Abstract
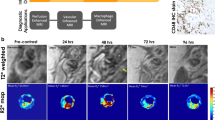
This study was to diagnose stroke patients based on the application of Fe2O3 super nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to explore the magnetic properties, colloidal stability, and particle electrical properties of Fe2O3 super nanoparticles, so that they could be better used in MRI contrast agents. In addition, the nursing management of the medical department was evaluated to enable stroke patients to recover better. The inpatients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in the Department of Neurology of Wuhan Third Hospital from September 2020 to April 2021 were selected and divided into a routine group and a control group. The Fe2O3 super nanoparticle magnetic solvent was prepared and mixed with contrast agent, and the MRI image was observed to inspect the brain ischemic lesions. The self-care situation and hospitalization expenses of patients were assessed, so as to evaluate the quality of nursing. The results suggested that the particles were 16 nm in diameter, and were the most stable when the electricity was at 16 V, so the ischemic focus of MRI could be obviously easy to observe. The score on self-care ability of patients in the control group was improved by 0.33, and that in the routine group was improved by 7.11 when they were discharged from the hospital, showing statistically obvious difference (P < 0.05). In addition, the use of Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles can identify hypoperfusion lesions and distinguish the ischemic core from the ischemic penumbra in a short time. While meeting the clinical needs, the Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles can provide quantitative hemodynamic information to better help diagnose lesions. At the same time, using day medical nursing management quality evaluation can better track the care of stroke patients and guide the formulation of individualized treatments, showing good potential in clinical application.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Bargavi P, Ramya R, Chitra S, Vijayakumari S, Riju Chandran R, Durgalakshmi D, Rajashree P, Balakumar S (2020) Bioactive, degradable and multi-functional three-dimensional membranous scaffolds of bioglass and alginate composites for tissue regenerative applications. Biomater Sci 8(14):4003–4025. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0bm00714e (Epub 2020 Jun 23 PMID: 32573600)
Chen KN, He L, Zhong LM, Ran YQ, Liu Y (2020) Meta-analysis of dyslipidemia management for the prevention of ischemic stroke recurrence in China. Front Neurol 19(11):483570. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.483570.PMID:33329292;PMCID:PMC7717969
Chrishtop VV, Mironov VA, Prilepskii AY, Nikonorova VG, Vinogradov VV (2021) Organ-specific toxicity of magnetic iron oxide-based nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 15(2):167–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2020.1842934 (Epub 2020 Nov 20 PMID: 33216662)
Chung H, Ko H, Jeon SJ, Yoon KH, Lee J (2018) Automatic lung segmentation with juxta-pleural nodule identification using active contour model and bayesian approach. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 18(6):1800513. https://doi.org/10.1109/JTEHM.2018.2837901.PMID:29910995;PMCID:PMC6001848
Gertsen EC, de Jongh C, Brenkman HJF, Mertens AC, Broeders IAMJ, Los M, Boerma D, Ten Bokkel HD, van Leeuwen L, Wessels FJ, van Hillegersberg R, Ruurda JP (2020) The additive value of restaging-CT during neoadjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 46(7):1247–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2020.04.002 (Epub 2020 Apr 14 PMID: 32349895)
Guo YY, Huang L, Zhang ZP, Fu DH (2020) Strategies for precise engineering and conjugation of antibody targeted-nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Curr Med Sci 40(3):463–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-020-2200-6 (Epub 2020 Jul 17 PMID: 32681251)
Hou Z, Liu Y, Xu J, Zhu J (2020) Surface engineering of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by polymer grafting: synthesis progress and biomedical applications. Nanoscale 12(28):14957–14975. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr03346d (PMID: 32648868)
Jose J, Kumar R, Harilal S, Mathew GE, Parambi DGT, Prabhu A, Uddin MS, Aleya L, Kim H, Mathew B (2020) Magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia in cancer treatment: an emerging tool. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(16):19214–19225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07231-2 (Epub 2019 Dec 28 PMID: 31884543)
Juthani R, Madajewski B, Yoo B, Zhang L, Chen PM, Chen F, Turker MZ, Ma K, Overholtzer M, Longo VA, Carlin S, Aragon-Sanabria V, Huse J, Gonen M, Zanzonico P, Rudin CM, Wiesner U, Bradbury MS, Brennan CW (2020) Ultrasmall core-shell silica nanoparticles for precision drug delivery in a high-grade malignant brain tumor model. Clin Cancer Res 26(1):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1834 (Epub 2019 Sep 12. PMID: 31515460; PMCID: PMC6942644)
Kadam R, Ghawali J, Waespy M, Maas M, Rezwan K (2020) Janus nanoparticles designed for extended cell surface attachment. Nanoscale 12(36):18938–18949. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr04061d (Epub 2020 Sep 11 PMID: 32914159)
MacKay-Lyons M, Billinger SA, Eng JJ, Dromerick A, Giacomantonio N, Hafer-Macko C, Macko R, Nguyen E, Prior P, Suskin N, Tang A, Thornton M, Unsworth K (2020) Aerobic exercise recommendations to optimize best practices in care after stroke: AEROBICS 2019 update. Phys Ther 100(1):149–156. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzz153.PMID:31596465;PMCID:PMC8204880
Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer R (2021) Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:101–124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8 (Epub 2020 Dec 4. PMID: 33277608; PMCID: PMC7717100)
Park SJ (2020) Protein-nanoparticle interaction: corona formation and conformational changes in proteins on nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 6(15):5783–5802. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S254808.PMID:32821101;PMCID:PMC7418457
Schäfer A, Burkhoff D, Bauersachs J (2019) Haemodynamic simulation and the effect of early left ventricular unloading in pre-shock acute coronary syndrome. ESC Heart Fail 6(3):457–463. https://doi.org/10.1002/ehf2.12417 (Epub 2019 Mar 12. PMID: 30861640; PMCID: PMC6487719)
Swierczynski P, Papież BW, Schnabel JA, Macdonald C (2018) A level-set approach to joint image segmentation and registration with application to CT lung imaging. Comput Med Imaging Graph 65:58–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2017.06.003 (Epub 2017 Jun 15. PMID: 28705410; PMCID: PMC5885990)
Tehrani BN, Basir MB, Kapur NK (2020) Acute myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock: should we unload the ventricle before percutaneous coronary intervention? Prog Cardiovasc Dis 63(5):607–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2020.09.001 (Epub 2020 Sep 11. PMID: 32920027)
Tramacere I, Boncoraglio GB, Banzi R, Del Giovane C, Kwag KH, Squizzato A, Moja L (2019) Comparison of statins for secondary prevention in patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Med 17(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-019-1298-5.PMID:30914063;PMCID:PMC6436237
van Dongen MME, Aarnio K, Martinez-Majander N, Pirinen J, Sinisalo J, Lehto M, Kaste M, Tatlisumak T, de Leeuw FE, Putaala J (2019) Use of statins after ischemic stroke in young adults and its association with long-term outcome. Stroke 50(12):3385–3392. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026992 (Epub 2019 Nov 8 PMID: 31699020)
Wang Z, Chang Z, Lu M, Shao D, Yue J, Yang D, Zheng X, Li M, He K, Zhang M, Chen L, Dong WF (2018) Shape-controlled magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for magnetically-mediated suicide gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials 154:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.047 (Epub 2017 Nov 4 PMID: 29128843)
Xu F, Zhu W, Shen Y, Wang J, Xu R, Qutesh C, Song L, Gan Y, Pu C, Hu H (2020) Radiomic-based quantitative CT analysis of pure ground-glass nodules to predict the invasiveness of lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 11(10):872. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00872.Erratum.In:FrontOncol.2020Oct30;10:608365.PMID:32850301;PMCID:PMC7432133
Zhang L, Haddouti EM, Welle K, Burger C, Kabir K, Schildberg FA (2020) Local cellular responses to metallic and ceramic nanoparticles from orthopedic joint arthroplasty implants. Int J Nanomed 11(15):6705–6720. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S248848.PMID:32982228;PMCID:PMC7494401
Zhang X, Li Y, Ma Z, He D, Li H (2021) Modulating degradation of sodium alginate/bioglass hydrogel for improving tissue infiltration and promoting wound healing. Bioact Mater 6(11):3692–3704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.03.038.PMID:33898873;PMCID:PMC8056275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
The study and all the participants were reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of Wuhan Third Hospital (NO. WHTH2020T053).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Hou, L. & Zhang, M. Diagnosis and treatment of stroke with Fe2O3 super nanoparticles and quality evaluation of nursing management in day medical department. Appl Nanosci 13, 3571–3578 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02728-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02728-8