Abstract
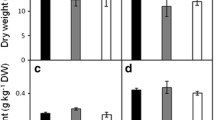
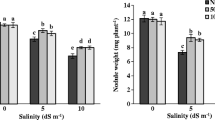
In this study, the effect of 100 mM NaCl on physiological and biochemical responses were investigated in nodules of two Medicago ciliaris lines differing in salt tolerance (TNC 1.8 and TNC 11.9). Results showed that, on the basis of growth and nitrogen fixation, the line TNC 1.8 proved more salt tolerant than TNC 11.9. The salt-induced oxidative stress (membrane lipid peroxidation, leghemoglobin degradation, antioxidant activities reduction) occurred similarly in nodules of both lines. The tolerant line TNC 1.8 showed a better capacity to preserve higher sucrolytic activities and maintained higher nodule malate concentration, although total organic acids decreased in both lines. The higher amount of organic acids in the tolerant line seems to be related to its capacity to maintain higher NH4 nodule concentration in comparison with the sensitive line. Although salt stress reduced concentrations of the majority of amino acid in both lines, the decrease of the most preponderant amino acids glycine, valine, aspartate and glutamate was more accentuated in the sensitive line TNC 11.9. However, alanine concentration increased in the nodules of this sensitive line, suggesting a higher incidence of stress-induced hypoxia. The present study provides further evidence that salt tolerance of nitrogen fixation in the tolerant line is linked to a more effective supply of malate to bacteroids which allows the synthesis of amino acids required to maintain both plant and nodule growth.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla MH, El-Enamy AE, Hamada AM, Abdel Wahab AM (2001) Element distribution in faba bean nodules under salinity and its effects on growth, nodulation and nitrogen fixation. Rostlinná Výroba 47:399–404
Appels MA, Haaker H (1991) Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase in pea root nodules 1 Participation in a malate/aspartate shuttle between plant and bacteroid. Plant Physiol 95:740–747
Arrese-Igor C, Gonzalez EM, Gordon AJ, Minchin FR, Galvez L, Royuela M, Cabrerizo PM, Aparicio-Tejo PM (1999) Sucrose synthase and nodule nitrogen fixation under drought and other environmental stresses. Symbiosis 27:189–212
Ashraf M, Bashir A (2003) Salt induced changes in some organic metabolites and ionic relations in nodules and other parts of two crop plants differing in salt tolerance. Flora 198:486–498
Baier MC, Barsch A, Küster H, Hohnjec N (2007) Antisense repression of the Medicago truncatula nodule-enhanced sucrose synthase leads to a handicapped nitrogen fixation mirrored by specific alterations in the symbiotic transcriptome and metabolome. Plant Physiol 145:1600–1618
Balibrea ME, Cayuela E, Artés F, Pérez-Alfocea F (1997) Salinity effects on some post-harvest quality factors in a commercial tomato hybrid. J Hortic Sci 72:885–892
Balibrea ME, Cuartero J, Bolarín MC, Pérez-Alfocea F (2003) Sucrolytic activities during fruit development of Lycopersicon genotypes differing in tolerance to salinity. Physiol Plant 118:38–46
Ben Salah I, Albacete A, Martínez Andújar C, Haouala R, Labidi N, Zribi F, Martinez V, Pérez-Alfocea F, Abdelly C (2009) Response of nitrogen fixation in relation to nodule carbohydrate metabolism in Medicago ciliaris lines subjected to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 166:477–488
Bianco C, Defez R (2009) Medicago truncatula improves salt tolerance when nodulated by an indole-3-acetic acid-overproducing Sinorhizobium meliloti strain. J Exp Bot 60:3097–3107
Borucki W, Sujkowska M (2008) The effects of sodium chloride-salinity upon growth, nodulation, and root nodule structure of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants. Acta Physiol Plant 30:293–301
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of proteins utilising the principal of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chinnusamy V, Jagendorf A, Zhu JK (2005) Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. Crop Sci 45:437–448
Dennison KL, Spalding EP (2000) Glutamate-gated calcium fluxes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:1511–1514
Dubos C, Huggins D, Grant GH, Knight MR, Campbell MM (2003) A role for glycine in the gating of plant NMDA-like receptors. Plant J 35:800–810
El-Hamdaoui A, Redondo-Nieto M, Torralba B, Rivella R, Bonilla I, Bolaños L (2003) Influence of boron and calcium on the tolerance to salinity of nitrogen fixing pea plants. Plant Soil 251:93–103
Fan TW-M, Higashi RM, Frenkiel TA, Lane AN (1997) Anaerobic nitrate and ammonium in flood-tolerant rice coleoptiles. J Exp Bot 48:1655–1666
Fougère F, Le Rudulier D, Streeter JG (1991) Effects of salt Stress on amino acid, organic acid, and carbohydrate composition of roots, bacteroids, and cytosol of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Physiol 96:1228–1236
Fries N (1953) Limiting factors in the growth of the pea seedling root. Physiol Plant 6:292–300
Gálvez S, Hirsh AM, Wycoff KL, Hunt S, Layzell DB, Kondorosi A, Crespi M (2000) Oxygen regulation of a nodule-located carbonic anhydrase in alfalfa. Plant Physiol 124:1059–1068
Garg N, Manchanda G (2008) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation on salt-induced nodule senescence in Cajanus cajan (pigeonpea). J Plant Growth Regul 27:115–124
Godel H, Seitz P, Verhoef M (1987) Automated analysis using combined OPA and FMOC-CI precolumn derivatization. LC-LG International 5:44–49
Gordon AJ, Minchin FR, James CL, Komina O (1999) Sucrose synthase in legume nodules is essential for nitrogen fixation. Plant Physiol 120:867–877
Hardy WFR, Holsten R, Jackson E, Burns E (1968) The acetylene ethylene assay for nitrogen fixation: lab and field assay for nitrogen evaluation. Plant Physiol 43:1185–1207
Hoffman NE, Bent AF, Hanson AD (1986) Induction of lactate dehydrogenase isozymes by oxygen deficit in barley root tissue. Plant Physiol 82:658–663
Jamet A, Sigaud S, Van de Sype G, Puppo A, Herouart D (2003) Expression of the bacterial catalase genes during Sinorhizobium meliloti-Medicago sativa symbiosis and their crucial role during the infection process. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:217–225
Jebara S, Jebara M, Limam F, Aouani ME (2005) Changes in ascorbate peroxidase, catalase, guaiacol peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) nodules under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 162:929–936
Kjeldahl JZ (1983) New methode zyr Besimming des stickstoffs in organischen Körpen. J Anal Chem 22:366–382
Lodwig E, Poole P (2003) Metabolism of Rhizobium bacteroids. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:37–78
López M, Herrera-Cervera JA, Iribarne C, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2008) Growth and nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus and Medicago truncatula under NaCl stress: nodule carbon metabolism. J Plant Physiol 165:641–650
Mengel K, Kirkby EA (2001) Plant nutrients. In: Dordrecht (ed.). Principles of plant nutrition, pp 1–14
Minchin FR, Witty JF (2005) Respiratory/carbon costs of symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legumes. In: Lambers H, Ribas-Carbo M (ed.) Plant respiration, pp 195–205
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Noctor G, Arisi AC, Jouanin L, Valadier MH, Roux Y, Foyer CH (1997) The role of glycine in determining the rate of glutathione synthesis in poplar. Possible implications for glutathione production during stress. Physiol Plant 100:255–263
O’Hara GW (2001) Nutritional constraints on root nodule bacteria affecting symbiotic nitrogen fixation: a review. Aust J Exp Agr 41:417–433
Oliva SR, Raitio H, Mingorance MD (2003) Comparison of two wet digestion procedures for multielement analysis of plant samples. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 34:2913–2923
Pelleschi S, Rocher JP, Prioul JL (1997) Effect of water restriction on carbohydrate metabolism and photosynthesis in mature maize leaves. Plant Cell Environ 20:493–503
Pladys D, Dimitrijevic L, Rigaud J (1991) Localization of a protease in protoplast preparations in infected cells of French bean nodules. Plant Physiol 97:1174–1180
Puppo A, Halliwell B (1988) Generation of hydroxyl radicals by soybean nodule leghemoglobin. Planta 173:405–410
Ramos MLG, Gordon AJ, Minchin FR, Sprint JI, Parsons R (1999) Effect of water stress on nodule physiology and biochemistry of a drought tolerant cultivar of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Ann Bot 83:57–63
Reggiani R, Cantu CA, Brambilla I, Bertani A (1988) Accumulation and interconversion of amino acids in rice roots under anoxia. Plant Cell Physiol 29:982–987
Reggiani R, Nebuloni M, Mattana M, Brambilla I (2000) Anaerobic accumulation of amino acids in rice roots: role of the glutamine synthetase/glutamate synthase cycle. Amino Acids 18:207–217
Ringli C, Keller B, Ryser U (2001) Glycine-rich proteins as structural components of plant cell walls. Mol Life Sci 58:1430–1441
Sakano K, Tazawa M (1984) Intracellular distribution of free amino acids between the vacuolar and extravacuolar compartments in internodal cells of Chara australis. Plant Cell Physiol 25:1477–1486
Sakano K, Tazawa M (1985) Metabolic conversion of amino acids loaded in the vacuole of Chara australis intemodal cells. Plant Physiol 78:673–677
Scebba F, Sebastiani L, Vitagliano C (1999) Protective enzymes against activated oxygen species in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings: responses to cold acclimation. J Plant Physiol 55:762–768
Serraj R, Fleurat-Lessard P, Jaillard B, Drevon JJ (1995) Structural changes in the inner-cortex cells of soybean root nodules are induced by short-term exposure to high salt or oxygen concentrations. Plant Cell Environ 18:455–462
Skinner JC, Street HE (1953) Studies on the growth of excised roots. II. Observations on the growth of excised groundsel roots. New Phytologist 53:44–67
Soussi M, Lluch C, Ocaña A (1999) Comparative study of nitrogen fixation and carbon metabolism in two chick-pea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars under salt stress. J Exp Bot 50:1701–1708
Srinivas ND, Rshami KR, Raghavarao KSMS (1999) Extraction and purification of a plant peroxidase by aqueous two-phase extraction coupled with gel filtration. Process Biochem 35:43–48
Streeter JG, Thompson JF (1972) Anaerobic accumulation of g-aminobutyric acid and alanine in radish leaves (Raphanus sativus L.). Plant Physiol 49:572–578
Trinchant JC, Rigaud J (1996) Bacteroid oxalate oxidase and soluble oxalate in nodules of faba beans (Vicia faba L.) submitted to water restricted conditions: possible involvement in nitrogen fixation. J Exp Bot 47:1865–1870
Tyerman SD, Whitehead LF, Day DA (1995) A channel-like transport for NH +4 on the symbiotic interface of N2-fixing plants. Nature 387:629–632
Vance CP, Gantt JS (1992) Control of nitrogen and carbon metabolism in root nodules. Physiol Plant 85:266–274
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Weatherburn MW (1979) Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39:971–974
White PR (1939) Glycine in the nutrition of excised tomato roots. Plant Physiol 14:527–538
Wilson DO, Reisenauer HM (1963) Determination of leghemoglobin in legume nodules. Anal Biochem 6:27–30
Zadeh HM, Naeini MB (2007) Effects of salinity stress on the morphology and yield of two cultivars of canola (Brassica napus L.). J Agr 6:409–414
Zilli CG, Balestrasse KB, Yannarelli GG, Polizio AH, Santa-Cruz DM, Tomaro ML (2008) Heme oxygenase up-regulation under salt stress protects nitrogen metabolism in nodules of soybean plants. Env Exp Bot 64:83–89
Zribi K, Badri Y, Saidi S, van Berkum P, Aouani ME (2007) Medicago ciliaris growing in Tunisian soils is preferentially nodulated by Sinorhizobium medicae. Aust J Soil Res 45:473–477
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology (LR10CBBC02) and by the Fundación Séneca (Communidad Autónoma de Murcia, Spain, project 08712/PI/08). We wish to thank the Laboratory of Legumes (LL) in the Center of Biotechnologies at the technopole of Borj Cedria in Tunis for the generous gift of Sinorhizobium medicae CI 1.12/E22 strain and M. ciliaris seeds. Grateful thanks are due to anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and for thorough editorial remarks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Salah, I., Slatni, T., Albacete, A. et al. Salt tolerance of nitrogen fixation in Medicago ciliaris is related to nodule sucrose metabolism performance rather than antioxidant system. Symbiosis 51, 187–195 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-010-0073-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-010-0073-3