Abstract
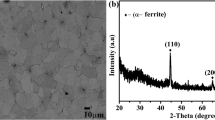
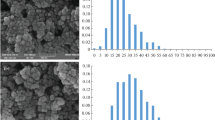
In complimenting a scarcity in the literature, an attempt on contrasting normalized electro-galvanization techniques is being pursued here. The alleged superior plated-overlay performance in association with pulse plating was verified opposite conventional direct-current plating in two types of acid baths contrasting in micro-throwing power under which chloride- and sulfate-based baths, epitomized the superior and inferior throwing power baths, respectively. It is granted that galvanizations stemming from chloride-bath plating reigned superior overall, as far as favorable performance is concerned, relative to their sulfate-based counter parts. However, nanocrystalline zinc deposit refinement, coherence and coverage were rendered more pronounced in attribution to shorter bursts of high amplitude pulsing. The nanocrystalline zinc canvas, nonetheless, seemed to retreat before a surge of incoherent micro-scale formations (dendritic, in case of chloride and flaky, in case of sulfate baths) with onset of prolonged pulsing ahead of ultimately succumbing to near extinction with DC-plating deployment. That being established, a noticeable tendency towards cracking and eventual spallation did emerge as a unique attribute of sulfate bath in response to embarking on longer pulsing intervals (namely, by a threshold of 0.1 ms). The evolution in nanostructure translated into a deteriorating corrosion performance that marked the progression towards extended pulsing times on the approach to DC-realms after potentiodynamic polarization testing.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shater A (2010) Intergranular corrosion of sensitized 20Cr-25Ni-Nb stainless steel nuclear fuel cladding materials. University of Manchester, Manchester, p 130
Al-Shater A, Engelberg D, Lyon S, Donohoe C, Walters S, Whillock G, Sherry A (2017) Characterization of the stress corrosion cracking behavior of thermally sensitized 20Cr-25Ni stainless steel in a simulated cooling pond environment. J Nucl Sci Technol 54:742–751
Angel K, Tsang HH, Bedair SS, Smith GL, Lazarus N (2018) Selective electroplating of 3D printed parts. Addit Manuf 20: 164–172
Cao R, Chang JH, Zhu HX, Mao GJ, Xu QW, Shi Y, Chen JH, Wang P-C (2018) Investigation of wire selection for CMT plug joining Mg AZ31-to-galvanized steel. J Manuf Process 32:65–76
Chandrasekar MS, Pushpavanam M (2008) Pulse and pulse reverse plating—conceptual, advantages and applications. Electrochim Acta 53(8): 3313–3322
Chandrasekar MS, Shanmugasigamani, Pushpavanam M (2010) Synergetic effects of pulse constraints and additives in electrodeposition of nanocrystalline zinc: corrosion, structural and textural characterization. Mater Chem Phys 124:516–528
Chang L, Zhou C-Y, Li J, He X-H (2018) Investigation on tensile properties of nanocrystalline titanium with ultra-small grain size. Comput Mater Sci 142: 135–144
Ciubotariu AC, Istrate GG (2016) Corrosion rate of steels DX51D and S220GD in different corrosion environment. Mircea cel Batran” Naval Acad Sci Bull 19(1):166–172
Dela Pena EM, Roy S (2018) Electrodeposited copper using direct and pulse currents from electrolytes containing low concentration of additives. Surf Coat Technol.339:101–110
Detor AJ, Schuh CA (January 2007) Tailoring and patterning the grain size of nanocrystalline alloys. Acta Mater 55(1):371–379
Esfahani M, Munir KS, Wen C, Zhang J, Durandet Y, Wang J, Wong YC (2018) Mechanical properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline and ultrafine-grained Zn-Sn coatings. Surf Coat Technol 333: 71–80
Fang JT, Estates PV (2018) Method and system of controlling alloy composition during electroplating. United States Patent, US 9,867,293 B1, 9 Jan 2018
Jantaping N, Schuh CA, Boonyongmaneerat Y (2017) Influences of crystallographic texture and nanostructural features on corrosion properties of electrogalvanized and chromate conversion coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 329:120–130
Kim H, Kim JG, Park JW, Chu CN (2018) Selective copper metallization of nonconductive materials using jet-circulating electrodeposition. Precis Eng 51:153–159
Kumar KS, Van Swygenhoven H, Suresh S (2003) Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys. Acta Mater 51:5743–5774
Li Q, Lu H, Cui J, An M, Li D (2016) Electrodeposition of nanocrystalline zinc on steel for enhanced resistance to corrosive wear. Surf Coat Technol 304:567–573
Li Q, Lu H, Cui J, An M, Li DY (2018) Elevate the corrosion potential of Zn coatings using ceramic nanoparticles. J Solid State Electrochem 22:1–7
Lu L, Shen Y, Chen X, Qian L, Lu K (2004) Ultrahigh strength and high electrical conductivity in copper. Science 304(5669): 422–426
Mosavat SH, Shariat MH, Bahrololoom ME (2012) Study of corrosion performance of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Zn–Ni alloy coatings. Corros Sci 59:81–87
Mouanga M, Ricq L, Douglade J, Berçot P (2009) Corrosion behaviour of zinc deposits obtained under pulse current electrodeposition: effects of coumarin as additive. Corros Sci 51:690–698
Paatsch W (1986) Pulsed electrodeposition of zinc and cadmium. In: Theory and practice of pulse plating. American Electroplaters and Surface Finishers Society (AESF), Orlando, Florida FI, pp 93–100
Pangarov NA (1962) The crystal orientation of electrodeposited metals. Electrochim Acta 7(1):139–146
Ramanauskas R (1999) Structural factor in Zn alloy electrodeposit corrosion. Appl Surf Sci 153:53–64
Ramanauskas R, Gudaviciute L, Juskenas R, Scit O (2007) “Structural and corrosion characterization of pulse plated nanocrystalline zinc coatings. Electrochim Acta 53:1801–1810
Rehrig DI, Leidheiser H Jr, Notis MR (1977) The influence of the current waveform on the morphology of pulse electrodeposited gold. Plating Surf Finish 64:40
Rossi B, Marquart S, Rossi G (2017) Comparative life cycle cost assessment of painted and hot-dip galvanized bridges. J Environ Manag 197:41–49
Saber K, Koch CC, Fedkiw PS (2003) Pulse current electrodeposition of nanocrystalline zinc. Mater Sci Eng A341:174–181
Schiøtz J, Jacobsen KW (2003) A maximum in the strength of nanocrystalline copper. Science 301(5638):1357–1359
Su Z, Tan L, Tao J, Zhang C, Yang R, Wen F (2018) Enhanced microwave absorption properties of FeNi nanocrystals decorating reduced graphene oxide. Physica Status Solidi B. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201700553
Sugiura N, Yonemura S, Maruyama N (2018) Cold rolled steel sheet, electrogalvanized cold-rolled steel sheet, hot-dip galvanized cold-rolled steel sheet, alloyed hot-dip galvanized cold rolled steel sheet, and manufacturing methods of the same. United States Patent, US 9, 879, 336 B2, 30 Jan 2018
Wang Y, Chen M, Zhou F, Ma E (2002) High tensile ductility in a nanostructured metal. Nature 419(6910):912–915
Wang B-W, Lee C-Y, Lee H-B (2018) The influences of monoethanolamine additive on the properties of nickel coating electroplated in post supercritical carbon dioxide mixed Watts bath. Surf Coat Technol 337:232–240
Xu W, Dávila LP (2017) Size dependence of elastic mechanical properties of nanocrystalline aluminum. Mater Sci Eng A 692:90–94
Ying T, Xingcai Z, Hong-Zhang G, Hai-Jie Y, Chungang L, Shi-Xun D, Xiushan L, Jie W, Song-Lin J (2017) Carbon nanotube/polyurethane films with high transparency, low sheet resistance and strong adhesion for antistatic application. R Soc Chem Adv 83(7):53018–53024
Youssef KM (2003) Synthesis, structure, and properties of nanocrystalline zinc by pulsed-current electrodeposition. North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Youssef KM, Koch CC, Fedkiw PS (2004b) Improved corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline zinc produced by pulse-current electrodeposition. Corros Sci 46:51–64
Youssef KM, Koch CC, Fedkiw PS (2008) Influence of pulse plating parameters on the synthesis and preferred orientation of nanocrystalline zinc from zinc sulfate electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 54:677–683
Youssef KM, Koch CC, Fedkiw PS (2014a) Influence of additives and pulse electrodeposition parameters on production of nanocrystalline zinc from zinc chloride electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 151(2):C103-C111
Acknowledgements
The investigation put forth was undertaken utilizing funds awarded by the university of Bahrain deanship of scientific research [UoB-DSR] under Grant No. [2013/13]. The authors would, expressly, wish to extend their gratitude for the efforts exerted by King Fahd University for Petroleum and Minerals through the center of excellence in nanotechnology, spearheaded by Dr. Zain H. Yamani, Dr. Abbas S. Hakeem and Mr. Omar W. Saadi in facilitating the investigative needs of the collaborative work at hand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshater, A.F., Hakeem, A.S., Saadi, O.W. et al. A correlative study amongst overlay nanostructure and emanating corrosion behavior of pulse-electroplated nanocrystalline zinc on carbon steel. Appl Nanosci 9, 289–304 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00982-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00982-x