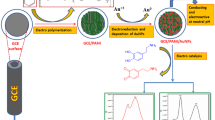
Abstract
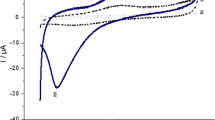
Simultaneous determination of small biologically important molecules is more significant for monitoring several diseases at physiological pH. Uric acid (C5H4N4O3) and ascorbic acid (C6H8O6), for instance, were once regarded as crucial components in the physiological processes of humans since they coexist in numerous biological matrices regularly, and monitoring their concentrations simultaneously indicates diseases like gout. In the present work, the gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were assembled on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) using electrodeposition of Au3+ ions for the simultaneous determination of C5H4N4O3 and C6H8O6. The deposited AuNPs were characterized using UV–visible spectroscopy, XPS, XRD, and AFM. Morphological analysis depicted that the particles are spherical with a size of 32 nm, and the particles are uniformly distributed on the electrode surface. The formation of gold oxide and its reduction peaks in cyclic voltammetry revealed the effective deposition of AuNPs on the GCE surface. The catalytic activity AuNPs modified GCE was analyzed by probing the oxidation of C5H4N4O3 and C6H8O6 at physiological pH (pH 7.2). The present modified electrode greatly enhanced the oxidation peak currents, and the potential of oxidation is also shifted to less positive potential compared to bare GCE. The AuNPs/GCE was used to determine C5H4N4O3 in the presence of a 50-fold high concentration of C6H8O6. The detection of 40 nM C5H4N4O3 was achieved using amperometry and a detection limit of 1.8 × 10–9 M (Signal/Noise = 3) was observed for the determination of uric acid in the concentration range from 4 × 10–8 to 4 × 10–5 M.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnoletti D, Cicero AFG, Borghi C (2021) The impact of uric acid and hyperuricemia on cardiovascular and renal systems. Cardiol Clin 39:365–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccl.2021.04.009
Al-Akraa IM, Asal YM, Mohammad AM (2019) Facile synthesis of a tailored-designed AU/PT nanoanode for enhanced formic acid, methanol, and ethylene glycol electrooxidation. J Nanomater 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2784708
Alba-Molina D, Puente Santiago AR, Giner-Casares JJ et al (2019) Tailoring the ORR and HER electrocatalytic performances of gold nanoparticles through metal-ligand interfaces. J Mater Chem A 7:20425–20434. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta05492h
Amal Raj M, Abraham John S (2014) Fast growth of gold nanorods on solid substrate using electrochemically deposited gold seeds. Electrochem Commun 45:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.05.007
Bazán-Díaz L, Mendoza-Cruz R, Velázquez-Salazar JJ et al (2018) Synthesis and properties of the self-assembly of gold-copper nanoparticles into nanoribbons. Langmuir 34:9394–9401. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04187
Chai Z, Childress A, Busnaina AA (2022) Directed assembly of nanomaterials for making nanoscale devices and structures: mechanisms and applications. ACS Nano 16:17641–17686. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c07910
Chen S, Chen W, Wang Y et al (2022) Facile one-pot method of AuNPs/PEDOT/CNT composites for simultaneous detection of dopamine with a high concentration of ascorbic acid and uric acid. RSC Adv 12:15038–15045. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra01262f
Edris NMA, Abdullah J, Kamaruzaman S et al (2018) Electrochemical reduced graphene oxide-poly(eriochrome black T)/gold nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Arab J Chem 11:1301–1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.09.002
Festa A, Haffner SM (2005) Inflammation and cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes: lessons from the diabetes control and complications trial. Circulation 111:2414–2415. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000167558.77793.E8
Filik H, Avan AA, Aydar S (2016) Simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and tryptophan with Azure A-interlinked multi-walled carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticles composite modified electrode. Arab J Chem 9:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.01.014
Gandhi AD, Murugan K, Umamahesh K et al (2019) Lichen Parmelia sulcata mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles: an eco-friendly tool against Anopheles stephensi and Aedes aegypti. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23886–23898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05726-6
Ganesan RM, Gurumallesh Prabu H (2019) Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using herbal Acorus calamus rhizome extract and coating on cotton fabric for antibacterial and UV blocking applications. Arab J Chem 12:2166–2174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.12.017
Gao S, Li H, Li M et al (2018) A gold-nanoparticle/horizontal-graphene electrode for the simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, guanine, and adenine. J Solid State Electrochem 22:3245–3254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-018-4019-7
Gonzalez MJ, Miranda-Massari JR (2014) New insights on Vitamin C and cancer. Springer, New York
Gorji MS, Razak KA, Cheong KY (2014) Deposition of gold nanoparticles on linker-free silicon substrate by spin-coating. Adv Mater Res 1024:124–127. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1024.124
Guin SK, Sharma HS, Aggarwal SK (2010) Electrosynthesis of lead nanoparticles on template free gold surface by potentiostatic triple pulse technique. Electrochim Acta 55:1245–1257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.10.005
Gupta R, Ganesan V (2015) Gold nanoparticles impregnated mesoporous silica spheres for simultaneous and selective determination of uric acid and ascorbic acid. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 219:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.018
Hepperle P, Baek WY, Nettelbeck H, Rabus H (2022) Deposition of Gold Nanoparticles on a Self-Supporting Carbon Foil. Part Part Syst Charact 39:2200136. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.202200136
Islam MT, Hasan MM, Shabik MF et al (2020) Electroless deposition of gold nanoparticles on a glassy carbon surface to attain methylene blue degradation via oxygen reduction reactions. Electrochim Acta 360:136966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136966
Jouyban A, Rahimpour E (2020) Optical sensors based on silver nanoparticles for determination of pharmaceuticals: An overview of advances in the last decade. Talanta 217:121071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121071
Kaminska I, Niedziolka-Jonsson J, Roguska A, Opallo M (2010) Electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles at a solid|ionic liquid|aqueous electrolyte three-phase junction. Electrochem Commun 12:1742–1745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2010.10.011
Kamińska I, Opallo M, Łaszcz A et al (2013) (Bio)electrocatalysis at tin-doped indium oxide nanoparticulate film decorated with gold. Electrochim Acta 106:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.05.089
Kong BS, Geng J, Jung HT (2009) Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene and gold nanoparticles by vacuum filtration and spontaneous reduction of gold ions. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/b821920f
Kumar S, Singh R (2021) Recent optical sensing technologies for the detection of various biomolecules: Review. Opt Laser Technol 134:106620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106620
Lou-Franco J, Das B, Elliott C, Cao C (2021) Gold nanozymes: from concept to biomedical applications. Nano-Micro Lett 13:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-020-00532-z
Manojkumar U, Kaliannan D, Srinivasan V et al (2023) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Brassica oleracea var. botrytis leaf extract: photocatalytic, antimicrobial and larvicidal activity. Chemosphere 323:138263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138263
Mazzara F, Patella B, Aiello G et al (2021) Electrochemical detection of uric acid and ascorbic acid using r-GO/NPs based sensors. Electrochim Acta 388:138652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138652
Mehravani B, Ribeiro AI, Zille A (2021) Gold nanoparticles synthesis and antimicrobial effect on fibrous materials. Nanomaterials 11:1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051067
Meng T, Jia H, An S et al (2020) Pd nanoparticles-DNA layered nanoreticulation biosensor based on target-catalytic hairpin assembly for ultrasensitive and selective biosensing of microRNA-21. Sens Actuators B Chem 323:128621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128621
Mosleh-Shirazi S, Kasaee SR, Dehghani F et al (2022) Investigation through the anticancer properties of green synthesized spinel ferrite nanoparticles in present and absent of laser photothermal effect. Ceram Int 49:11293–11301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.329
Noreen S, Tahir MB, Hussain A et al (2022) Emerging 2D-Nanostructured materials for electrochemical and sensing application-A review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 47:1371–1389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.10.044
Padayatty SJ, Levine M (2016) Vitamin C: the known and the unknown and Goldilocks. Oral Dis 22:463–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12446
Patil AB, Zheng C, Ma L et al (2020) Flexible and disposable gold nanoparticles-N-doped carbon-modified electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid. Nanotechnology 32:65502. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/abc388
Rafatmah E, Hemmateenejad B (2020) Dendrite gold nanostructures electrodeposited on paper fibers: Application to electrochemical non-enzymatic determination of glucose. Sens Actuators B Chem 304:127335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127335
Raj MA, Revin SB, John SA (2011) Selective determination of 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in the presence of ascorbic acid using 4-(dimethylamino) pyridine capped gold nanoparticles immobilized on gold electrode. Colloids Surf B 87:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.05.039
Rodriguez P, Plana D, Fermin DJ, Koper MTM (2014) New insights into the catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles for CO oxidation in electrochemical media. J Catal 311:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2013.11.020
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C et al (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112:2739–2779. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2001178
Shariq M, Friedrich B, Budic B et al (2018) Successful synthesis of gold nanoparticles through ultrasonic spray pyrolysis from a gold(III) nitrate precursor and their interaction with a high electron beam. ChemistryOpen 7:533–542. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.201800101
Shu H, Cao L, Chang G et al (2014) Direct electrodeposition of gold nanostructures onto glassy carbon electrodes for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Electrochim Acta 132:524–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.04.031
Steinberg CEW (2022) Vitamin C—“An Apple a Day Keeps the Veterinarian Away.” Aquatic Animal Nutrition. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 867–908
Stozhko N, Bukharinova M, Galperin L, Brainina K (2018) A nanostructured sensor based on gold nanoparticles and nafion for determination of uric acid. Biosensors 8:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8010021
Tan C, Zhao J, Sun P et al (2020) Gold nanoparticle decorated polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanosheets as a modified electrode for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. New J Chem 44:4916–4926. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj00166j
Wang H, XIAO LG, CHU XF, et al (2016) Rational design of gold nanoparticle/graphene hybrids for simultaneous electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Chinese J Anal Chem 44:e1617–e1625. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(16)60983-0
Wang L, Meng T, Zhao D et al (2020) An enzyme-free electrochemical biosensor based on well monodisperse Au nanorods for ultra-sensitive detection of telomerase activity. Biosens Bioelectron 148:111834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111834
Yang L, Huang N, Lu Q et al (2016) A quadruplet electrochemical platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen based on a ferrocene derivative functional Au NPs/carbon dots nanocomposite and graphene. Anal Chim Acta 903:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.021
Yang Z, Zhang D, Wang D (2020) Carbon monoxide gas sensing properties of metal-organic frameworks-derived tin dioxide nanoparticles/molybdenum diselenide nanoflowers. Sens Actuators B Chem 304:127369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127369
Yu Y, Naik SS, Oh Y et al (2021) Lignin-mediated green synthesis of functionalized gold nanoparticles via pulsed laser technique for selective colorimetric detection of lead ions in aqueous media. J Hazard Mater 420:126585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126585
Zeng S, Yong KT, Roy I et al (2011) A review on functionalized gold nanoparticles for biosensing applications. Plasmonics 6:491–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9228-1
Zhao Y, Zhou J, Jia Z et al (2019) In-situ growth of gold nanoparticles on a 3D-network consisting of a MoS2/rGO nanocomposite for simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 186:92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3222-7
Zhao C, Xiao J, Liu T et al (2022) Electrochemical sensor based on glass carbon electrode modified with graphene quantum dots (GQDs) for detection of uric acid. Int J Electrochem Sci 17:ArticleID:22096. https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.09.17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors declare that no conflicts of interest for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Denisdon, S., Kumar, P.S., Jeevagan, A.J. et al. Simultaneous detection of uric and ascorbic acids by AuNPs electrodeposited on the GCE surface. Appl Nanosci 13, 5949–5958 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-023-02869-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-023-02869-4