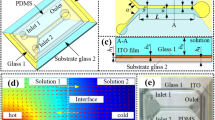
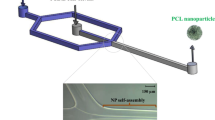
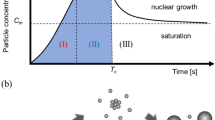
Abstract
Noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) have potential for use in many optical and electronic applications due to their shape- and size-dependent properties. However, it remains a significant challenge to synthesize size- and shape-controlled NPs on a large scale while maintaining their unique properties. We have demonstrated a simple and effective microreactor based on a microfluidic chip and liquid peristaltic pump for the synthesis of monodispersed Au NPs. This reactor allows for the continuous high-flux synthesis of Au NPs with precisely controlled sizes. The effects of reaction temperature, reaction time, flow ratio of the two inlets, and amount of surfactant agent are investigated in this study. The uniform and ultrafine Au NPs were synthesized by directly controlling the temperature, flow rate, surfactant concentration, and flow rate ratio. Moreover, the Au NPs are fabricated controllably, continuously, and stably on a large scale with this system. The proposed system thus contributes to the large-scale industrial production of NPs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boutonnet M, Kizling J, Stenius P et al (1982) The preparation of monodisperse colloidal metal particles from microemulsions. Colloids Surf 5(3):209–225
Cabeza VS, Kuhn S, Kulkarni AA et al (2012) Size-controlled flow synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a segmented flow microfluidic platform. Langmuir 28(17):7007
Chou KS, Chang YC, Chiu LH (2012) Studies on the continuous precipitation of silver nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(13):4905–4910
Cobley CM, Chen J, Cho EC et al (2011) Gold nanostructures: a class of multifunctional materials for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 42(15):44–56
Demello AJ (2006) Control and detection of chemical reactions in microfluidic systems. Nature 442(7101):394–402
Dreaden EC, Alkilany AM, Huang X et al (2012) The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2740–2779
Gauvin M, Wan Y, Arfaoui I, Pileni MP (2014) Mechanical properties of Au supracrystals tuned by flexible ligand interactions. J Phys Chem C 118(9):5005
Gijs MAM, Lacharme F, Lehmann U (2010) Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem Rev 110(3):1518–1563
Gutierrez L, Gomez L, Irusta S et al (2011) Comparative study of the synthesis of silica nanoparticles in micromixer–microreactor and batch reactor systems. Chem Eng J 171(2):674–683
Hemling M, Crooks JA, Oliver PM et al (2014) Microfluidics for high school chemistry students. J Chem Educ 91(1):112
Huang J, Lin L, Li Q et al (2008) Continuous-Flow Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Lixivium of Sundried Cinnamomum camphora Leaf in Tubular Microreactors. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(16):6081–6090
Khan AK, Rashid R, Murtaza G et al (2014) Gold nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in drug delivery. Trop J Pharm Res 13(7):1169–1177
Kück A, Steinfeldt M, Prenzel K, et al (2011) Green nanoparticle production using micro reactor technology, p 2074
Kumar DVR, Kasture M, Prabhune AA et al (2010) Continuous flow synthesis of functionalized silver nanoparticles using bifunctional biosurfactants. Green Chem 12(4):609–615
Kurup GK, Basu AS (2012) Field-free particle focusing in microfluidic plugs. Biomicrofluidics 6(2):22008
Lazarus LL, Riche CT, Marin BC et al (2012) Two-phase microfluidic droplet flows of ionic liquids for the synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(6):3077–3083
Li YF, Chen C (2011) Fate and toxicity of metallic and metal-containing nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Small 7(21):2965–2980
Li J, Wang X, Wang C et al (2007) The enhancement effect of gold nanoparticles in drug delivery and as biomarkers of drug-resistant cancer cells. ChemMedChem 2(3):374–378
Lin XZ, And ADT, Yang H (2004) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in a continuous flow tubular microreactor. Nano Lett 4(11):2227–2232
Liu H, Huang J, Zhang H et al (2017) Plant-mediated synthesis in a microfluidic chip yields spherical Ag nanoparticles and PSD simulation by a PBE-assisted strategy. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 92:2546–2553
Lohse SE, Eller JR, Sivapalan ST et al (2013) A simple microfluidic benchtop reactor system for the high-throughput synthesis and functionalization of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and shapes. ACS Nano 7(5):4135
Melancon MP, Elliott AM, Shetty A et al (2011) Near-infrared light modulated photothermal effect increases vascular perfusion and enhances polymeric drug delivery. J Control Release 156(2):265–272
Niu G, Zhang L, Ruditskiy A et al (2018) A Droplet-reactor system capable of automation for the continuous and scalable production of noble-metal nanocrystals. Nano Lett 18:3879–3884
Patil GA, Bari ML, Bhanvase BA et al (2012) Continuous synthesis of functional silver nanoparticles using microreactor: effect of surfactant and process parameters. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 62(9):69–77
Ren F, Bhana S, Norman DD et al (2013) Gold nanorods carrying paclitaxel for photothermal-chemotherapy of cancer. Bioconjug Chem 24(3):376–386
Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P et al (2009) Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir 25(24):13840–13851
Sau TK, Pal A, Jana NR et al (2001) Size controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles using photochemically prepared seed particles. J Nanopart Res 3(4):257–261
Schaeffer N, Wan Y, Pileni MP (2014) Hierarchy in Au nanocrystal ordering in supracrystals: III. Competition between van der Waals and Dynamic Processes. Langmuir 30(24):7177
Sheng TH, Yu LL, Maeda H (2008) Controlled synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles in capillary micro-flow reactor. J Nanopart Res 10(1):209–215
Song H, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF (2010) A microfluidic system for controlling reaction networks in time. Angew Chem Int Ed 115(7):792–796
Taylor GI (1960) Deposition of a viscous fluid on the wall of a tube. J Fluid Mech 10(2):161–165
Tu ST, Yu X, Luan W et al (2010) Development of micro chemical, biological and thermal systems in China: a review. Chem Eng J 163(3):165–179
Wang J, Zhao H, Zhu Y et al (2017) Shape controlled synthesis of CdSe nanocrystals via a programmed microfluidic process. J Phys Chem C 121(6):3567–3572
Xiao Z, Ji C, Shi J et al (2012) DNA self-assembly of targeted near-infrared-responsive gold nanoparticles for cancer thermo-chemotherapy. Angew Chem Int Ed 51(47):11853–11857
Xu Z, Lu C, Riordon J et al (2016) Microfluidic manufacturing of polymeric nanoparticles: comparing flow control of multiscale structure in single-phase staggered herringbone and two-phase reactors. Langmuir 32(48):12781
Yagi M, Sato T (2003) Temperature-controlled charge transfer mechanism in a polymer film incorporating a redox molecule as studied by potential-step chronocouloabsorptometry. J Phys Chem B. 107(21):4975–4981
Yang RJ, Hou HH, Wang YN et al (2016a) Micro-magnetofluidics in microfluidic systems: a review. Sens Actuators B Chem 224:1–15
Yang L, Nieves-Remacha MJ, Jensen KF (2016b) Simulations and analysis of multiphase transport and reaction in segmented flow microreactors. Chem Eng Sci 169:106–116
Zhang Z, Wang L, Wang J et al (2012) Mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorods as a light-mediated multifunctional theranostic platform for cancer treatment. Adv Mater 24(11):1418–1423
Zhang L, Wang Y, Tong L et al (2013) Seed-mediated synthesis of silver nanocrystals with controlled sizes and shapes in droplet microreactors separated by air. Langmuir 29(50):15719–15725
Zhao Y, Su Y, Chen G et al (2017) Effect of surface properties on the flow characteristics and mass transfer performance in microchannels. Chem Eng Sci 65(5):1563–1570
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51771170, 51871196), Yunnan Applied Basic Research Project (2018FB090, 2017FB080), and the fund of the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies for Comprehensive Utilization of Platinum Metals (SKL-SPM-2018013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ma, S., Li, A. et al. Continuous high-flux synthesis of gold nanoparticles with controllable sizes: a simple microfluidic system. Appl Nanosci 10, 661–669 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01214-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01214-y