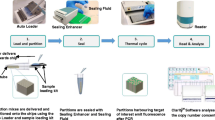
Abstract
Taking into account the limits of current genotyping methodologies, we have established a versatile direct PCR method on intact microtissue samples without prior DNA isolation. A simple and standard protocol was developed and validated on a wide range of living organisms including bacterial and fungal strains, plant species and human samples. This allows reliable amplification of target genomic DNA fragment directly from source material using minimal amount of tissue which makes DNA purification irrelevant for a number of biological applications. The direct PCR technique established here represents an excellent alternative to traditional amplification methods used for real-time detection. Since this approach was efficiently and universally applied for high-throughput molecular screening, its implementation will offer new insights for several investigations in human health, biomedical diagnosis, plant biotechnology, as well as in applied environmental and food microbiology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I, Islam M, Arshad W, Mannan A, Ahmad W, Mirza B (2009) High-quality plant DNA extraction for PCR: an easy approach. J Appl Genet 50(2):105–107
AlShahni MM, Makimura K, Yamada T, Satoh K, Ishihara Y, Takatori K, Sawada T (2009) Direct colony PCR of several medically important fungi using Ampdirect® Plus. Jpn J Infect Dis 62:164–167
Ben-Amar A, Oueslati S, Ghorbel A, Mliki A (2012) Prediction and early detection of mycotoxigenic Fusarium culmorum in wheat samples by direct PCR-based procedure. Food Control 23:506–510
Bickley J, Short JK, McDowell DG, Parkes HC (1996) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of Listeria monocytogenes in diluted milk and reversal of PCR inhibition caused by calcium ions. Lett Appl Microbiol 22:153–158
Cao M, Fu Y, Guo Y, Pan J (2009) Chlamydomonas (Chlorophyceae) colony PCR. Protoplasma 235:107–110
Cascella R, Strafella C, Ragazzo M, Zampatti S, Borgiani P, Gambardella S, Pirazzoli A, Novelli G, Giardina E (2015) Direct PCR: a new pharmacogenetic approach for the inexpensive testing of HLA-B* 57:01. Pharmacogn J 15:196–200
Chong GLM, Van De Sande WWJ, Dingemans GJH, Gaajetaan GR, Vonk AG, Hayette MP, Van Tegelen DWE, Simons GFM, Rijnders BJA (2015) Validation of a new Aspergillus real-time PCR assay for direct detection of Aspergillus and azole resistance of Aspergillus fumigatus on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J Clin Microbiol 53(3):868–874
Del Valle Mendoza J, Silva Caso W, Tinco Valdez C, Pons MJ, Del Valle LJ, Casabona Oré V, Champin Michelena D, Bazán Mayra J, Zavaleta Gavidea V, Vargas M, Ruiz J (2014) Diagnosis of Carrion’s disease by direct blood PCR in thin blood smear negative samples. PLos One 9(3):e92283. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092283
Eszik I, Lantos I, Önder K, Somogyvári F, Burián K, Endrész V, Virok DP (2016) High dynamic range detection of Chlamydia trachomatis growth by direct quantitative PCR of the infected cells. J Microbiol Methods 120(1):15–22
Fode-Vaughan KA, Maki JS, Benson JA, Collins P (2003) Direct PCR detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett Appl Microbiol 37:239–243
Gouveia N, Brito P, Serra A, Balsa F, Andrade L, Bento MS, Cunha P, Bogas V, Lopes V, Porto MJ (2015) Direct amplification of reference samples with Globalfiler® PCR amplification kit. Forensic Sci Int. doi:10.1016/j.fsigss.2015.09.055
Gray K, Crowle D, Scott P (2014) Direct amplification of casework bloodstains using the Promega PowerPlex® 21PCR amplification system. Forensic Sci Int 12:86–92
Hayashida M, Iwao-Koizumi K, Murata S, Kinoshita K (2009) Single-tube genotyping from a human hair root by direct PCR. Anal Sci 25:1487–1489
Kovačević-Grujičić N, Davidivic S, Takic D, Mojsin M, Stevanovic M (2012) Direct PCR amplification of the HVSI region in mitochondrial DNA from buccal cell swabs. Arch Biol Sci Belgrade 64(3):851–858
Mannerlöf M, Tenning P (1997) Screening transgenic plants by multiplex PCR. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15:38–45
Nishimura N, Nakayama T, Tonoike H, Kojima K, Kato S (2000) Direct polymerase chain reaction from whole blood without DNA isolation. Ann Clin Biochem 37:674–680
Pathmanathan SG, Cardona-Castro N, Sa´nchez-Jime´nez MM, Correa-Ochoa MM, Puthucheary SD, Thong KL (2003) Simple and rapid detection of Salmonella strains by direct PCR amplification of the hilA gene. J Med Microbiol 52:773–778
Rogers HI, Parkes HC (1999) Direct PCR amplification from leaf discs. Plant Sci 143:183–186
Sharma R, Kumar V, Mohapatra T, Khandelwal V, Vyas GK (2012) A simple and non destructive method of direct-PCR for plant systems. J Plant Biol 55:114–122
Shokralla S, Singer GAC, Hajibabaei M (2010) Direct PCR amplification and sequencing of specimens’ DNA from preservative ethanol. Biotechniques 48(3):233–234
Tomida M, Saito T (2004) The human hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) gene is transcriptionally activated by leukemia inhibitory factor through the stat binding element. Oncogene 23(3):679–686
Turner S, Pryer KM, Miao VPW, Palmer JD (1999) Investigating deep phylogenetic relationships among cyanobacteria and plastids by small subunit rRNA sequence analysis. J Eukaryot Microbiol 46:327–338
Watson RJ, Blackwell B (2000) Purification and characterization of a common soil component which inhibit the polymerase chain reaction. Can J Microbiol 46:633–642
Werblow A, Flechl E, Klimpel S, Zittra C, Lebl K, Kieser K, Laciny A, Silbermayr K, Melaun C, Fuehrer HP (2016) Direct PCR of indigenous and invasive mosquito species: a time- and cost-effective technique of mosquito barcoding. Med Vet Entomol 30(1):8–13
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee SJ, Taylor W (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and application. Academic Press, San Diego
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Andrea Devlin for proofreading this manuscript and Prof. Michael Florian Mette (Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research, IPK-Gatersleben, Germany) for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ABA designed the work, developed the direct PCR technology, analyzed data and wrote the body of the paper; SO helped in the experimental work, microbiological assays and data analysis. AM co-ordinated the project together with ABA. All authors reviewed, edited and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
We confirm that all experiments are approved by the committee and research studies conducted here using human samples. Experiments were performed in accordance with the relevant government’s regulatory guidelines and regulations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Amar, A., Oueslati, S. & Mliki, A. Universal direct PCR amplification system: a time- and cost-effective tool for high-throughput applications. 3 Biotech 7, 246 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0890-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0890-7