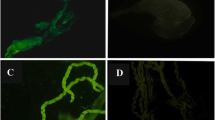
Abstract
Issues, like emerging insecticide resistance in Anopheles mosquitoes, have led to a breakdown in many vector control programs. In this study, a recombinant Escherichia coli with plasmid expressing a green fluorescent protein (E.coli-GFP) was used as a paratransgenesis model to determine: the possibility of E. coli-GFP trans-stadial transmission. The effect of the water microflora, of bacteria-impregnated sugar solutions, and of blood-feeding on E. coli-GFP colonization and localization within An. stephensi tissues, were studied. The results demonstrated the persistence of E. coli-GFP during molting and metamorphosis events and its trans-stadial transmission. Also the efficacy of bacteria-impregnated sugar solutions for transferring the bacteria to the adult mosquito’s midgut was shown. A blood meal dramatically increased the number of bacteria within 24–48 h post feeding. In addition to fluorescence microscope evaluation, GFP gene PCR amplification showed the presence of the bacteria in the midgut of larvae, pupae, and adults up to 13 days after eclosion. Massive colonization of bacteria was observed in the larvae and in the adult mosquito’s malpighian tubules which may play a role in retaining bacteria in adult mosquitos. The results of this study showed that E. coli could be used as a laboratory model in paratransgenesis studies for the evaluation of various effector molecules as anti-parasite agents for malaria and filariasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy S, Weiss B, Attardo G (2008) Paratransgenesis applied for control of tsetse transmitted sleeping sickness. Adv Exp Med Biol 627:35–48. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-78225-6_3
Andreadis TG (2005) Evolutionary strategies and adaptations for survival between mosquito-parasitic microsporidia and their intermediate copepod hosts: a comparative examination of Amblyospora connecticus and Hyalinocysta chapmani (Microsporidia: Amblyosporidae). Folia parasitologica 52(1–2):23–35
Apte-Deshpande A, Paingankar M, Gokhale MD, Deobagkar DN (2012) Serratia odorifera a midgut inhabitant of Aedes aegypti mosquito enhances its susceptibility to dengue-2 virus. PLoS One 7(7):e40401
Azari-Hamidian S, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Javadian E, Abai MR, Mobedi I, Linton YM, Harbach RE (2009) Distribution and ecology of mosquitoes in a focus of dirofilariasis in northwestern Iran, with the first finding of filarial larvae in naturally infected local mosquitoes. Med Vet Entomol 23(2):111–121. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2915.2009.00802.x
Beard CB, Cordon-Rosales C, Durvasula RV (2002) Bacterial symbionts of the triatominae and their potential use in control of Chagas disease transmission. Annu Rev Entomol 47:123–141. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145144
Benedict M (2007) Methods in Anopheles research. Malaria Research and Reference Reagent Resource Center, Atlanta
Bisi DC, Lampe DJ (2011) Secretion of anti-Plasmodium effector proteins from a natural Pantoea agglomerans isolate by using PelB and HlyA secretion signals. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(13):4669–4675
Boissière A, Tchioffo MT, Bachar D, Abate L, Marie A, Nsango SE, Shahbazkia HR, Awono-Ambene PH, Levashina EA, Christen R (2012) Midgut microbiota of the malaria mosquito vector Anopheles gambiae and interactions with Plasmodium falciparum infection. PLoS Pathogens 8(5):e1002742
Breman JG, Egan A, Keusch GT (2001) The intolerable burden of malaria: a new look at the numbers. AmJTrop Med Hyg 64(1–2 Suppl):iv–vii
Brengues C, Hawkes NJ, Chandre F, McCarroll L, Duchon S, Guillet P, Manguin S, Morgan JC, Hemingway J (2003) Pyrethroid and DDT cross-resistance in Aedes aegypti is correlated with novel mutations in the voltage-gated sodium channel gene. Med Vet Entomol 17(1):87–94
Chandre F, Darrier F, Manga L, Akogbeto M, Faye O, Mouchet J, Guillet P (1999a) Status of pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles gambiae sensu lato. Bull World Health Organ 77(3):230–234
Chandre F, Manguin S, Brengues C, Dossou Yovo J, Darriet F, Diabate A, Carnevale P, Guillet P (1999b) Current distribution of a pyrethroid resistance gene (kdr) in Anopheles gambiae complex from west Africa and further evidence for reproductive isolation of the Mopti form. Parassitologia 41(1–3):319–322
Chapelle F (2001) Ground-Water Microbiology and Geochemistry, John Wily & Sons
Chavshin AR, Oshaghi MA, Vatandoost H, Pourmand MR, Raeisi A, Enayati AA, Mardani N, Ghoorchian S (2012) Identification of bacterial microflora in the midgut of the larvae and adult of wild caught Anopheles stephensi: a step toward finding suitable paratransgenesis candidates. Acta Trop 121(2):129–134
Coutinho-Abreu IV, Zhu KY, Ramalho-Ortigao M (2010) Transgenesis and paratransgenesis to control insect-borne diseases: current status and future challenges. Parasitol Int 59(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2009.10.002
Damiani C, Ricci I, Crotti E, Rossi P, Rizzi A, Scuppa P, Capone A, Ulissi U, Epis S, Genchi M, Sagnon N, Faye I, Kang A, Chouaia B, Whitehorn C, Moussa GW, Mandrioli M, Esposito F, Sacchi L, Bandi C, Daffonchio D, Favia G (2010) Mosquito-bacteria symbiosis: the case of Anopheles gambiae and Asaia. Microb Ecol 60(3):644–654. doi:10.1007/s00248-010-9704-8
Enayati AA, Vatandoost H, Ladonni H, Townson H, Hemingway J (2003) Molecular evidence for a kdr-like pyrethroid resistance mechanism in the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles stephensi. Med Vet Entomol 17(2):138–144
Fang W, Vega-Rodríguez J, Ghosh AK, Jacobs-Lorena M, Kang A, St. Leger RJ (2011) Development of transgenic fungi that kill human malaria parasites in mosquitoes. Science 331(6020):1074–1077. doi:10.1126/science.1199115
Favia G, Ricci I, Damiani C, Raddadi N, Crotti E, Marzorati M, Rizzi A, Urso R, Brusetti L, Borin S (2007) Bacteria of the genus Asaia stably associate with Anopheles stephensi, an Asian malarial mosquito vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(21):9047–9051
Favia G, Ricci I, Marzorati M, Negri I, Alma A, Sacchi L, Bandi C, Daffonchio D (2008) Bacteria of the genus Asaia: a potential paratransgenic weapon against malaria. Adv Exp Med Biol 627:49–59. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-78225-6_4
Gautam NK, Tapadia MG (2010) Ecdysone signaling is required for proper organization and fluid secretion of stellate cells in the Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster. Int J Dev Biol 54(4):635–642. doi:10.1387/ijdb.092910ng
Gonzalez-Ceron L, Santillan F, Rodriguez MH, Mendez D, Hernandez-Avila JE (2003) Bacteria in midguts of field-collected Anopheles albimanus block Plasmodium vivax sporogonic development. J Med Entomol 40(3):371–374
Hill CA, Kafatos FC, Stansfield SK, Collins FH (2005) Arthropod-borne diseases: vector control in the genomics era. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(3):262–268. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1101
Howard AF, Koenraadt CJ, Farenhorst M, Knols BG, Takken W (2010) Pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles gambiae leads to increased susceptibility to the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana. Malar J 9:168. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-9-168
Hunt R, Edwardes M, Coetzee M (2010) Pyrethroid resistance in southern African Anopheles funestus extends to Likoma Island in Lake Malawi. Parasit Vectors 3:122. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-3-122
Kan SP, Rajah KV, Dissanaike AS (1977) Survey of dirofilariasis among dogs in seremban, Malaysia. Vet Parasitol 3(2):177–181
Li J, McLellan S, Ogawa S (2006) Accumulation and fate of green fluorescent labeled Escherichia coli in laboratory-scale drinking water biofilters. Water Res 40(16):3023–3028
Lindh J, Borg-Karlson A, Faye I (2008) Transstadial and horizontal transfer of bacteria within a colony of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae) and oviposition response to bacteria-containing water. Acta Trop 107:242–250
Lindh JM, Terenius O, Eriksson-Gonzales K, Knols BG, Faye I (2006) Re-introducing bacteria in mosquitoes–a method for determination of mosquito feeding preferences based on coloured sugar solutions. Acta Trop 99(2–3):173–183. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2006.07.008
Lindh JM, Terenius O, Faye I (2005) 16S rRNA gene-based identification of midgut bacteria from field-caught Anopheles gambiae sensu lato and A. funestus mosquitoes reveals new species related to known insect symbionts. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7217–7223. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.11.7217-7223.2005
Lundström JO, Andersson AC, Bäckman S, Schäfer ML, Forsman M, Thelaus J (2011) Transstadial transmission of Francisella tularensis holarctica in mosquitoes, Sweden. Emerg Infect Dis 17(5):794
Magesa SM, Aina O, Curtis CF (1994) Detection of pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles mosquitos. Bull World Health Organ 72(5):737–740
McJunkin JE, de los Reyes EC, Irazuzta JE, Caceres MJ, Khan RR, Minnich LL, Fu KD, Lovett GD, Tsai T, Thompson A (2001) La Crosse encephalitis in children. New England. Journal of Medicine 344(11):801–807
Moll RM, Romoser WS, Modrzakowski MC, Moncayo AC, Lerdthusnee K (2001) Meconial peritrophic membranes and the fate of midgut bacteria during mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) metamorphosis. J Med Entomol 38(1):29–32
Munhenga G, Masendu HT, Brooke BD, Hunt RH, Koekemoer LK (2008) Pyrethroid resistance in the major malaria vector Anopheles arabiensis from Gwave, a malaria-endemic area in Zimbabwe. Malar J 7:247. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-7-247
Muro A, Genchi C, Cordero M, Simón F (1999) Human dirofilariasis in the European union. Parasitology Today 15(9):386–389
Oshaghi MA, Yaaghoobi F, Abaie MR (2006) Pattern of mitochondrial DNA variation between and within Anopheles stephensi (Diptera: Culicidae) biological forms suggests extensive gene flow. Acta Trop 99(2–3):226–233
Pidiyar VJ, Jangid K, Patole MS, Shouche YS (2004) Studies on cultured and uncultured microbiota of wild culex quinquefasciatus mosquito midgut based on 16 s ribosomal RNA gene analysis. AmJTrop Med Hyg 70(6):597–603
Pumpuni CB, Demaio J, Kent M, Davis JR, Beier JC (1996) Bacterial population dynamics in three anopheline species: the impact on Plasmodium sporogonic development. AmJTrop Med Hyg 54(2):214–218
Rani A, Sharma A, Rajagopal R, Adak T, Bhatnagar R (2009) Bacterial diversity analysis of larvae and adult midgut microflora using culture-dependent and culture-independent methods in lab-reared and field-collected Anopheles stephensi-an Asian malarial vector. BMC Microbiol 9(1):96
Ranson H, N’Guessan R, Lines J, Moiroux N, Nkuni Z, Corbel V (2011) Pyrethroid resistance in African anopheline mosquitoes: what are the implications for malaria control? Trends Parasitol 27(2):91–98. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2010.08.004
Reese SM, Petersen JM, Sheldon SW, Dolan MC, Dietrich G, Piesman J, Eisen RJ (2011) Transmission efficiency of Francisella tularensis by adult american dog ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Journal of medical entomology 48(4):884–890
Ren X, Hoiczyk E, Rasgon JL (2008) Viral paratransgenesis in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. PLoS Pathog 4(8):e1000135. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000135
Riehle MA, Jacobs-Lorena M (2005) Using bacteria to express and display anti-parasite molecules in mosquitoes: current and future strategies. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 35(7):699–707. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2005.02.008
Riehle MA, Moreira CK, Lampe D, Lauzon C, Jacobs-Lorena M (2007) Using bacteria to express and display anti-Plasmodium molecules in the mosquito midgut. Int J Parasitol 37(6):595–603. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.12.002
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, vol 1. CSHL press
Sarrazin S, Mossadegh-Keller N, Fukao T, Aziz A, Mourcin F, Vanhille L, Kelly Modis L, Kastner P, Chan S, Duprez E, Otto C, Sieweke MH (2009) MafB restricts M-CSF-dependent myeloid commitment divisions of hematopoietic stem cells. Cell 138(2):300–313
Singh SR, Hou SX (2009) Multipotent stem cells in the Malpighian tubules of adult Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol 212(Pt 3):413–423. doi:10.1242/jeb.024216
Straif SC, Mbogo CN, Toure AM, Walker ED, Kaufman M, Toure YT, Beier JC (1998) Midgut bacteria in Anopheles gambiae and An. funestus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Kenya and Mali. J Med Entomol 35(3):222–226
Terenius O, de Oliveira CD, Pinheiro WD, Tadei WP, James AA, Marinotti O (2008) 16S rRNA gene sequences from bacteria associated with adult Anopheles darlingi (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes. J Med Entomol 45(1):172–175
Theis JH (2005) Public health aspects of dirofilariasis in the United States. Vet Parasitol 133:157–180
Turell MJ, Saluzzo JF, Tammariello RF, Smith JF (1990) Generation and transmission of Rift Valley fever viral reassortants by the mosquito Culex pipiens. J Gen Virol 71(10):2307–2312
Vatandoost H, Mashayekhi M, Abaie MR, Aflatoonian MR, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Sharifi I (2005) Monitoring of insecticides resistance in main malaria vectors in a malarious area of Kahnooj district, Kerman province, southeastern Iran. J Vector Borne Dis 42(3):100–108
Vatandoost H, Oshaghi MA, Abaie MR, Shahi M, Yaaghoobi F, Baghaii M, Hanafi-Bojd AA, Zamani G, Townson H (2006) Bionomics of Anopheles stephensi Liston in the malarious area of Hormozgan province, southern Iran, 2002. Acta Trop 97(2):196–203. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.11.002
Wang S, Fang W, Vega-Rodriguez J, Ghosh A, Leger RS, Jacobs-Lorena M (2011a) Fighting Malaria with engineered fungi and bacteria. In: Molecular and population biology of disease vectors, Orthodox Academy of Crete Kolymbari, Greece
Wang Y, Gilbreath TM 3rd, Kukutla P, Yan G, Xu J (2011b) Dynamic gut microbiome across life history of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae in Kenya. PLoS One 6(9):e24767. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024767
Wang S, Ghosh AK, Bongio N, Stebbings KA, Lampe DJ, Jacobs-Lorena M (2012) Fighting malaria with engineered symbiotic bacteria from vector mosquitoes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
WHO (2010) World malaria report 2010. World Health Organization.
Acknowledgment
Authors would like to thank Eng. Abaei, MR. and Eng. Rafie, F. for their assistance in An. stephensi rearing. This study was financially supported by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS). The authors also thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and Professor David Richardson for assistance with editing and improving the English.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
ARC did the experiments, analyzed the results and wrote the draft of manuscript, MAO and HV designed the study and coordinated the team works, BY and FZ assist the bacterial experiments and AR reviewed the manuscript and finalized the study design.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavshin, A.R., Oshaghi, M.A., Vatandoost, H. et al. Escherichia coli expressing a green fluorescent protein (GFP) in Anopheles stephensi: a preliminary model for paratransgenesis. Symbiosis 60, 17–24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-013-0231-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-013-0231-5