Abstract
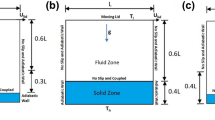
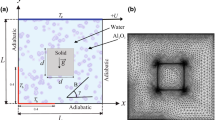
The limitless capability of the mixed convection cooling to secure practical implementation in wide range of technology makes it the current cynosure for research purposes. This paper centralizes on the two-dimensional simulation of steady-state mixed heat convection of dissimilar aqueous-based nanofluids in a square figured cavity having mono/dual movable lids to impart laminar fluid movement. For a cavity, the forced convection is imparted by giving momentum to one of the lid is categorized as lid-driven cavity. In this article, three cavity types—Standard lid, Uni-directive lids, Bi-directive lids—based on the three fluidic patterns of the flow field generated by different configurations of movable lids are investigated by employing Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)/Copper oxide (CuO)/Multi-Walled Carbon Nano Tubes (MWCNT) in pure water as the working fluid. Additionally, the influences of various operational variables such as Re (1100–1900), Gr (20,000, 13,000, 5000), and additive volume percentage of nanoparticles (1%, 3%, and 5%) are analyzed. Grid sensitivity analysis has been carried out for the sizes of (50 × 50, 100 × 100, 125 × 125, 150 × 150, 175 × 175, and 200 × 200) and selected an optimum grid as 175 × 175. The movement of the lid is framed by setting velocity to the one or more edges of the cavity. It is detected that cavity with uni-directive lids delivers greater heat transmission rates than bi-directive and standard lid. At (Grashof number) Gr = 20,000 and (Reynolds number) Re = 1500, the mean Nu of pure water in Uni-directive and Bi-directive lids is greater than Standard lid by a factor of 61.03% and 48.58%, respectively. Similar behavior is exhibited by all the heat transmission nanofluids. Increment in Gr, Re, and nanoparticle additive concentration is found to have a positive impact on heat transmission. Addition of 5% of Al2O3, CuO, and MWCNT nanoparticles in water results in the improvement of mean Nu by 37.1%, 60.03%, and 1028.1%, respectively, for mixed heat convection at Gr = 20,000 and Re = 1100. MWCNT/H2O nanofluid has the best heat transmission characteristics followed by CuO/H2O and Al2O3/H2O for the same volumetric addition concentration of nanoparticles.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity
- \(f\) :
-
Fluid
- \({\text{np}}\) :
-
Nanoparticle
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature
- \(L\) :
-
Length of the lid
- \(\beta\) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- avg:
-
Average
- \(h\) :
-
Hot
- \(c\) :
-
Cold
- \(u\) :
-
Velocity
- \(D\) :
-
Diameter
- vol:
-
Volumetric
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density
- \(\phi\) :
-
Volume concentration
- \(C_{{\text{p}}}\) :
-
Specific heat
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(K_{{\text{B}}}\) :
-
Boltzmann constant
- \({\text{Gr}}\) :
-
Grashof number
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- \({\text{Nu}}\) :
-
Nusselt number
- \(g\) :
-
Gravitational constant
References
Abdellahoum C, Mataoui A, Abu-Hamdeh N, Öztop HF (2015) Effects of different models of thermal conductivity on turbulent nanofluid flow through rectangular cavity in duct. J Mol Liqs 212:915–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.10.049
Ali FH, Hamzah HK, Egab K, Arici M, Shahsavar A (2020) Non-Newtonian nanofluid natural convection in a U-shaped cavity under magnetic field. Int J Mech Sci 186:105887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105887
Aljabair S, Ekaid AL, Ibrahim SH, Alesbe I (2021) Mixed convection in sinusoidal lid driven cavity with non-uniform temperature distribution on the wall utilizing nanofluid. Heliyon 7(5):e06907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06907
Armaghani T, Sadeghi MS, Rashad AM, Mansour MA, Chamkha AJ, Dogonchi AS, Nabwey HA (2021) MHD mixed convection of localized heat source/sink in an Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluid in L-shaped cavity. Alex Eng J 60(3):2947–2962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.01.031
Colak E, Ekici O, Oztop HF (2021) Mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with partially heated porous block. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 126:105450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105450
Fabregat A, Pallarès J (2020) Heat transfer and boundary layer analyses of laminar and turbulent natural convection in a cubical cavity with differently heated opposed walls. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 151:119409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119409
Filali A, Khezza L, Semmari H, Matar O (2021) Application of artificial neural network for mixed convection in a square lid-driven cavity with double vertical or horizontal oriented rectangular blocks. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 129:105644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105644
Gangawane KM, Oztop HF (2020) Mixed convection in the heated semi-circular lid-driven cavity for non-Newtonian power-law fluids: effect of presence and shape of the block. Chin J Chem Eng 28(5):1225–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.03.005
Garoosi F, Bagheri G, Rashidi MM (2015) Two phase simulation of natural convection and mixed convection of the nanofluid in a square cavity. Powder Technol 275(2015):239–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.02.013
Goodarzi H, Akbari OA, Sarafraz MM, Karchegani MM, Safaei MR, Sheikh Shabani GA (2019) Numerical simulation of natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid with Cu, MWCNT, and Al2O3 nanoparticles in a cavity with different aspect ratios. J Therm Sci Eng Appl 10(1115/1):4043809
Hadavand M, Yousefzadeh S, Akbari OA, Pourfattah F, Nguyen HM, Asadi A (2019) A numerical investigation on the effects of mixed convection of Ag-water nanofluid inside a sim-circular lid-driven cavity on the temperature of an electronic silicon chip. Appl Therm Eng 162:114298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114298
Hasan MN, Khondokar Samiuzzaman S, Haque H, Sumon Saha Md, Islam Q (2015) Mixed convection heat transfer inside a square cavity filled with Cu-water nanofluid. Procedia Eng 105:438–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.05.031
Hasib MH, Saddam Hossen Md, Saha S (2015) Effect of tilt angle on pure mixed convection flow in trapezoidal cavities filled with water-Al2O3 nanofluid. Procedia Eng 105:388–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.05.024
Hassanzadeh R, Rahimi R, Khosravipour A, Mostafavi S, Pekel H (2020) Analysis of natural convection in a square cavity in the presence of a rotating cylinder with a specific number of roughness components. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 116:104708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2020.104708
Ho CJ, Liu WK, Chang YS, Lin CC (2010) Natural convection heat transfer of alumina-water nanofluid invertical square enclosures: an experimental study. Int J Therm Sci 49(8):1345–1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2010.02.013
Hosseini M, Mustafa MT, Jafaryar M, Mohammadian E (2014) Nanofluid in tilted cavity with partially heated walls. J Mol Liqs 199:545–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.09.051
Hussein AK (2018) Entropy generation due to the transient mixed convection in a three- dimensional right-angle triangular cavity. Int J Mech Sci 146–147:141–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.07.012
Janjanam N, Nimmagadda R, Asirvatham LG, Harish R, Wongwises S (2021) Conjugate heat transfer performance of stepped lid-driven cavity with Al2O3 /water nanofluid under forced and mixed convection. SN Applied Sciences 3(6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04592-7
Kasaeipoor A, Ghasemi B, Aminossadati SM (2015) Convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a vented T-shaped cavity in the presence of magnetic field. Int J Therm Sci 94:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.02.014
Li Z, Barnoon P, Toghraie D, Dehkordi RB, Afrand M (2019) Mixed convection of non-Newtonian nanofluid in an H-shaped cavity with cooler and heater cylinders filled by a porous material: two phase approach. Adv Powder Technol 30(11):2666–2685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.08.014
Louaraychi A, Lamsaadi M, Naïmi M, El Harfi H, Kaddiri M, Raji A, Hasnaoui M (2019) Mixed convection heat transfer correlations in shallow rectangular cavities with single and double-lid driven boundaries. Int J Heat Mass Transf 132:394–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.11.164
Mondal P, Mahapatra TR (2021) MHD double-diffusive mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid in a trapezoidal cavity. Int J Mech Sci 208:106665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106665
Nazari S, Ellahi R, Sarafraz MM, Safaei MR, Asgari A, Akbari OA (2020) Numerical study on mixed convection of a non-Newtonian nanofluid with porous media in a two lid-driven square cavity. J Therm Anal Calorim 140(3):1121–1145
Nimmagadda R, Chereches EI, Chereches M (2021) Heat transfer performance of uni-directional and bi-directional lid-driven cavities using nanoparticle enhanced ionic liquids (NEILS). Int J Thermophys 42:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-021-02814-z
Rajarathinam M, Nithyadevi N, Chamkha AJ (2018) Heat transfer enhancement of mixed convection in an inclined porous cavity using Cu-water nanofluid. Adv Powder Technol 29(3):590–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.11.032
Razera AL, da Fonseca RJC, Isoldi LA, dos Santos ED, Rocha LAO, Biserni C (2018) Constructal design of a semi-elliptical fin inserted in a lid-driven square cavity with mixed convection. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126 Part B:81–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.05.157
Rui Z, Li J, Ma J, Cai H, Nie B, Peng H (2020) Comparative study on natural convection melting in square cavity using lattice Boltzmann method. Results Phys 18:103274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103274
Sáchica D, Treviño C, Martínez-Suástegui L (2020) Numerical study of magnetohydrodynamic mixed convection and entropy generation of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a channel with two facing cavities with discrete heating. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 86:108713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108713
Saqib Shah S, Haq RU, Al-Kouz W (2021) Mixed convection analysis in a split lid-driven trapezoidal cavity having elliptic shaped obstacle. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 126:105448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105448
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF (2019) MHD mixed convection of nanofluid in a flexible walled inclined lid-driven L-shaped cavity under the effect of internal heat generation. Physica A 534:122144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2019.122144
Shahid H, Yaqoob I, Khan WA, Rafique A (2021) Mixed convection in an isosceles right triangular lid driven cavity using multi relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 128:105552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105552
Sheikholeslami M (2017) Magnetic field influence on CuO–H2O nanofluid convective flow in a permeable cavity considering various shapes for nanoparticles. Int J Hydrog Energy 42(31):19611–19621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.06.121
Sheremet MA, Roşca NC, Roşca AV, Pop I (2018) Mixed convection heat transfer in a square porous cavity filled with a nanofluid with suction/injection effect. Comput Math Appl 76(11–12):2665–2677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2018.08.069
Soomro FA, Haq RU, Algehyne EA, Tlili I (2020) Thermal performance due to magnetohydrodynamics mixed convection flow in a triangular cavity with circular obstacle. J Energy Storage 31:101702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101702
Tizakast Y, Kaddiri M, Lamsaadi M (2021) Double-diffusive mixed convection in rectangular cavities filled with non-Newtonian fluids. Int J Mech Sci 208:106667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106667
Turkyilmazoglu M (2022) Driven flow motion by a dually moving lid of a square cavity. Eur J Mech B/fluids 94:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2022.02.005
Wong HF, Ahmad N, Siri Z, Noor NFM (2021) Viscous heating and cooling process in a mixed convection cavity with free-slip effect. Case Stud Therm Eng 28:101349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2021.101349
Yousefzadeh S, Rajabi H, Ghajari N, Sarafraz MM, Akbari OA, Goodarzi M (2020) Numerical investigation of mixed convection heat transfer behavior of nanofluid in a cavity with different heat transfer areas. J Therm Anal Calorim 140(6):2779–2803
Zhang X, Ying Xu, Zhang J, Amin Rahmani S, Sajadi M, Zarringhalam M, Toghraie D (2021) Numerical study of mixed convection of nanofluid inside an inlet/outlet inclined cavity under the effect of Brownian motion using Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM). Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 126:105428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2021.105428
Zhang H, Nie X, Bokov DO, Toghraie D, Akbari OA, Montazerifar F, Pourfattah F, Esmaeili Y, Khodaparast R (2022) Numerical study of mixed convection and entropy generation of water-Ag nanofluid filled semi-elliptic lid-driven cavity. Alex Eng J 61(11):8875–8896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2022.02.028
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Teja, P.N.S., Gugulothu, S.K., Reddy, P.D.S. et al. Mixed convective heat transmission of laminar flow field in a mono/dual moving lid-type square figured cavity packed with diverse aqueous-based nanofluids. Appl Nanosci 13, 3887–3903 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02621-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02621-4