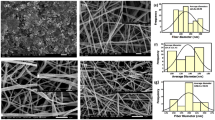
Abstract
The objective of this study is to investigate the adsorption behavior of an electrospun ceria-nanofiber adsorbent in removing pollutants from a simulated solution. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction were used to characterize this nanofiber composite. Adsorption parameters including contact time, pH, starting arsenic concentration, and adsorbent dose were optimized using batch adsorption studies. After copper was added to nanofiber, maximum removal efficiencies were increased to 96.5% under optimal conditions (1.2 g/L adsorbate dose; 2.0 ppm initial As(III) concentration; and pH of 5.0). Furthermore, the response surface methodology was also successfully applied to the design optimization of the process with central composite design. The Temkin isotherm model (R2 = 0.98) better described the adsorption equilibrium results. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model was followed by adsorption experimental data. Other kinetics theories, such as Elovich, intra-particle, and film diffusion, were also used to develop a better understanding of the adsorption mechanism. The viability of a copper/ceria composite nanofiber in the removal of arsenic demonstrates an emerging candidate in the removal of pollutants from wastewater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Usman ARA, Hussain Q, Al-Farraj ASF et al (2020) Fabrication and evaluation of silica embedded and zerovalent iron composited biochars for arsenate removal from water. Environ Pollut 266:115256
Al-Hetlani E, Rajendran N, BabuVelappan A, Amin MO et al (2021) Design and synthesis of a nanopolymer for CO2 capture and wastewater treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 60:8664–8676
Babaee Y, Mulligan CN, Rahaman MS (2018) Removal of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) from aqueous solutions through adsorption by Fe/Cu nanoparticles. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:63–71
Bhateria R, Singh R (2019) A review on nanotechnological application of magnetic iron oxides for heavy metal removal. J Water Process Eng 31:100845
Brandes R, Belosinschi D, Brouillette F, Chabot B (2019) A new electrospun chitosan/phosphorylated nanocellulose biosorbent for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103477
Bulin C, Li B, Zhang Y, Zhang B (2020) Removal performance and mechanism of nano α-Fe2O3/graphene oxide on aqueous Cr(VI). J Phys Chem Solids 147:109659
Cai W, Weng X, Chen Z (2019) Highly efficient removal of antibiotic rifampicin from aqueous solution using green synthesis of recyclable nano-Fe3O4. Environ Pollut 247:839–846
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Saravanan A, Joshiba AG et al (2017) Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 5(3):2782–2799
Chai WS, Cheun JY, Kumar PS, Mubashir M et al (2021) A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J Clean Prod 296:126589
Cui Q, Dong X, Wang J, Li M (2008) Direct fabrication of cerium oxide hollow nanofibers by electrospinning. J Rare Earths 26:664–669
Cui J, Li F, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Ma W, Huang C (2020) Electrospun nanofiber membranes for wastewater treatment applications. Sep Purif Technol 250:117116
Fang Y, Wen J, Zhang H, Wang Q, Hu X (2020) Enhancing Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by magnetic core-shell structured NZVI@MOF derivative hybrids. Environ Pollut 260:114021
Fatima B, Siddiqui SI, Nirala RK, Vikrant K et al (2021) Facile green synthesis of ZnO–CdWO4 nanoparticles and their potential as adsorbents to remove organic dye. Environ Pollut 271:116401
Foong CY, Wirzal MDH, Bustam MA (2020) A review on nanofibers membrane with amino-based ionic liquid for heavy metal removal. J Mol Liq 297:111793
Gautham V, Chinglenthoiba C, John J et al (2020) Enhancement of soot combustion in diesel particulate filters by ceria nanofiber coating. Appl Nanosci 10:2429–2438
Ghosh S, Prabhakar R, Samadder SR (2019) Performance of γ-aluminum oxide nanoparticles for arsenic removal from groundwater. Clean Techn Environ Policy 21:121–138
Hang C, Li Q, Gao S, Shang JK (2012) As(III) and As(V) adsorption by hydrous zirconium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by a hydrothermal process followed with heat treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:353–361
He W, Wang Q, Zhu Y, Wang K, Mao J, Xue X et al (2021) Innovative technology of municipal wastewater treatment for rapid sludge sedimentation and enhancing pollutants removal with nano-material. Bioresour Technol 324:124675
Hu JS, Zhong LS, Song WG, Wan LJ (2008) Synthesis of hierarchically structured metal oxides and their application in heavy metal ion removal. Adv Mater 20:2977–2982
Hu Q, Liu Y, Gu X, Zhao Y (2017) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of different arsenic species on mesoporous MnFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Chemosphere 181:328–336
Inchaurrondo N, Luca CD, Mori F, Pintar A et al (2019) Synthesis and adsorption behavior of mesoporous alumina and Fe-doped alumina for the removal of dominant arsenic species in contaminated waters. J Environ Chem Eng 7(1):102901
Khare N, Bajpai J, Bajpai AK (2021) Efficient graphene-coated iron oxide (GCIO) nanoadsorbent for removal of lead and arsenic ions. Environ Technol 42(14):2187–2201
Kumar A, Sharma SK, Sharma G, Guo C et al (2021) Silicate glass matrix@Cu2O/Cu2V2O7 p–n heterojunction for enhanced visible light photo-degradation of sulfamethoxazole: high charge separation and interfacial transfer. J Hazard Mater 402:123790
Liu Z, Chen J, Zhou R et al (2008) Influence of ethanol washing in precursor on CuO–CeO2 catalysts in preferential oxidation of CO in excess hydrogen. Catal Lett 123:102
Ma J, Zhao J, Zhu Z, Li L, Yu F (2019) Effect of microplastic size on the adsorption behavior and mechanism of triclosan on polyvinyl chloride. Environ Pollut 254:113104
Mudzielwana R, Gitari MW, Ndungu P (2020) Enhanced As(III) and As(V) adsorption from aqueous solution by a clay based hybrid sorbent. Front Chem 7:913
Nicomel NR, Leus K, Folens K, Van Der Voort P et al (2016) Technologies for arsenic removal from water: current status and future perspectives. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(1):62
Olivera S, Chaitra K, Venkatesh K, Muralidhara HB, Inamuddin AAM et al (2018) Cerium dioxide and composites for the removal of toxic metal ions. Environ Chem Lett 16:1233–1246
Olteanu M, Baraitaru A, Panait AM et al (2019) Advanced SiO2 composite materials for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 230:179
Ordonez D, Valencia A, Elhakiem H, Chang N-B, Wanielista MP (2020) Adsorption thermodynamics and kinetics of advanced green environmental media (AGEM) for nutrient removal and recovery in agricultural discharge and stormwater runoff. Environ Pollut 266:115172
Pal DB, Singh P, Mishra PK (2017) Composite ceria nanofiber with different copper loading using electrospinning method. J Alloys Compd 694:10–16
Paschalidou P, Theocharis CR (2019) Surface properties of ceria synthesised using Triton-X based reverse microemulsions. RSC Adv 9(12):7025–7031
Pholosi A, Naidoo EB, Ofomaja AE (2020) Intraparticle diffusion of Cr(VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: a comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S Afr J Chem Eng 32:39–55
Pratush A, Kumar A, Hu Z (2018) Adverse effect of heavy metals (As, Pb, Hg, and Cr) on health and their bioremediation strategies: a review. Int Microbiol 21(3):97–106
Qin H, Hu T, Zhai Y, Lu N, Aliyeva J (2020) The improved methods of heavy metals removal by biosorbents: a review. Environ Pollut 258:113777
Raitano SRJ, Yi N, Zhang L, Chan S-W, Flytzani-Stephanopoulos M (2012) Structure sensitivity of the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction on Cu–CeO2 catalysts. Catal Today 180:68–80
Selvakumar A, Rangabhashiyam S (2019) Biosorption of rhodamine B onto novel biosorbents from Kappaphycus alvarezii, Gracilaria salicornia and Gracilaria edulis. Environ Pollut 255:113291
Sharma G, Kumar A, Naushad M, Thakur B et al (2021) Adsorptional-photocatalytic removal of fast sulphon black dye by using chitin-cl-poly(itaconic acid-co-acrylamide)/zirconium tungstate nanocomposite hydrogel. J Hazard Mater 416:125714
Sharma G, Kumar A, Ghfar AA, García-Peñas A et al (2022) Fabrication and characterization of xanthan gum-cl-poly(acrylamide-co-alginic acid) hydrogel for adsorption of cadmium ions from aqueous medium. Gels 8(1):23
Shen L, Wang J, Li Z, Fan L et al (2020) A high-efficiency Fe2O3@microalgae composite for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution. J Water Process Eng 33:101026
Wang L, Zhao Y, Zhang J (2017) Electrospun cerium-based TiO2 nanofibers for photocatalytic oxidation of elemental mercury in coal combustion flue gas. Chemosphere 185:690–698
Wang L, Shi C, Wang L, Pan L et al (2020) Rational design, synthesis, adsorption principles and applications of metal oxide adsorbents: a review. Nanoscale 12:4790–4815
Yang D, Li L, Chen B, Shi S, Nie J, Ma G (2019) Functionalized chitosan electrospun nanofiber membranes for heavy-metal removal. Polymer 163:74–85
Yuan X, Xue N, Han Z (2021) A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years. J Environ Sci 101:217–226
Zhang Y, Shi R, Yang P, Song X, Zhu Y, Ma Q (2016) Fabrication of electronspun porous CeO2 nanofibers with large surface area for pollutants removal. Ceram Int 42:14028–14035
Zhong LS, Hu JS, Cao AM, Liu Q et al (2007) 3D flowerlike ceria micro/nanocomposite structure and its application for water treatment and CO removal. Chem Mater 19:1648–1655
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge to Department of chemical engineering IIT (BHU) Varanasi and Birla Institute of Technology Ranchi for providing characterization facilities. The authors are grateful to Scientific Research Deanship at King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia for their financial support through the Large Research Group Project under grant number (RGP.02-87-43).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the co-authors have seen the final manuscript and agreed with the submission to the journal.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest between authors.
Research on human participants and/or animals
There is no involvement of human or animal cell in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, D.B., Singh, A., Saini, R. et al. Studies on adsorption behavior of electrospun nanofibers for pollutant remediation from simulated wastewater. Appl Nanosci 13, 3721–3733 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02516-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02516-4