Abstract
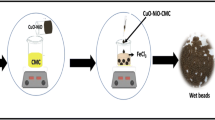
In this work, nickel oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by precipitation method from nickel nitrate solution with basic pH, followed by calcination at 550 °C. The ex-situ made nickel oxide nanoparticles were mixed with carboxymethyl cellulose biopolymer in 1:2 proportions for nanocomposite preparation in aqueous media. The mixed nanoparticles and polymer aqueous solution were extruded drop-wise from the sterile syringe into a gently agitating 0.02 M solution of AlCl3·3H2O. As a result of this process, the nanocomposite beads were synthesized with a size of ~ 1.5–2 mm. These nanocomposite beads were then characterized by UV–visible, Fourier-transform infra-red spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy. To monitor catalytic activity of synthesized nanocomposite, it was applied for the reduction of methylene blue dye. The nanocomposite beads showed excellent activity for detoxification of methylene blue dye. Rate of reaction for methylene blue reduction was calculated using data obtained from UV–visible spectrophotometry which was 0.1482 min−1 according to the pseudo first-order kinetics. The recyclability of NiO-CMC up to five consecutive cycles revealed its stability in aqueous medium. This work showed that nanocomposite beads have excellent catalytic efficacy against remediation of toxic pollutants in wastewater.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CMC:
-
Carboxy methylcellulose polymer
- NiO:
-
Nickel oxide
- NiO-CMC:
-
Carboxy methyl cellulose beads containing nickel oxide nanoparticles
- MB:
-
Methylene blue dye
- CF-Au:
-
Cellulose fibers supported gold nanoparticles
- Ag/MR:
-
Macroporous resin supported silver nanoparticles
- rGO-SiW:
-
Silicotungstic acid decorated reduced graphene oxide
References
Ahmad I, Kamal T, Khan SB, Asiri AM (2016) An efficient and easily retrievable dip catalyst based on silver nanoparticles/chitosan-coated cellulose filter paper. Cellulose 23:3577–3588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1053-4
Al-Ghamdi YO, Khan SA (2020) Stabilization of zero-valent Au nanoparticles on carboxymethyl cellulose layer coated on chitosan-CBV 780 zeolite Y sheets: assessment in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and dyes. Cellulose 27:8827–8841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03379-0
Ali F, Khan SB, Kamal T et al (2017) Bactericidal and catalytic performance of green nanocomposite based on chitosan/carbon black fiber supported monometallic and bimetallic nanoparticles. Chemosphere 188:588–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.118
Ali N, Awais KT et al (2018) Chitosan-coated cotton cloth supported copper nanoparticles for toxic dye reduction. Int J Biol Macromol 111:832–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.092
Anchan S, Pai S, Sridevi H et al (2019) Biogenic synthesis of ferric oxide nanoparticles using the leaf extract of Peltophorum pterocarpum and their catalytic dye degradation potential. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 20:101251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101251
Anjum F, Gul S, Khan MI, Khan MA (2019) Efficient synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using guar gum as stabilizer and their applications as catalyst in reduction reactions and degradation of azo dyes. Green Process Synth 9:63–76. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2020-0008
Bashir AKH, Razanamahandry LC, Nwanya AC et al (2019) Biosynthesis of NiO nanoparticles for photodegradation of free cyanide solutions under ultraviolet light. J Phys Chem Solids 134:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.05.048
Cai C, Zhou K, Guo H et al (2019) Enhanced hole extraction by NiO nanoparticles in carbon-based perovskite solar cells. Electrochim Acta 312:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.04.191
Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint C (2010) Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Res 44:2997–3027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039
Coşkuner Filiz B (2020) The role of catalyst support on activity of copper oxide nanoparticles for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Adv Powder Technol 31:3845–3859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.07.026
Das R, Sypu VS, Paumo HK et al (2019) Silver decorated magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@PPy-MAA/Ag) as highly active catalyst towards reduction of 4-nitrophenol and toxic organic dyes. Appl Catal B Environ 244:546–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.11.073
Dhas SD, Maldar PS, Patil MD et al (2020) Synthesis of NiO nanoparticles for supercapacitor application as an efficient electrode material. Vacuum 181:109646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109646
Ezema FI, Ekwealor ABC, Osuji RU (2007) Optical properties of chemical bath deposited nickel oxide (NiO) thin films. J Optoelectron Adv Mater 9:1898–1903
Ezhilarasi AA, Vijaya JJ, Kaviyarasu K et al (2016) Green synthesis of NiO nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera extract and their biomedical applications: cytotoxicity effect of nanoparticles against HT-29 cancer cells. J Photochem Photobiol B 164:352–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.10.003
Gao Z, Fan G, Liu M et al (2018) Dandelion-like cobalt oxide microsphere-supported RuCo bimetallic catalyst for highly efficient hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Appl Catal B Environ 237:649–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.026
García-Cerda LA, Bernal-Ramos KM, Montemayor SM et al (2011) Preparation of hcp and fcc Ni and Ni/NiO nanoparticles using a citric acid assisted pechini-type method. J Nanomater 2011:e162495. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/162495
Gholamali I, Yadollahi M (2020) Doxorubicin-loaded carboxymethyl cellulose/Starch/ZnO nanocomposite hydrogel beads as an anticancer drug carrier agent. Int J Biol Macromol 160:724–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.232
Godiya CB, Cheng X, Li D et al (2019) Carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel for cascaded treatment/reuse of heavy metal ions in wastewater. J Hazard Mater 364:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.076
Harrad MA, Valerga P, Puerta MC et al (2011) Ni(0)-CMC-Na nickel colloids in sodium carboxymethyl-cellulose: catalytic evaluation in hydrogenation reactions. Molecules 16:367–372. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16010367
He J, Schill L, Yang S, Riisager A (2018) Catalytic transfer hydrogenation of bio-based furfural with NiO nanoparticles. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:17220–17229. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04579
Hosseinian L, Weiner M, Levin MA, Fischer GW (2016) Methylene blue: magic bullet for vasoplegia? Anesth Analg 122:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000001045
Hussain S, Maqbool Z, Ali S et al (2013) Biodecolorization of reactive black-5 by a metal and salt tolerant bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. RA20 isolated from Paharang drain effluents in Pakistan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.09.018
Ilgin P, Ozay O, Ozay H (2019) A novel hydrogel containing thioether group as selective support material for preparation of gold nanoparticles: synthesis and catalytic applications. Appl Catal B Environ 241:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.066
Islam MdT, Dominguez N, Ahsan MdA et al (2017) Sodium rhodizonate induced formation of gold nanoparticles supported on cellulose fibers for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. J Environ Chem Eng 5:4185–4193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.08.017
Jiang S, Wang L, Duan Y et al (2021) A novel strategy to construct supported silver nanocomposite as an ultra-high efficient catalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 283:119592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119592
Kamal T, Khan SB, Asiri AM (2016) Nickel nanoparticles-chitosan composite coated cellulose filter paper: an efficient and easily recoverable dip-catalyst for pollutants degradation. Environ Pollut 218:625–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.07.046
Kamal T, Khan SB, Haider S et al (2017) Thin layer chitosan-coated cellulose filter paper as substrate for immobilization of catalytic cobalt nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 104:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.157
Kamal T, Ahmad I, Khan SB, Asiri AM (2018) Agar hydrogel supported metal nanoparticles catalyst for pollutants degradation in water. Desalination Water Treat 136:290–298. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.23230
Kamal T, Ahmad I, Khan SB et al (2019a) Microwave assisted synthesis and carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized copper nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose nanofibers support for pollutants degradation. J Polym Environ 27:2867–2877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01565-1
Kamal T, Ahmad I, Khan S, Asiri AM (2019b) Bacterial cellulose as support for biopolymer stabilized catalytic cobalt nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.057
Kamal T, Ahmad I, Khan SB, Asiri AM (2019c) Bacterial cellulose as support for biopolymer stabilized catalytic cobalt nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 135:1162–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.057
Kamal T, Ahmad I, Khan SB, Asiri AM (2019d) Anionic polysaccharide stabilized nickel nanoparticles-coated bacterial cellulose as a highly efficient dip-catalyst for pollutants reduction. React Funct Polym 145:104395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.104395
Khalil A, Ali N, Khan A et al (2020) Catalytic potential of cobalt oxide and agar nanocomposite hydrogel for the chemical reduction of organic pollutants. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.140
Khalil A, Ali N, Asiri AM et al (2021) Synthesis and catalytic evaluation of silver@nickel oxide and alginate biopolymer nanocomposite hydrogel beads. Cellulose 28:11299–11313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04248-0
Khan MM, Lee J, Cho MH (2014) Au@TiO2 nanocomposites for the catalytic degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue: an electron relay effect. J Ind Eng Chem 20:1584–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.08.002
Khan MSJ, Kamal T, Ali F et al (2019) Chitosan-coated polyurethane sponge supported metal nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. Int J Biol Macromol 132:772–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.205
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink H-P, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200460587
Miraki M, Karimi-Maleh H, Taher MA et al (2019) Voltammetric amplified platform based on ionic liquid/NiO nanocomposite for determination of benserazide and levodopa. J Mol Liq 278:672–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.01.081
Nwanya AC, Offiah SU, Amaechi IC et al (2015) Electrochromic and electrochemical supercapacitive properties of room temperature PVP capped Ni(OH)2/NiO thin films. Electrochim Acta 171:128–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.05.005
Nwanya AC, Ndipingwi MM, Ikpo CO et al (2020) Zea mays lea silk extract mediated synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles as positive electrode material for asymmetric supercabattery. J Alloys Compd 822:153581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153581
Paul SC, Bhowmik S, Nath MR et al (2020) Silver nanoparticles synthesis in a green approach: size dependent catalytic degradation of cationic and anionic dyes. Orient J Chem 36:353–360
Rinaldi FG, Arif AF, Ogi T et al (2017) Strong metal-support interactions (SMSIs) between Pt and Ti3+ on Pt/TiOx nanoparticles for enhanced degradation of organic pollutant. Adv Powder Technol 28:2987–2995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.09.007
Sartaj S, Ali N, Khan A et al (2020) Performance evaluation of photolytic and electrochemical oxidation processes for enhanced degradation of food dyes laden wastewater. Water Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.182
Sharma G, Kumar A, Sharma S et al (2019) Novel development of nanoparticles to bimetallic nanoparticles and their composites: a review. J King Saud Univ Sci 31:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2017.06.012
Shlyapnikov YM, Shlyapnikova EA, Morozov VN (2014) Carboxymethyl cellulose film as a substrate for microarray fabrication. Anal Chem 86:2082–2089. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac403604j
Sohni S, Gul K, Ahmad F et al (2017) Highly efficient removal of acid red-17 and bromophenol blue dyes from industrial wastewater using graphene oxide functionalized magnetic chitosan composite. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24349
Thangaraj V, Mahmud S, Li W et al (2018) Greenly synthesised silver-alginate nanocomposites for degrading dyes and bacteria. IET Nanobiotechnol 12:47–51. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0074
Thomas M, Naikoo GA, Sheikh MUD et al (2016) Effective photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye using alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite hydrogel under direct sunlight irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 327:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.05.005
Ucar A, Findik M, Gubbuk IH et al (2017) Catalytic degradation of organic dye using reduced graphene oxide–polyoxometalate nanocomposite. Mater Chem Phys 196:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.04.047
Wahid F, Mohammadzai I, Khan A et al (2013) Removal of toxic metals with activated carbon prepared from Salvadora persica. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.054
Wang L-Y, Wang M-J (2016) Removal of heavy metal ions by poly(vinyl alcohol) and carboxymethyl cellulose composite hydrogels prepared by a freeze-thaw method. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:2830–2837. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00336
Acknowledgements
The Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia has funded this project, under grant no. (KEP-33-130-42). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR for technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, F., Gulzar, T., Kiran, S. et al. Nickel oxide and carboxymethyl cellulose composite beads as catalyst for the pollutant degradation. Appl Nanosci 12, 3585–3595 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02345-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02345-5