Abstract
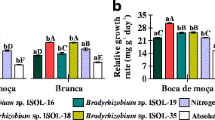
Lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) is an important legume species that establishes symbiosis with rhizobia, mainly of the Bradyrhizobium genus. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficiency of rhizobia of the genus Bradyrhizobium in symbiosis with lima bean, in both Leonard jars and in pots with a Latossolo Amarelo distrófico (Oxisol). In the experiment in Leonard jars, 17 strains isolated from nodules of the three legume subfamilies, Papilionoideae (Vigna unguiculata, Pterocarpus sp., Macroptilium atropurpureum, Swartzia sp., and Glycine max), Mimosoideae (Inga sp.), and Caesalpinioideae (Campsiandra surinamensis) and two uninoculated controls, one with a low concentration (5.25 mg L−1) and another with a high concentration (52.5 mg L−1) of mineral nitrogen (N) were evaluated. The six strains that exhibited the highest efficiency in Leonard jars, isolated from nodules of Vigna unguiculata (UFLA 03–144, UFLA 03–84, and UFLA 03–150), Campsiandra surinamensis (INPA 104A), Inga sp. (INPA 54B), and Swartzia sp. (INPA 86A), were compared to two uninoculated controls, one without and another with 300 mg N dm−3 (NH4NO3) applied to pots with samples of an Oxisol in the presence and absence of liming. In this experiment, liming did not affect nodulation and plant growth; the INPA 54B and INPA 86A strains stood out in terms of shoot dry matter production and provided increases of approximately 48% in shoot N accumulation compared to the native rhizobia populations. Our study is the first to indicate Bradyrhizobium strains isolated from the three legume subfamilies are able to promote lima bean growth via biological nitrogen fixation in soil conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes JEL, Gomes RLF, Lopes ÂCA, Araújo ASF, Carmo M, Lyra CP, Figueiredo MVB (2011) Symbiotic efficiency of rhizobia isolated from nodules of lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.). R Bras Ci Solo 35:751–757. doi:10.1590/S0100-06832011000300011
Boiero L, Perrig D, Masciarelli O, Penna C, Cassán F, Luna V (2007) Phytohormone production by three strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and possible physiological and technological implications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:874–880. doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0731-9
Bonilla I, Bolaños L (2009) Mineral nutrition for legume-rhizobia symbiosis: B, Ca, N, P, S, K, Fe, Mo, Co, and Ni: a review. Sustain Agric Rev 1:253–274. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9654-9_13
Costa Neto VP, Mendes JBS, Araújo ASF, Alcântara Neto F, Bonifacio A, Rodrigues AC (2017) Symbiotic performance, nitrogen flux and growth of lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) varieties inoculated with different indigenous strains of rhizobia. Symbiosis (in press)
Costa EM, Nóbrega RSA, Ferreira LVM, Amaral FHC, Nóbrega JCA, Silva AFT, Moreira FMS (2014) Growth and yield of the cowpea cultivar BRS Guariba inoculated with rhizobia strains in Southwest Piauí. Semin Cienc Agrar 35:3073–3084. doi:10.5433/1679-0359.2014v35n6p3073
Ferreira DF (2011) Sisvar: a computer statistical analysis system. Cienc Agrotec 35:1039–1042. doi:10.1590/S1413-70542011000600001
Ferreira PAA, Bomfeti CA, Soares BL, Moreira FMS (2012) Efficient nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium strains isolated from amazonian soils are highly tolerant to acidity and aluminium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1947–1959. doi:10.1007/s11274-011-0997-7
Ferreira LVM, Nóbrega RSA, Nóbrega JCA, Aguiar FL, Moreira FMS, Pacheco LP (2013) Biological nitrogen fixation in production of Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp, family farming in Piauí, Brazil. J Agr Sci 5:153–160. doi:10.5539/jas.v5n4p153
Florentino LA, Guimarães AP, Rufini M, Silva K, Moreira FMS (2009) Sesbania virgata Stimulates the occurrence of its microsymbiont in soils but does not inhibit microsymbionts of other species. Sci Agric 66:667–676. doi:10.1590/S0103-90162009000500012
Fofana B, Baudoin JP, Vekemans X, Debouck DG, Du Jardin P (1999) Molecular evidence for an Andean origin and a secondary gene pool for the lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) using chloroplast DNA. Theor Appl Gen 98:202–212. doi:10.1007/s001220051059
Fred EB, Waksman SA (1928) Laboratory manual of general microbiology: with special reference to the microorganisms of the soil. McGraw-Hill, New York
Fritschi FB, Ray JD (2007) Soybean leaf nitrogen, chlorophyll content, and chlorophyll a/b ratio. Photosynthetica 45:92–98. doi:10.1007/s11099-007-0014-4
Guimarães AA, Jaramillo PMD, Nóbrega RSA, Florentino LA, Silva KB, Moreira FMS (2012) Genetic and symbiotic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria isolated from agricultural soils in the western Amazon by using cowpea as the trap plant. Appl Environ Microb 78:6726–6733. doi:10.1128/AEM.01303-12
Guimarães AA, Florentino LA, Almeida KA, Lebbe L, Silva KB, Willems A, Moreira FMS (2015) High diversity of Bradyrhizobium strains isolated from several legume species and land uses in Brazilian tropical ecosystems. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:433–441. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2015.06.006
Hartwig UA (1998) The regulation of symbiotic N2 fixation: a conceptual model of N feedback from the ecosystem to the gene expression level. Perspect Plant Ecol 1:92–120. doi:10.1078/1433-8319-00054
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Agric Exp Stn (Circular, n.347). Univ. of California, Berkeley, California
Jaramillo PMD, Guimarães AA, Florentino LA, Silva KB, Nóbrega RSA, Moreira FMS (2013) Symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacterial populations trapped from soils under agroforestry systems. Sci Agric 70:397–404. doi:10.1590/S0103-90162013000600004
Lima AS, Nóbrega RSA, Barberi A, Silva K, Ferreira DF, Moreira FMS (2009) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria communities occurring in soils under different uses in the western Amazon region as indicated by nodulation of siratro (Macroptilium atropurpureum). Plant Soil 319:127–145. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9855-2
Lodeiro AR, Lagares A, Martínez EN, Favelukes G (1995) Early interactions of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli and bean roots: specificity in the process of adsorption and its requirement of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1571–1579
López-López A, Negrete-Yankelevich S, Rogel MA, Ormeño-Orrillo E, Martínez J, Martínez-Romero E (2013) Native bradyrhizobia from Los Tuxtlas in Mexico are symbionts of Phaseolus lunatus (lima bean). Syst Appl Microbiol 36:33–38. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2012.10.006
Maquet A, Vekemans XZ, Baudoin JP (1999) Phylogenetic study on wild allies of lima bean, Phaseolus lunatus L. (Fabaceae) and implications on its origin. Plant Syst Evol 218:43–54. doi:10.1007/BF01087033
Marra LM, Oliveira SM, Soares CRF, Moreira FMS (2011) Solubilisation of inorganic phosphates by inoculant strains from tropical legumes. Sci Agric 68:603–609. doi:10.1590/S0103-90162011000500015
Matsubara M, Zúñiga-Dávila D (2015) Phenotypic and molecular differences among rhizobia that nodulate Phaseolus lunatus in the Supe valley in Peru. Ann Microbiol 65:1803–1808. doi:10.1007/s13213-015-1054-9
Moreira FMS, Gillis M, Pot B, Kersters K, Franco AA (1993) Characterization of rhizobia isolated from different divergence groups of tropical Leguminosae by comparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of their total proteins. Syst Appl Microbiol 16:135–146. doi:10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80258-4
Moreira FMS, Haukka K, Young JPW (1998) Biodiverity of rhizobia isolated from a wide range of forest legumes in Brazil. Mol Ecol 7:889–895. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294x.1998.00411.x
Moreira FMS, Carvalho TS, Siqueira JO (2010) Effect of fertilizers, lime and inoculation with rhizobia and mycorrhizal fungi on the growth of four leguminous tree species in a low-fertility soil. Biol Fertil Soils 46:771–779. doi:10.1007/s00374-010-0477-5
Norris DO (1958) Rhizobium needs magnesium, not calcium. Nature 182:734–735. doi:10.1038/182734a0
Oliveira-Longatti SM, Marra LM, Moreira FMS (2014) Bacteria isolated from soils of the western Amazon and from rehabilitated bauxite-mining areas have potential as plant growth promoters. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:1239–1250. doi:10.1007/s11274-013-1547-2
Ormeno-Orrillo E, Vinuesa P, Zúñiga-Davila D, Martinez-Romero E (2006) Molecular diversity of native bradyrhizobia isolated from (Phaseolus lunatus L.) in Peru. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:253–262. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2005.09.002
Remans R, Ramaekers L, Schelkens S, Hernandez G, Garcia A, Reyes JL, Mendez N, Toscano V, Mulling M, Galvez L, Vanderleyden J (2008) Effect of Rhizobium-Azospirillum coinoculation on nitrogen fixation and yield of two contrasting Phaseolus vulgaris L. genotypes cultivated across different environments in Cuba. Plant Soil 312:25–37. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9606-4
Ribeiro PRA, Santos JV, Costa EM, Lebbe L, Assis ES, Louzada MO, Guimarães AA, Willems A, Moreira FMS (2015) Symbiotic efficiency and genetic diversity of soybean bradyrhizobia in Brazilian soils. Agric Ecosyst Environ 212:85–93. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2015.06.017
Rufini M, Ferreira PAA, Soares BL, Oliveira DP, Andrade MJB, Moreira FMS (2011) Symbiosis of nitrogen fixing bacteria with common bean in different pH values. Pesq Agrop Brasileira 46:81–88. doi:10.1590/S0100-204X2011000100011
Rufini M, Silva MAP, Ferreira PAA, Cassetari AS, Soares BL, Andrade MJB, Moreira FMS (2013) Symbiotic efficiency and identification of rhizobia that nodulate cowpea in a Rhodic Eutrudox. Biol Fertil Soils 50:115–122. doi:10.1007/s00374-013-0832-4
Rufini M, Oliveira DP, Trochmann A, Soares BL, Andrade MJB, Moreira FMS (2014) Bradyrhizobium strains in symbiosis with dwarf pigeon pea under greenhouse and field conditions. Pesq Agrop Brasileira 49:197–206. doi:10.1590/S0100-204X2014000300006
Singleton PW, Tavares JW (1986) Inoculation response of legumes in relation to the number and effectiveness of indigenous rhizobium populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1013–1018
Soares ALL, Ferreira PAA, Pereira JPAR, Vale HMM, Lima AS, Andrade MJB, Moreira FMS (2006) Agronomic efficiency of selected rhizobia strains and diversity of native nodulating populations in Perdões (MG - Brazil). II – beans. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 30:795–802. doi:10.1590/S0100-06832006000500006
Soares BL, Ferreira PAA, Oliveira-Longatti SM, Marra LM, Rufini M, Andrade MJB, Moreira FMS (2014) Cowpea symbiotic efficiency, pH and aluminum tolerance in nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Sci Agric 71:17–180. doi:10.1590/S0103-90162014000300001
Thies JE, Bohlool BB, Singleton PW (1991) Subgroups of the cowpea miscellany: symbiotic specificity within Bradyrhizobium spp. for Vigna unguiculata, Phaseolus lunatus, Arachis hypogaea, and Macroptilium atropurpureum. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1540–1545
Acknowledgements
We thank the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel [Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)] and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development [Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq)] for financial support and for granting scholarships. We also thank the Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Maranhão [Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia do Maranhão (IFMA)] for granting soil for the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins da Costa, E., de Almeida Ribeiro, P.R., de Lima, W. et al. Lima bean nodulates efficiently with Bradyrhizobium strains isolated from diverse legume species. Symbiosis 73, 125–133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-017-0473-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-017-0473-8