Abstract
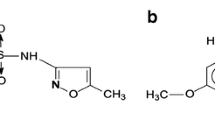
Unrestricted and reckless use of antibiotics has resulted in their accumulation in environment. This, in turn, has led to the emergence of multiple drug-resistant microbes. The present study focuses on degradation of ciprofloxacin (CIP) by an edible white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Effect of CIP was determined on radial growth and biomass of P. ostreatus. Titrimetric and spectrophotometric assays were carried out to assess the degrading potential of P. ostreatus towards CIP. It was found that CIP has a stimulatory effect on growth and enzyme activity of P. ostreatus. Maximum enzyme (glucanase, ligninases, laccase) production was observed at the highest concentration of CIP (500 ppm). Antibiotic degradation of about 68.8, 94.25 and 91.34% was estimated after 14 days of incubation at 500 ppm CIP using Titrimetric, Indigo carmine and Methyl orange assay, respectively. Degradation of CIP was further validated by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and microbiological analysis. HPLC analysis revealed 95.07% degradation while microbiological test also exhibited a decreased antimicrobial activity of degraded products against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study wherein P. ostreatus was used for the degradation of ciprofloxacin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SA, Kadam JA, Mane VP, Patil SS, Baig MMV (2009) Biological efficiency and nutritional contents of Pleurotus florida (Mont.) Singer cultivated on different agro-wastes. Nat Sci 7(1):44–48
Basavaiah K, Nagegowda P, Somashekar BC, Ramakrishna V (2006) Spectrophotometric and titrimetric determination of CIP based on reaction with cerium (IV) Sulfate. Sci Asia 32:403–409
Batt AL, Kim S, Aga DS (2007) Comparison of the occurrence of antibiotics in four fullscale wastewater treatment plants with varying designs and operations. Chemosphere 68(3):428–435
Bucht B, Eriksson KE (1968) Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the rot fungus Stereum sanguinolentum for the breakdown of cellulose. I. Studies on the enzyme production. Arch Biochem Biophys 124(1):135–141
Butaye P, Devriese LA, Haesebrouck F (2003) Antimicrobial growth promoters used in animal feed: effects of less well known antibiotics on gram-positive bacteria. Clin Microbiol 16(2):175–188
Collins PJ, Field JA, Teunissen P, Dobson ADW (1997) Stabilization of lignin peroxidases in white rot fungi by tryptophan. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(7):2543–2548
Dhawan S, Lal R, Hanspal M, Kuhad RC (2005) Effect of antibiotics on growth and laccase production from Cyathus bulleri and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Biores Technol 96:1415–1418
Dibner JJ, Richards JD (2005) Antibiotic growth promoters in agriculture: history and mode of action. Poult Sci 84(4):634–643
Espindola LHS, Espindola FS, Freitasi GRD, Brandeburgo MAM (2007) Biodegradation of red 40 dye by the mushroom Pleurotus florida. Biosci J 23(3):90–93
Froehner SC, Eriksson KEL (1974) Induction of Neurospora crassa laccase with protein synthesis inhibitors. J Bacteriol 120(1):450–457
Guo X, Zhu Z, Li H (2014) Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Mol Liq 198:169–172
Hernandez F, Rivera A, Ojeda A, Zayas T, Cedillo L (2012) Photochemical degradation of the CIP antibiotic and its microbiological validation. J Environ Sci Eng A1:448–453
Hubicka U, Zmudzki P, Talik P, Witek BZ, Krzek J (2013) Photodegradation assessment of CIP, moxifloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin in the presence of excipients from tablets by UPLC-MS/MS and DSC. Chem Cent J 7:133
Jegatheesan M, Kumaran MS, Eyini M (2012) Enhanced production of laccase enzyme by the white-rot mushroom fungus Pleurotus florida using response surface methodology. Int J Curr Res 4(10):025–031
Kuwahara M, Glenn JK, Morgan MA, Gold MH (1984) Separation and characterization of two extracellular H2O2-dependent oxidases from ligninolytic cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. KEBS Lett 69(2):247–250
Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, Zaidi AKM, Wertheim HFL, Sumpradit N, Vlieghe E, Hara GL, Gould IM, Goossens H, Greko C, So AD, Bigdeli M, Tomson G, Woodhouse W, Ombaka E, Peralta AQ, Qamar FN, Mir F, Kariuki S, Bhutta ZA, Coates A, Bergstrom R, Wright GD, Brown ED, Cars O (2013) Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 13(12):1057–1098
Martens R, Wetzstein HG, Zadrazil F, Capelari M, Hoffmann P, Schmeer N (1996) Degradation of the fluoroquinolone enrofloxacin by wood-rotting fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(11):4206–4209
Miles RD, Butcher GD, Henry PR, Littell RC (2006) Effect of antibiotic growth promoters on broiler performance, intestinal growth parameters, and quantitative morphology. Poult Sci 85(3):476–485
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Nijhu RS, Jhankar YM, Sutradhar KB (2011) Development of an assay method for simultaneous determination of CIP and naproxen by UV spectrophotometric method. Stamford J Pharma Sci 4(1):84–90
Noverr MC, Noggle RM, Toews GB, Huffnagle GB (2004) Role of antibiotics and fungal microbiota in driving pulmonary allergic responses. Infect Immun 72(9):4996–5003
Praveen K, Usha KY, Rajasekhar Reddy B (2012) Effect of antibiotics on ligninolytic enzymes production from Stereum ostrea and Phanerochaete chrysosporium under submerged fermentation. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(3):135–138
Rana IS, Rana AS (2011) Lignocellulolytic enzyme profile of Agaricus and Pleurotus species cultured on used tea leaves substrate. Adv Bio Tech 11(6):10–14
Rodríguez-Rodríguez CE, García-Galán MA, Blánquez P, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D, Caminal G, Vicent T (2012) Continuous degradation of a mixture of sulfonamides by Trametes versicolor and identification of metabolites from sulfapyridine and sulfathiazole. J Hazard Mater 213–214:347–354
Rogalski J, Lundell TK, Leonowicz A, Hatakka AI (1991) Influence of aromatic compounds and lignin on production of ligninolytic enzymes by Phlebia radiata. Phytochem 30(9):2869–2872
Sandhu DK, Arora DS (1985) Laccase production by Polyporus sanguineus under different nutritional and environmental conditions. Experimentia 41:355–356
Shah Z, Dighe A, Londhe V (2015) Pharmacoeconomic study of various brands of antibiotic medications in India. World J Parma Res 4(3):1600–1606
Singh MP, Pandey AK, Vishwakarma SK, Srivastava AK, Pandey VK (2012) Extracellular xylanase production by Pleurotus species on lignocellulosic wastes under in vivo condition using novel pretreatment. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 58(1):170–173
Singh RN, Sahoo S, Mishra U, Garnaik B, Sahoo SK, Hati D (2013) Stability indicating RP-HPLC method development and validation of norfloxacin. Am J Adv Drug Deliv 1(5):743–758
Tellez MT, Diaz R, Sanchez C, Godinez GD (2013) Hydrolytic enzymes produced by Pleurotus species. Afr J Microbiol Res 7(4):276–281
Thillaimaharani KA, Sharmila K, Thangaraju P, Karthick M, Kalaiselvam M (2013) Studies on antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of oyster mushroom Pleurotus florida. Int J Pharm Sci Res 4(4):1540–1545
Tien M, Kirk TK (1984) Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H2O2-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81(8):2280–2284
Wegener HC, Aarestrup FM, Jensen LB, Hammerum AM, Bager F (1999) Use of antimicrobial growth promoters in food animals and Enterococcus faecium resistance to therapeutic antimicrobial drugs in Europe. Emerg Infect Dis 5(3):329–335
Wetzstein HG, Stadler M, Tichy HV, Dalhoff A, Karl W (1999) Degradation of CIP by basidiomycetes and identification of metabolites generated by the brown rot fungus Gloeophyllum striatum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(5):1556–1563
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S.K., Khajuria, R. & Kaur, L. Biodegradation of ciprofloxacin by white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus . 3 Biotech 7, 69 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0684-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0684-y