-1 genome, by searching against a customized B. thuringiensis toxin proteins database containing 653 protein or peptide sequences retrieved from public accessible resources and PCR/clone results in our laboratory (e value = 1e − 5). These putative toxins consist of 42 to 1216 amino acids. The molecular weights are ranged from 4.86 to 137.28 kDa. The isoelectric point of these candidate toxins varied from 4.3 to 10.06, and 16 out of which had a pH greater than 7.0. The analysis of tertiary structure and PFAM domain showed that 12 potential plasmid toxins may share higher similarity (9/12 QMEAN4 score > 0.3) with known Bt toxins. In addition, functional annotation indicated that these 12 potential toxins were involved in “sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore” and “toxin activity”. Moreover, multiple alignment and phylogenetic analysis were carried out to elucidate the evolutionary relationship among 101 known crystal or toxin proteins from public database and them with MEGA 6.0. It indicated that PS2160P2_1 and PS2160P2_153 may be potential Cry4-like toxins in Bt S2160-1. This research may lay the foundation for future functional analysis of Bt S2160-1 toxin proteins to reveal their biological roles.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTGs:
-
Candidate toxin genes
- TER-CTGs:
-
Candidate toxin genes with tertiary structure
- CD-CTGs:
-
Candidate toxin genes with conserved domain
- GO-CTGs:
-
Candidate toxin genes with GO annotations
References
Azizoglu U, Ayvaz A, Yilmaz S, Karaborklu S, Temizgul R (2016) Expression of cry1Ab gene from a novel Bacillus thuringiensis strain SY49-1 active on pest insects. Braz J Microbiol [Publ Braz Soc Microbiol] 47:597–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.04.011
Bellile KG, Vonesh JR (2016) Bioinsecticide and leaf litter combination increases oviposition and reduces adult recruitment to create an effective ovitrap for Culex mosquitoes. J Vector Ecol J Soc Vector Ecol 41:123–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvec.12203
Berry C et al (2002) Complete sequence and organization of pBtoxis, the toxin-coding plasmid of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5082–5095
Biasini M et al (2014) SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucl Acids Res 42:W252–W258. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku340
Bravo A, Gill SS, Soberon M (2007) Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon Off J Int Soc Toxinol 49:423–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.11.022
Conesa A, Gotz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genom 2008:619832. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/619832
Crickmore NZD, Feitelson J (2016) Bacillus thuringiensis toxin nomenclature http://www.lifesci.sussex.ac.uk/Home/Neil_Crickmore/Bt/
Crickmore N et al (1998) Revision of the nomenclature for the Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:807–813
Fang XJ, Zhang Z (2012) Bt S2160-1, a high mosquitocidal strain of Bacillus thuringiensis. Bt Res 3:29–32 doi. https://doi.org/10.5376/bt.2012.03.0005
Federici BA (1999) Bacillus thuringiensis. In: Bellows TS, Gordh G, Fisher TW (eds) Handbook of biological control. Academic Press, San Diego: 517–548
Finn RD et al (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucl Acids Res 44:D279-285 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Galitsky N, Cody V, Wojtczak A, Ghosh D, Luft JR, Pangborn W, English L (2001) Structure of the insecticidal bacterial delta-endotoxin Cry3Bb1 of Bacillus thuringiensis Acta crystallographica Section D. Biol Crystallogr 57:1101–1109
Guan P et al (2012) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis serovar Sichuansis strain MC28. J Bacteriol 194:6975. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01861-12
Guan P et al (2014) Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. sichuansis strain MC28 produces a novel crystal protein with activity against Culex quinquefasciatus larvae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:1417–1421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1548-1
Itsko M, Manasherob R, Zaritsky A (2005) Partial restoration of antibacterial activity of the protein encoded by a cryptic open reading frame (cyt1Ca) from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis by site-directed mutagenesis. J Bacteriol 187:6379–6385. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.18.6379-6385.2005
Jouzani GS, Valijanian E, Sharafi R (2017) Bacillus thuringiensis: a successful insecticide with new environmental features and tidings. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:2691–2711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8175-y
Kelker MS et al (2014) Structural and biophysical characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal proteins Cry34Ab1 and Cry35Ab. PLoS One 9(1):e112555. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112555
Kiefer F, Arnold K, Kunzli M, Bordoli L, Schwede T (2009) The SWISS-MODEL repository and associated resources. Nucl acids Res 37:D387–D392. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn750
Kirouac M, Vachon V, Noel JF, Girard F, Schwartz JL, Laprade R (2002) Amino acid and divalent ion permeability of the pores formed by the Bacillus thuringiensis toxins Cry1Aa and Cry1Ac in insect midgut brush border membrane vesicles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1561:171–179
Letunic I, Bork P (2016) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees Nucl Acids Res 44:W242-245 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw290
Manasherob R, Itsko M, Sela-Baranes N, Ben-Dov E, Berry C, Cohen S, Zaritsky A (2006) Cyt1Ca from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: production in Escherichia coli and comparison of its biological activities with those of other Cyt-like proteins. Microbiology 152:2651–2659. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28981-0
Nagata H et al (2009) Identification of the binding domain of Streptococcus oralis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase for Porphyromonas gingivalis major fimbriae. Infect Immun 77:5130–5138. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00439-09
Palma L, Munoz D, Berry C, Murillo J, Caballero P (2014) Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: an overview of their biocidal activity. Toxins 6:3296–3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6123296
Poornima K, Selvanayagam P, Shenbagarathai R (2010) Identification of native Bacillus thuringiensis strain from South India having specific cytocidal activity against cancer cells. J Appl Microbiol 109:348–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04697.x
Schnepf E et al (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev MMBR 62:775–806
Tabashnik BE, Brevault T, Carriere Y (2013) Insect resistance to Bt crops: lessons from the first billion acres. Nat Biotechnol 31:510–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2597
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Vachon V, Laprade R, Schwartz JL (2012) Current models of the mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins: a critical review. J Invertebr Pathol 111:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2012.05.001
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy. server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552
Zhang W et al (2012) Characterization of a new highly mosquitocidal isolate of Bacillus thuringiensis—an alternative to Bti? J Invertebr Pathol 109:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2011.11.003
Zhang W et al (2014) Identification of a mosquitocidal toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis using mass spectrometry. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:3273–3277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1744-7
Zhong HWY, Zhou Y, Huang FY, Zhang WF, Zhang Y (2013) Draft genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis strain S2160-1 with high mosquitocidal activity. Bt Res 4:29–31
Acknowledgements
This work was part of the project “China National Bt Strains Resource Initiative (BtSRI)” funded by Hainan Institute of Tropical Agricultural Resources in Hainan province (HITAR). All the intellectual property rights are owned by HITAR in Hainan province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest declared.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Zhou, Y., Wu, Z. et al. Computational identification and evolutionary analysis of toxins in Mosquitocidal Bacillus thuringiensis strain S2160-1. 3 Biotech 8, 293 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1313-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1313-0