Abstract
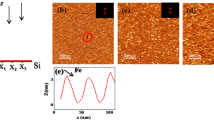
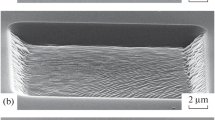
In recent years, ion-beam irradiation (IBI) has been proven an effective approach for the mass production of nanopatterns on the surfaces of wide range of materials. However, the role of different ion beam masses (Ar and Kr) needs attention for potential use of ripple patterns in wettability applications. In this work, we present a systematic study on the growth of ripple patterns for the two different projectiles of Ar+ and Kr+ and, furthermore, their anisotropic behaviour of wettability. An increase in wavelength and amplitude of ripples on Si (100) surface with increase in ion beam energy from 60 to100 keV has been observed. Wavelength of ripples is found to be higher for the Ar+ as compared to Kr+ at each irradiation energy value. A power law dependency of ripple wavelength on ion beam energy has been proposed as λ ~ Em, where ‘m’ is found to be 0.48 ± 0.0008 for Ar+ and 0.85 ± 0.06 for Kr+ beam, which shows the importance of mass re-distribution in ripples growth. Furthermore, observed variation in the contact angle is found to be deviated from Wenzel's law which is attributed to a reduction in the surface free energy of ion implanted Si ripple surfaces. Hence, the near surface damage under the incorporation of Ar/Kr atoms alters the chemical composition and which is effectively controlling the anisotropic wettability of ripples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradley RM, Harper JM (1988) Theory of ripple topography induced by ion bombardment. J Vac Sci Technol Vac Surf Films 6:2390–2395
Carter G, Vishnyakov V (1996) Roughening and ripple instabilities on ion-bombarded Si. Phys Rev B 54:17647
Castro M, Cuerno R (2012) Hydrodynamic approach to surface pattern formation by ion beams. Appl Surf Sci 258:4171–4178
Castro M, Gago R, Vázquez L, Muñoz-García J, Cuerno R (2012) Stress-induced solid flow drives surface nanopatterning of silicon by ion-beam irradiation. Phys Rev B 86:214107
Castro M, Gago R, Vázquez L, Muñoz-García J, Cuerno R (2013) Energy dependence of the ripple wavelength for ion-beam sputtering of silicon: experiments and theory. AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP, USA, pp 380–385
Chini T, Sanyal M, Bhattacharyya S (2002) Energy-dependent wavelength of the ion-induced nanoscale ripple. Phys Rev B 66:153404
Eklund EA, Bruinsma R, Rudnick J, Williams RS (1991) Submicron-scale surface roughening induced by ion bombardment. Phys Rev Lett 67:1759
Elson JM, Bennett JM (1995) Calculation of the power spectral density from surface profile data. Appl Opt 34:201–208
Erlebacher J, Aziz MJ, Chason E, Sinclair MB, Floro JA (1999) Spontaneous pattern formation on ion bombarded Si (001). Phys Rev Lett 82:2330
Erlebacher J, Aziz MJ, Chason E, Sinclair MB, Floro JA (2000) Nonlinear amplitude evolution during spontaneous patterning of ion-bombarded Si (001). J Vac Sci Technol Vac Surf Films 18:115–120
Garg S, Datta D, Ghatak J, Thakur I, Khare K, Kanjilal D et al (2016) Tunable wettability of Si through surface energy engineering by nanopatterning. RSC Adv 6:48550–48557
Habenicht S, Bolse W, Feldermann H, Geyer U, Hofsäss H, Lieb K et al (2000) Ripple topography of ion-beam–eroded graphite: a key to ion-beam–induced damage tracks. EPL 50:209
Hara S, Izumi S, Kumagai T, Sakai S (2005) Surface energy, stress and structure of well-relaxed amorphous silicon: a combination approach of ab initio and classical molecular dynamics. Surf Sci 585:17–24
Kardar M, Parisi G, Zhang Y-C (1986) Dynamic scaling of growing interfaces. Phys Rev Lett 56:889
Kumar T, Kumar M, Gupta G, Pandey RK, Verma S, Kanjilal D (2012) Role of surface composition in morphological evolution of GaAs nano-dots with low-energy ion irradiation. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:552
Kumar T, Singh U, Kumar M, Ojha S, Kanjilal D (2014) Tuning of ripple patterns and wetting dynamics of Si (100) surface using ion beam irradiation. Curr Appl Phys 14:312–317
Kumar T, Panchal V, Kumar A, Kanjilal D (2016) Nano-pits on GaAs (1 0 0) surface: preferential sputtering and diffusion. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 379:52–56
Lopez-Cazalilla A, Ilinov A, Bukonte L, Nordlund K, Djurabekova F, Norris S et al (2018a) Simulation of redistributive and erosive effects in a-Si under Ar+ irradiation. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 414:133–140
Lopez-Cazalilla A, Chowdhury D, Ilinov A, Mondal S, Barman P, Bhattacharyya S et al (2018b) Pattern formation on ion-irradiated Si surface at energies where sputtering is negligible. J Appl Phys 123:235108
Lopez-Cazalilla A, Djurabekova F, Ilinov A, Fridlund C, Nordlund K (2020) Direct observation of ion-induced self-organization and ripple propagation processes in atomistic simulations. Mater Res Lett 8:110–116
Madi CS, Anzenberg E, Ludwig KF Jr, Aziz MJ (2011) Mass redistribution causes the structural richness of ion-irradiated surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 106:066101
Makeev MA, Barabási A-L (1997) Ion-induced effective surface diffusion in ion sputtering. Appl Phys Lett 71:2800–2802
Makeev MA, Cuerno R, Barabasi A-L (2002) Morphology of ion-sputtered surfaces. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 197:185–227
Möller W, Eckstein W (1984) Tridyn—a TRIM simulation code including dynamic composition changes. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect B 2:814–818
Munoz-Garcia J, Vazquez L, Castro M, Gago R, Redondo-Cubero A, Moreno-Barrado A et al (2014) Self-organized nanopatterning of silicon surfaces by ion beam sputtering. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 86:1–44
Nordlund K (1995) Molecular dynamics simulation of ion ranges in the 1–100 keV energy range. Comput Mater Sci 3:448–456
Norris SA, Samela J, Bukonte L, Backman M, Djurabekova F, Nordlund K et al (2011) Molecular dynamics of single-particle impacts predicts phase diagrams for large scale pattern formation. Nat Commun 2:276
Park S, Kahng B, Jeong H, Barabási A-L (1999) Dynamics of ripple formation in sputter erosion: nonlinear phenomena. Phys Rev Lett 83:3486
Prinz GA (1999) Magnetoelectronics applications. J Magn Magn Mater 200:57–68
Rusponi S, Costantini G, Boragno C, Valbusa U (1998) Ripple wave vector rotation in anisotropic crystal sputtering. Phys Rev Lett 81:2735
Stamp G, Ong Y, Kumar R, Zhou C (2006) DECADA: tool for discrete-event control and diagnosis analysis. In: 2006 8th International Workshop on Discrete Event Systems: IEEE, p 396–397.
Wenzel RN (1936) Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind Eng Chem 28:988–994
Yadav R, Kumar T, Baranwal V, Kumar VM, Priya P et al (2017) Fractal characterization and wettability of ion treated silicon surfaces. J Appl Phys 121:055301
Young T (1805) III. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Phil Trans R Soc London 95:65–87
Zdyb A, Olchowik J, Mucha M (2006) Dependence of GaAs and Si surface energy on the misorientation angle of crystal planes. Mater Sci-Pol 24:1109–1114
Ziberi B, Frost F, Höche T, Rauschenbach B (2005) Ripple pattern formation on silicon surfaces by low-energy ion-beam erosion: experiment and theory. Phys Rev B 72:235310
Acknowledgements
The help received from Dr. Indra Sulania, IUAC, New Delhi for AFM characterization is gratefully acknowledged here. We are also thankful to Dr. D. Kanjilal, IUAC, New Delhi, for helping in experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors’ have no conflict of interest with other work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vandana, Kumar, T., Ojha, S. et al. Energy-dependent surface nanopatterning of Si (100) for different projectiles: a tunable anisotropic wettability of ripple surface. Appl Nanosci 13, 3189–3196 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01975-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01975-5