Abstract
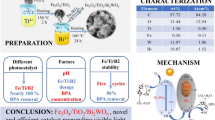
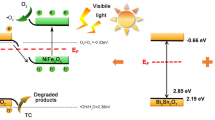
A ternary arrow down dual S-scheme nano photocatalyst ZnIn2S4/Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 composed of microspheres of ZnIn2S4, layered Bi2O2CO3, and magnetic ZnFe2O4 has been prepared for RhB degradation. The ZnIn2S4/Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 degraded 99.8% of RhB in 90 min, and its photocatalytic activity toward RhB degradation was highest as compared to pure ZnIn2S4 (36.38%), Bi2O2CO3 (19.56%), ZnFe2O4 (16.65%) and binary Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 (43.82%) composite. The Langmuir–Hinshelwood kinetics model was found for RhB degradation for all photocatalysts. The rate constant of the ZnIn2S4/Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 hybrid photocatalyst was 0.177 min−1, which is 12.73, 29.84, and 38.06 times greater than pure ZnIn2S4, Bi2O2CO3, and ZnFe2O4, respectively. UV–Vis, EIS, and PL measurements indicate that the synergistic effect is brought on by an expanded range of light absorption, lower charge separation resistance, and decreased recombination of e−/h+ pairs. The significant decrease in photocatalytic activity with radical scavengers established that •O2−, •OH, and h+ were the active free radicals, and •O2− was the leading one during the degradation of RhB. The dual S-scheme electron transfer mechanism has been proposed because lesser energy electrons and holes were destroyed, and charge carriers with higher redox potentials were retained. The photocatalysts' good magnetic separation and photostability were confirmed after four reuse cycles and maintained 87% degradation efficiency.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors confirm that all the data and materials as well as a software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Chachvalvutikul A, Pudkon W, Luangwanta T et al (2019) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by a direct Z-scheme Bi2S3/ZnIn2S4 photocatalyst. Mater Res Bull 111:53–60
Chen Z-J, Guo H, Liu H-Y et al (2022) Construction of dual S-scheme Ag2CO3/Bi4O5I2/g-C3N4 heterostructure photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation for tetracycline. Chem Eng J 438:135471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135471
Cheng H, Huang B, Yang K et al (2010) Facile Template-Free Synthesis of Bi2O2CO3 Hierarchical Microflowers and Their Associated Photocatalytic Activity. ChemPhysChem 11:2167–2173. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200901017
Deng X, Wang D, Li H et al (2022) Boosting interfacial charge separation and photocatalytic activity of 2D/2D g-C3N4/ZnIn2S4 S-scheme heterojunction under visible light irradiation. J Alloys Compd 894:162209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162209
Dutta V, Sharma S, Raizada P et al (2020) Recent progress on bismuth-based Z-scheme semiconductor photocatalysts for energy and environmental applications. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104505
Guo W, Huang L, Zhao B et al (2021) Synthesis of the ZnFe2O4/ZnSnO3 nanocomposite and enhanced gas sensing performance to acetone. Sens Actuators B Chem 346:130524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130524
Guo W, Huang L, Liu X et al (2022) Enhanced isoprene gas sensing performance based on p-CaFe2O4/n-ZnFe2O4 heterojunction composites. Sens Actuators B Chem 354:131243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.131243
He J, Cheng Y, Wang T et al (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic performances and magnetic recovery capacity of visible-light-driven Z-scheme ZnFe2O4/AgBr/Ag photocatalyst. Appl Surf Sci 440:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.219
Huang H, Tian N, Jin S et al (2014) Syntheses, characterization and nonlinear optical properties of a bismuth subcarbonate Bi2O2CO3. Solid State Sci 30:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2014.01.010
Jiang R, Wu D, Lu G et al (2019) Modified 2D–2D ZnIn2S4/BiOCl van der Waals heterojunctions with CQDs: Accelerated charge transfer and enhanced photocatalytic activity under vis- and NIR-light. Chemosphere 227:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.038
Jiang S, Zheng H, Sun X et al (2022) New and highly efficient Ultra-thin g-C3N4/FeOCl nanocomposites as photo-Fenton catalysts for pollutants degradation and antibacterial effect under visible light. Chemosphere 290:133324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133324
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2004) TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: A review. Appl Catal B Environ 49:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010
Kumar Y, Kumar R, Raizada P et al (2021) Novel Z-Scheme ZnIn2S4-based photocatalysts for solar-driven environmental and energy applications: Progress and perspectives. J Mater Sci Technol 87:234–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.01.051
Kumar Y, Kumar R, Raizada P et al (2022a) Recent progress on elemental sulfur based photocatalysts for energy and environmental applications. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135477
Kumar Y, Kumar R, Raizada P et al (2022b) Current status of hematite (α-Fe2O3) based Z-scheme photocatalytic systems for environmental and energy applications. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107427
Kumar Y, Sudhaik A, Sharma K et al (2023) Construction of magnetically separable novel arrow down dual S-scheme ZnIn2S4/BiOCl/FeVO4 heterojunction for improved photocatalytic activity. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 435:114326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.114326
Le QV, Nguyen V-H, Nguyen TD et al (2021) Light-driven reduction of carbon dioxide: Altering the reaction pathways and designing photocatalysts toward value-added and renewable fuels. Chem Eng Sci 237:116547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2021.116547
Li F, Dong B (2017) Construction of novel Z-scheme Cu2O/graphene/α-Fe2O3 nanotube arrays composite for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int 43:16007–16012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.021
Li J, Zhang X, Wang T et al (2020a) Construction of layered hollow Fe3O4/Fe1−xS @MoS2 composite with enhanced photo-Fenton and adsorption performance. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103762
Li Z, Wu Z, He R et al (2020b) In2O3-x(OH)y/Bi2MoO6 S-scheme heterojunction for enhanced photocatalytic performance. J Mater Sci Technol 56:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.02.061
Liu Y, Ren H, Lv H et al (2018) Synthesis of magnetic Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 composite with improved photocatalytic activity and easy recyclability. Appl Surf Sci 433:610–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.081
Mamba G, Mishra A (2016) Advances in magnetically separable photocatalysts: smart, recyclable materials for water pollution mitigation. Catalysts 6:79. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6060079
Mezohegyi G, van der Zee FP, Font J et al (2012) Towards advanced aqueous dye removal processes: A short review on the versatile role of activated carbon. J Environ Manage 102:148–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.02.021
Monshi A, Foroughi MR (2012) Modified scherrer equation to estimate more accurately nano-crystallite size using XRD. World J Nano Sci Eng 2(154):160
Narzary S, Alamelu K, Raja V, Jaffar Ali BM (2020) Visible light active, magnetically retrievable Fe3O4@SiO2@g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite as efficient photocatalyst for removal of dye pollutants. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104373
Nguyen V-H, Do HH, Van Nguyen T et al (2020) Perovskite oxide-based photocatalysts for solar-driven hydrogen production: progress and perspectives. Sol Energy 211:584–599
Pan Y, Yuan X, Jiang L et al (2018) Recent advances in synthesis, modification and photocatalytic applications of micro/nano-structured zinc indium sulfide. Chem Eng J 354:407–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.028
Rajendran R, Vignesh S, Suganthi S et al (2022) g-C3N4/TiO2/CuO S-scheme heterostructure photocatalysts for enhancing organic pollutant degradation. J Phys Chem Solids 161:110391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110391
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00080-8
Singh P, Sharma K, Hasija V et al (2019) Systematic review on applicability of magnetic iron oxides–integrated photocatalysts for degradation of organic pollutants in water. Mater Today Chem 14:100186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2019.08.005
Tahir AA, Wijayantha KGU (2010) Photoelectrochemical water splitting at nanostructured ZnFe2O4 electrodes. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 216:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2010.07.032
Wang J, Zhang Q, Deng F et al (2020) Rapid toxicity elimination of organic pollutants by the photocatalysis of environment-friendly and magnetically recoverable step-scheme SnFe2O4/ZnFe2O4 nano-heterojunctions. Chem Eng J 379:122264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122264
Wang L, Yin H, Wang S et al (2022a) Ni2+-assisted catalytic one-step synthesis of Bi/BiOCl/Bi2O2CO3 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. Appl Catal B Environ 305:121039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.121039
Wang Z, Bai Y, Li Y et al (2022b) Bi2O2CO3/red phosphorus S-scheme heterojunction for H2 evolution and Cr(VI) reduction. J Colloid Interface Sci 609:320–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.136
Xiao S, Li Y, Hu J et al (2015) One-step synthesis of nanostructured Bi–Bi2O2CO3–ZnO composites with enhanced photocatalytic performance. CrystEngComm 17:3809–3819. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CE00338E
Xu Q, Zhang L, Cheng B et al (2020) S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst. Chem 6:1543–1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2020.06.010
Yao S, Zhou S, Wang J et al (2019) Optimizing the synthesis of SnO2/TiO2/RGO nanocomposites with excellent visible light photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Photochem Photobiol Sci 18:2989–2999. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9pp00242a
Yuan W-H, Xia Z-L, Li L (2013) Synthesis and photocatalytic properties of core–shell TiO2@ZnIn2S4 photocatalyst. Chin Chem Lett 24:984–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2013.06.011
Zhang S, Li J, Zeng M et al (2013) In situ synthesis of water-soluble magnetic graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst and its synergistic catalytic performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:12735–12743. https://doi.org/10.1021/am404123z
Zhang M, Arif M, Hua Y et al (2021) Direct Z-scheme α-MnO 2 @MnIn 2 S 4 hierarchical photocatalysts with atomically defined junctions for improved photocatalytic activities. Nanoscale Adv 3:812–822. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NA00848F
Zhang J, Pan Z-H, Yang Y et al (2022a) Boosting the catalytic activity of a step-scheme In2O3/ZnIn2S4 hybrid system for the photofixation of nitrogen. Chin J Catal 43:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63801-9
Zhang R, Cai L, Zhao C et al (2022b) Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by 3D flower-like g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/Bi2O2CO3 and its effect on the growth of lettuce seedlings. Diam Relat Mater 129:109362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109362
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2021/6), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors affirm that they have no known financial or interpersonal conflicts that would have appeared to have impacted the research presented in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, Y., Sharma, K., Sudhaik, A. et al. Fabrication of magnetically retrievable ZnIn2S4/Bi2O2CO3/ZnFe2O4 dual S-scheme heterojunction for superior photocatalytic activity. Appl Nanosci 13, 4129–4142 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02743-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02743-9