Abstract
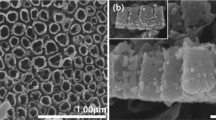
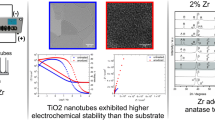
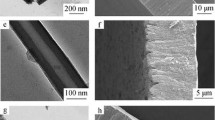
In general, Ti alloys are commonly used as biomaterials for implants. However, in the case of such alloys, the high elastic modulus causes stress shielding effects and bacterial growth, reducing their biocompatibility. In order to improve it, new alloys composed of Ti–Nb–Ag–Pt were developed in this study because it is possible to reduce the elastic modulus by adding an alloying element, such as Nb, and to reduce the bacterial activity by adding Ag and Pt elements. The following studies were conducted with the aim of manufacturing and forming nanotubes on the surface to greatly improve the biocompatibility. Ti–xNb–Ag–Pt alloys were manufactured using a vacuum arc furnace in an Ar atmosphere, homogenized for 1 h at 1050 °C, and then quenched at 0 °C. The formation of nanotubes on the surfaces of the alloys was performed using the anodization method with an applied voltage of 30 V in 1 M H3PO4 + 0.8 wt% NaF for 1 h at 25 °C. The formed nanotube surfaces were analyzed by optical microscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, nanoindentation tests, and antibacterial tests. Antibacterial activity was evaluated according to the ISO 22196:2007 method, for which S. aureus (NBRC122135) was used. The microstructure of Ti–10Nb–Ag–Pt was a needle-like structure, and Ti–50Nb–Ag–Pt presented both an equiaxed structure and a needle-like structure. The size of the nanotube diameter decreased as the Nb content increased. The Ag and Pt elements were evenly distributed on the nanotube-formed alloy surfaces. The Vickers hardness and the elastic modulus value decreased as the Nb content increased. Following the nanotube formation, the Vickers hardness and elastic modulus values decreased by thrice, and only the nanotube-formed Ti–xNb alloys containing Ag and Pt showed the antibacterial activity effect.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byeon IS, Choe HC (2017) Surface characteristics of nanotube formed Ti–25Nb–xZr alloys. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17(4):2655–2660. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.13326
Byeon IS, Park SY, Choe HC (2017) Electrochemical characteristics of nanotubular Ti–25Nb–xZr ternary alloys for dental implant materials. J Korean Dent Sci 10(1):10–21. https://doi.org/10.5856/JKDS.2017.10.1.10
Choe HC, Kim WG, Jeong YH (2010) Surface characteristics of HA coated Ti–30Ta–xZr and Ti–30Nb–xZr alloys after nanotube formation. Surf Coat Technol 205:S305–S311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.08.020
Fikeni L, Annan KA, Mutombo K, Machaka R (2020) Effect of Nb content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of binary Ti–Nb alloys. Mater Today Proc 38(2):913–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.315
Gao J, Wang M (2021) Atomic layer deposition of TaN thin film on Ti–6Al–4V dental implant for enhanced anti-corrosion and anti-bacterial properties. J Phys Chem Solids 150:109806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109806
Kaseem M, Choe HC (2019) Electrochemical and bioactive characteristics of the porous surface formed on Ti–xNb alloys via plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf Coat Technol 378:125027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.125027
Kim SP, Choe HC (2019) Functional elements coatings on the plasma electrolytic oxidation-treated Ti–6Al–4V alloy by electrochemical precipitation method. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 19(7):4344–4349. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2019.16278
Kim HJ, Choe HC (2020) Magnesium, silicon, and hydroxyapatite deposition on the Ti–xNb–2Ag–2Pt alloy by co-sputtering after nanotube formation. Surf Coat Technol 404:126487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126487
Kim SP, Cho HR, Choe HC (2021) Bioactive element coatings on nano-mesh formed Ti–6Al–4V alloy surface using plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf Coat Technol 406:126649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126649
Lee TK, Lee SW, Kim IS, Moon YH, Kim HS, Park CH (2020) Breaking the limit of young’s modulus in low-cost Ti–Nb–Zr alloy for biomedical implant applications. J Alloys Compd 828:154401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154401
Li J, Mutreja I, Tredinnick S, Jermy M, Hooper GJ, Woodrield TBF (2020) Hydrodynamic control of titania nanotube formation on Ti–6Al–4V alloys enhances osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Mater Sci Eng 109:110562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110562
Lockman Z, Sreekantan S, Ismail S, Schmidt-Mende L, MacManus-Driscoll JL (2010) Influence of anodisation voltage on the dimension of titania nanotubes. J Alloys Compd 503(2):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.12.093
Mazigi O, Kannan MB, Xu J, Choe HC, Ye Q (2017) Biocompatibility and degradation of a low elastic modulus Ti–35Nb–3Zr alloy: nanosurface engineering for enhanced degradation resistance. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00563
Mishra S, Chowdhary R (2019) PEEK materials as an alternative to titanium in dental implants: a systematic review. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 21(1):208–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12706 (Epub 2018 Dec 27)
Mohan L, Dennis C, Padmapriya N, Anandan C, Rajendran N (2020) Effect of electrolyte temperature and anodization time on formation of TiO2 nanotubes for biomedical applications. Mater Today Commun 23:101103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101103
Park SY, Choe HC (2017) Manganese coatings on hydroxyapatite-deposited Ti–29Nb–xHf alloys after nanomesh formation. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:2661–2665. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.13331
Ponomarev VA, Orlov EA, Malikov NA, Tarasov YV, Sheveyko AN, Permyakova ES, Kuptsov KA, Dyatlov IA, Ignatov SG, Ilnitskaya AS, Gloushankova NA, Subramanian B, Shtansky DV (2020) Ag(Pt) nanoparticles-decorated bioactive yet antibacterial Ca- and P-doped TiO2 coatings produced by plasma electrolytic oxidation and ion implantation. Appl Surf Sci 516:146068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146068
Saji VS, Choe HC (2009) Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of nanotubular Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloy in ringer’s solution. Corros Sci 51(8):1658–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.04.013
Szaraniec B, Goryczka T (2017) Structure and properties of Ti–Ag alloys produced by powder metallurgy. J Alloy Compd 709:464–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.155
Torrento JE, Grandini CR, Sousa TSP, Rocha LA, Gonçalves TM, Sottovia L, Rangel EC, Cruz NC, Correa KRN (2020) Bulk and surface design of MAO-treated Ti–15Zr–15Mo–Ag alloys for potential use as biofunctional implants. Mater Lett 269:127661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127661
Wang X, Zhang L, Guo Z, Jian Y, Tao X, Liu L (2016) Study of low-modulus biomedical β Ti–Nb–Zr alloys based on single-crystal elastic constants modeling. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 62:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.04.040
Yu JM, Choe HC (2018) Mg-containing hydroxyapatite coatings on Ti–6Al–4V alloy for dental materials. Appl Surf Sci 432:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.263
Funding
This research was supported by NRF: 2016R1D1A1B0101654215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HRC contributed to formal analysis, writing, data collection, data analysis, and data interpretation; HCC was involved in writing, review and editing, funding acquisition, study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, resources, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests, ethical interests, or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence work reported in this paper.
Informed consent statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study. The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Availability of data and material
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, HR., Choe, HC. Antibacterial activity and surface characteristics of nanotube-formed Ti–xNb–Ag–Pt alloy. Appl Nanosci 12, 3321–3327 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02450-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02450-5