Abstract
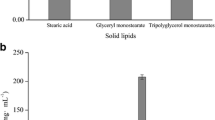
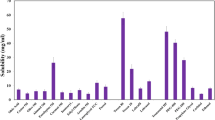
Vemurafenib (VEM) is a recently licensed chemotherapeutic medication for the treatment of melanoma. Since the medicine is frequently taken orally, it can easily cause damage to important organs as well as to its low absorption. In this work, solid in oil nanodispersion (SON) was adapted to prepare a topical vemurafenib to target skin melanoma at early stages. SON is a unique oil-based dispersion that has been developed for revolutionary medication delivery methods. Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic bioactive drugs have the potential to be carried and delivered by this system. In our method, water and cyclohexane were removed from the W/O emulsion precursor containing 100 mg VEM by lyophilization, followed by redispersion of the surfactant–drug complex in another oil carrier, isopropyl myristate (IPM) to adjust VEM concentration (10 mg/ml). High energy techniques were used to produce VEM as SONs, with sucrose fatty acid ester surfactant (sucrose monolaurate, L195) in various ratios, as well as control was prepared by dispersing pure VEM in IPM (10 mg/ml). The preparations were evaluated for in vitro release through dialysis bag and ex vivo permeation experiments through Albino Wistar rat abdomen skin to simulate human skin as well as particle size, pH, partition coefficient, and entrapment efficiency. SON formula containing VEM-L195 complex in the ratio of 1:6.6 (F3) shows acceptable partition coefficient (Log P > 1), pH values appropriate for skin melanoma application, acceptable particle sizes, and good VEM entrapment efficiency. F3 was found to be released in vitro in a sustained pattern (9% in 1 h and 100% after 24 h) through the dialysis membrane compared to the control (25.9% in 1 h and 95.8% after 24 h). Ex vivo VEM permeability through rat abdomen skin was considerably (P < 0.05) higher for SON-F3 versus control (72% and 29%, respectively). Such SON formulation could be able to deliver VEM topically in an effective, sustained, and safe manner to treat early diagnosed skin melanoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 January 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-024-03024-3
References
Abdel-Messih HA, Ishak RAH, Geneidi AS, Mansour S (2019) Tailoring novel soft nano-vesicles ‘Flexosomes’ for enhanced transdermal drug delivery: optimization, characterization and comprehensive ex vivo–in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 560:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.01.072
Abu-Rumman A (2021) Transformational leadership and human capital within the disruptive business environment of academia. World J Educ Technol 13(2):178–187. https://doi.org/10.18844/wjet.v13i2.5652
Abu-Rumman A, Al Shraah A, Al-Madi F et al (2021) Entrepreneurial networks, entrepreneurial orientation, and performance of small and medium enterprises: are dynamic capabilities the missing link? J Innov Entrep 10:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-021-00170-8
Ahmed AB, Das G (2019) Effect of menthol on the transdermal permeation of aceclofenac from microemulsion formulation. Int J Appl Pharm 11:117–122. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2019v11i2.30988
Alavi T, Rezvanian M, Ahmad N, Mohamad N, Ng SF (2019) Pluronic-F127 composite film loaded with erythromycin for wound application: formulation, physicomechanical and in vitro evaluations. Drug Deliv Transl Res 9:508–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-017-0450-z
Alhayani B, Abdallah AA (2020) Manufacturing intelligent Corvus corone module for a secured two way image transmission under WSN. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-02-2020-0107
Alhayani BSA, llhan H (2021) Visual sensor intelligent module based image transmission in industrial manufacturing for monitoring and manipulation problems. J Intell Manuf 32:597–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01590-1
Alhayani B, Abbas ST, Mohammed HJ et al (2021) Intelligent secured two-way image transmission using corvus corone module over WSN. Wirel Pers Commun. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08484-2
Al-Hayani B, Ilhan H (2020) Efficient cooperative image transmission in one-way multi-hop sensor network. Int J Electr Eng Educ 57(4):321–339
Almajidi YQ, Albaderi AA, Fadhel H (2019) Enhance solubility and prolong release of prochlorperazine maleate using floating nanoemulsion in situ gel. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 12:537. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2019.v12i1.30486
Anderson RA, Polack AE (1968) The stability of sucrose monolaurate: rate of formation of lauric acid. J Pliarni Pharmac 20:249–254
Anderson NH, Bauer M, Boussac N, Khan-malek R, Munden P (1998) An evaluation of fit factors and dissolution efficiency for the comparison of in vitro dissolution profiles. J Pharm Biomed Anal 17:811–822
Cázares-Delgadillo J, Naik A, Kalia YN, Quintanar-Guerrero D, Ganem-Quintanar A (2005) Skin permeation enhancement by sucrose esters: a pH-dependent phenomenon. Int J Pharm 297:204–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.03.020
da Silva JD, Gomes MV, Cabral LM, de Sousa VP (2019) Evaluation of the in vitro release and permeation of Cordia verbenacea DC essential oil from topical dosage forms. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 53:101173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101173
Edge SB, Compton CC (2010) The american joint committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol 17:1471–1474. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
Elmowafy M, Musa A, Alnusaire TS, Shalaby K, Fouda MMA, Salama A et al (2021) Olive oil/pluronic oleogels for skin delivery of quercetin: In vitro characterization and ex vivo skin permeability. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111808
Ghosh V, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2013) Ultrasonic emulsification of food-grade nanoemulsion formulation and evaluation of its bactericidal activity. Ultrason Sonochem 20:338–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.08.010
Gokhale JP, Mahajan HS, Surana SS (2019) Quercetin loaded nanoemulsion-based gel for rheumatoid arthritis: in vivo and in vitro studies. Biomed Pharmacother 112:108622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108622
Guo B, Liu H, Li Y, Zhao J, Yang D, Wang X et al (2014) Application of phospholipid complex technique to improve the dissolution and pharmacokinetic of probucol by solvent-evaporation and co-grinding methods. Int J Pharm 474:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.08.006
Gupta V, Trivedi P (2018) In vitro and in vivo characterization of pharmaceutical topical nanocarriers containing anticancer drugs for skin cancer treatment. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813687-4.00015-3
Hardiningtyas SD, Wakabayashi R, Kitaoka M, Tahara Y, Minamihata K, Goto M et al (2018) Mechanistic investigation of transcutaneous protein delivery using solid-in-oil nanodispersion: a case study with phycocyanin. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 127:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.01.020
He R, Cui D, Gao F (2009) Preparation of fl uorescence ethosomes based on quantum dots and their skin scar penetration properties. Mater Lett 63:1662–1664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.05.003
Honeywell-nguyen PL, Frederik PM, Bomans PHH, Junginger HE, Bouwstra JA (2002) Transdermal delivery of pergolide from surfactant-based elastic and rigid vesicles: characterization and in vitro transport studies. Pharm Res 19:991–997
Horbert R, Pinchuk B, Davies P, Alessi D, Peifer C (2015) Photoactivatable prodrugs of antimelanoma agent vemurafenib. ACS Chem Biol 10:2099–2107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00174
Hubbe MA, McLean DS, Stack KR, Lu X, Strand A, Sundberg A (2020) Self-assembly of alkyl chains of fatty acids in papermaking systems: A review of related pitch issues, hydrophobic sizing, and pH Effects. BioResources 15:4591–4635. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.2.4591-4635
Hussein AA (2014) Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of mebendazole preparation and evaluation of liquid and solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of mebendazole self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of mebendazole. Iraqi J Pharm Sci 23:2014
Jain S, Patel N, Shah MK, Khatri P, Vora N (2017) Recent advances in lipid-based vesicles and particulate carriers for topical and transdermal application. J Pharm Sci 106:423–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2016.10.001
Kaur G (2019) TPGS loaded topical nanoemulgel of mefenamic acid for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ijppr 15:64–107
Kaur R, Ajitha M (2019) Transdermal delivery of fluvastatin loaded nanoemulsion gel: Preparation, characterization and in vivo anti-osteoporosis activity. Eur J Pharm Sci 136:104956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2019.104956
Khan KA (1975) The concept of dissolution efficiency. J Pharm Pharmacol 27:48–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1975.tb09378.x
Khudhur AQ, Maraie NK, Raauf AM (2020) Highlight on lipids and its use for covalent and non-covalent conjugations. Al Mustansiriyah J Pharm Sci 20
Kim H, Jung S, Yeo S, Kim D, Na YC, Yun G et al (2019) Characteristics of skin deposition of itraconazole solubilized in cream formulation. Pharmaceutics 11(4):195
Kitaoka M, Wakabayashi R, Kamiya N, Goto M (2016) Solid-in-oil nanodispersions for transdermal drug delivery systems. Biotechnol J 11:1375–1385. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201600081
Kwekha-Rashid AS, Abduljabbar HN, Alhayani B (2021) Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases analysis using machine-learning applications. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01868-7
Londhe VY, Bhasin B (2019) Transdermal lipid vesicular delivery of iloperidone: Formulation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 183:110409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110409
Lopes LB, Collett JH, Bentley MVLB (2005) Topical delivery of cyclosporin A: an in vitro study using monoolein as a penetration enhancer. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 60:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2004.12.003
Malakar J, Sen SO, Nayak AK, Sen KK (2011) Development and evaluation of microemulsions for transdermal delivery of insulin. ISRN Pharm. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/780150
Malvern (2012) Zetasizer nano basic guide 66
Maraie NK, Almajidi Q (2017) Effect of different mucoadhesive polymers on release of ondansetron HCl from intranasal mucoadhesive in situ gel. Ajps 17:76
Martins M, Azoia NG, Ribeiro A, Shimanovich U, Silva C, Cavaco-Paulo A (2013) In vitro and computational studies of transdermal perfusion of nanoformulations containing a large molecular weight protein. Colloids Surf B 108:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.02.032
Martins M, Azoia NG, Shimanovich U, Matamá T, Gomes AC, Silva C et al (2014) Design of novel BSA/hyaluronic acid nanodispersions for transdermal pharma purposes. Mol Pharm 11:1479–1488. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp400657g
Mishra VVBK, Bhanja SB, Panigrahi BB (2019) Development and evaluation of nanoemulsion gel for transdermal delivery of valdecoxib. Res J Pharm Technol 12:600–610. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00107.0
Moribe K, Shibata M, Furuishi T, Higashi K, Tomono K, Yamamoto K (2010) Effect of particle size on skin permeation and retention of piroxicam in aqueous suspension. Chem Pharm Bull 58:1096–1099. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.58.1096
Omar MM, Hasan OA, El Sisi AM (2019) Preparation and optimization of lidocaine transferosomal gel containing permeation enhancers: a promising approach for enhancement of skin permeation. Int J Nanomed 14:1551–1562. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S201356
Pharmacology C (2009) Center for Drug Evaluation and Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmaceutics Review (S). Food Drug Adm 1–5
Piao H, Kamiya N, Hirata A, Fujii T, Goto M (2008) A novel solid-in-oil nanosuspension for transdermal delivery of diclofenac sodium. Pharm Res 25:896–901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-007-9445-7
Prasanthi D, Lakshmi PK (2012) Development of ethosomes with taguchi robust design-based studies for transdermal delivery of alfuzosin hydrochloride. Int Curr Pharm J 1:370–375. https://doi.org/10.3329/icpj.v1i11.12063
Ramadon D, McCrudden MTC, Courtenay AJ, Donnelly RF (2021) Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems: current trends and applications. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-00909-6
Sato K, Sugibayashi K, Morimoto Y (1988) Effect and mode of action of aliphatic esters on the in vitro skin permeation of nicorandil. Int J Pharm 43:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(88)90055-5
Serra CHR, Chang KH, Dezani TM, Porta V, Storpirtis S (2015) Dissolution efficiency and bioequivalence study using urine data from healthy volunteers: a comparison between two tablet formulations of cephalexin. Braz J Pharm Sci 51:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-82502015000200016
Shah N et al (2013) Improved human bioavailability of vemurafenib, a practically insoluble drug, using an amorphous polymer-stabilized solid dispersion prepared by a solvent-controlled coprecipitation process. J Pharm Sci 102:967–981. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23425
Shende P, Vaidya J, Gaud RS (2018) Pharmacotherapeutic approaches for transportation of anticancer agents via skin. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:S423–S433. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1498349
Sun J, Zhai W (2012) Effect of particle size on solubility, dissolution rate , and oral bioavailability: evaluation using coenzyme Q 10 as naked nanocrystals. Int J Nanomed 5733–5744
Swetter SM, Tsao H, Bichakjian CK, Curiel-Lewandrowski C, Elder DE, Gershenwald JE et al (2019) Guidelines of care for the management of primary cutaneous melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 80:208–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.08.055
Szuts A, Pallagi E, Regdon G, Aigner Z, Szabó-Révész P (2007) Study of thermal behaviour of sugar esters. Int J Pharm 336:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.11.053
Tahara Y, Honda S, Kamiya N, Piao H, Hirata A, Hayakawa E et al (2008) A solid-in-oil nanodispersion for transcutaneous protein delivery. J Control Release 131:14–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.07.015
Tahara Y, Kaneko T, Toita R, Yoshiyama C, Kitaoka T, Niidome T et al (2012) A novel double-coating carrier produced by solid-in-oil and solid-in-water nanodispersion technology for delivery of genes and proteins into cells. J Control Release 161:713–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.05.001
Tannock IF, Rotin D (1989) Acid pH in tumors and its potential for therapeutic exploitation. Cancer Res 49:4373–4384
Todo H (2017) Transdermal permeation of drugs in various animal species. Pharmaceutics 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9030033
Viswanad V, Anju PG, Kumar GS, Nair SG (2019) Formulation development and in-vitro characterisation of ethosomes for the enhanced transdermal delivery of clotrimazole. Int J Res Pharm Sci 10:874–882. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v10i2.270
Yang Q, Liu S, Gu Y, Tang X, Wang T, Wu J (2019) Development of sulconazole-loaded nanoemulsions for enhancement of transdermal permeation and antifungal activity. Int J Nanomed 14:3955–3966. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S206657
Yutani R, Kikuchi T, Teraoka R, Kitagawa S (2014) Efficient delivery and distribution in skin of chlorogenic acid and resveratrol induced by microemulsion using sucrose laurate. Chem Pharm Bull 62:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c13-00820
Zou L, Ding W, Zhang Y, Cheng S, Li F, Ruan R et al (2018) Peptide-modified vemurafenib-loaded liposomes for targeted inhibition of melanoma via the skin. Biomaterials 182:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.013
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad/Iraq (www. uomustansiriyah. edu. iq) for supporting this work.
Funding
No funding by yourself supported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-024-03024-3
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Almajidi, Y.Q., Maraie, N.K. & Raauf, A.M.R. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Utilization of solid in oil nanodispersion to prepare a topical vemurafenib as potential delivery system for skin melanoma. Appl Nanosci 13, 2845–2856 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02158-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02158-y