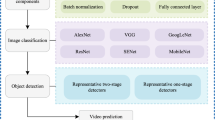
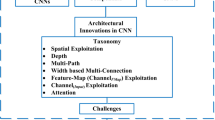
Abstract
This paper aims to improve the accuracy and efficiency of image aesthetic classification in environmental art design and provide a more professional and convenient method. Based on the Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) and Convolution Neural Network (CNN) Deep Learning (DL) algorithm, the current situation and shortcomings of the existing image aesthetic classification are analyzed. Thereupon, the MEC technology is combined with CNN, and the MEC-based Image Recognition (IR) architecture and parallel Deep CNN-based aesthetic evaluation method are proposed. Then, the environmental art design images are analyzed and classified using the proposed method. Experiments are designed to verify the performance of the proposed methods. The results show that the average Response Time (RT) of different images recognition under the mobile cellular network and WiFi network is more than 2000 ms and less than 1000 ms, respectively. Comparison of the transmission speeds given different images indicates that the IR RT under the proposed MEC Hierarchical Discriminant Analysis (MECHDA) architecture is faster than the other three: the MECHDA architecture occupies a smaller bandwidth, with a constant 1kB image transmission traffic. Additionally, the aesthetic classification accuracy of the proposed model in A large-scale database for aesthetic visual analysis data set has reached 85.3%. In the data set of the CUHK Photo Quality Dataset (CUNK-PQ), the accuracy of aesthetic classification has reached 93%. The environmental art design pre-analysis and beauty collection classification method proposed enables the computer to help humans make more accurate image aesthetic analysis and classification. It improves the efficiency and accuracy of image aesthetic classification and provides a reference for research in related fields.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bozhko J, Teryokhina J, Lapunova K et al (2020) The production technology of the ceramic brick soft molding based on opoka-like rocks. Mater Sci Forum 1011:79–84
Carballal A, Cedron F, Santos I et al (2021) Minimal neural network topology optimization for aesthetic classification. Neural Comput Appl 33(10):1–13
Chandra B (2019) Robust heartbeat detection from multimodal data via CNN-based generalizable information fusion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 66(3):710–717
Chen M, Liu W, Wang T et al (2021) Edge intelligence computing for mobile augmented reality with the deep reinforcement learning approach. Computer Networks 195:108186
Ditria EM, Jinks EL, Connolly RM (2021) Automating the analysis of fish grazing behavior from videos using image classification and optical flow. Anim Behav 177(3–4):31–37
Fu Y, Yang X, Yang P et al (2021) Energy-efficient offloading and resource allocation for mobile edge computing enabled mission-critical internet-of-things systems. EURASIP J Wirel Commun Netw 2021(1):1–16
Gan J, Jiang K, Tan H et al (2020) Facial beauty prediction based on lighted deep convolution neural network with feature extraction strengthened. Chin J Electron 29(2):312–321
Guo G, Wang H, Yang Y et al (2020) Large margin deep embedding for aesthetic image classification. Sci China (Inf Sci) 63(01):229–231
He L, Ma J, Mo R et al (2019) Designated verifier proxy blind signature scheme for unmanned aerial vehicle network based on mobile edge computing. Secur Commun Netw 2019(3–4):1–12
Jin X, Wu L, Li X et al (2019) ILGNet: inception modules with connected local and global features for efficient image aesthetic quality classification using domain adaptation. IET Comput Vision 13(2):206–212
Kim Y, Ahn H, Park S et al (2021) Performance evaluation of the effect of traffic decentralization with mobile edge computing. ICT Express 7(2):191–195
Klinger M, Bandi V, Giannasi S et al (2021) Gynecomastia: ultrasound-confirmed classification pertainent to surgical correction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(4):1397–1403
Lenne OD, Vandenbosch L, Smits T et al (2021) Framing real beauty: a framing approach to the effects of beauty advertisements on body image and advertising effectiveness. Body Image 37(5–6):255–268
Mukherjee A, Dey N, De D (2020) EdgeDrone: QoS aware MQTT middleware for mobile edge computing in opportunistic internet of drone things. Comput Commun 152:93–108
Passricha V, Aggarwal RK (2019) PSO-based optimized CNN for Hindi ASR. Int J Speech Technol 22(4):1123–1133
Petrov A, Pernot JP, Giannini F et al (2020) Understanding the relationships between aesthetic properties and geometric quantities of free-form surfaces using machine learning techniques. Int J Interact Des Manufact (IJIDeM) 14:451–465
Shan N, Cui X, Gao Z (2020) “DRL + FL”: An intelligent resource allocation model based on deep reinforcement learning for mobile edge computing—ScienceDirect. Comput Commun 160:14–24
Sherber N, Green JB, Chiu A et al (2020) 15885 The beauty image assessment study: perspectives of US millennials, generation X, and baby boomers on esthetic treatments. J Am Acad Dermatol 83(6):AB49
Su Y, Chou C, Chu Y et al (2019) A finger-worn device for exploring chinese printed text with using CNN algorithm on a micro IoT processor. IEEE Access 99:1–1
Tang P, Liang Q, Yan X et al (2020) GP-CNN-DTEL: global-part CNN model with data-transformed ensemble learning for skin lesion classification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 99:1–1
Wang Z (2020) Multi-attention-based cross-domain beauty product image retrieval. Sci China (Inf Sci) 63(02):95–97
Wang G, Zuluaga MA, Li W et al (2019) DeepIGeoS: a deep interactive geodesic framework for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(7):1559–1572
Xie N, Li X, Li K et al (2019) Statistical karyotype analysis using CNN, and geometric optimization. IEEE Access 99:1–1
Zhai Y, Cao H, Deng W et al (2019) BeautyNet: joint multiscale CNN and transfer learning method for unconstrained facial beauty prediction. Comput Intell Neurosci 2019:1–14
Zhang X, Gao X, Lu W et al (2019) A gated peripheral-foveal convolutional neural network for unified image aesthetic prediction. IEEE Trans Multimed 21(11):2815–2826
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Ko, Y.C. Application of mobile edge computing combined with convolutional neural network deep learning in image analysis. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 13 (Suppl 3), 1186–1195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01583-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01583-0