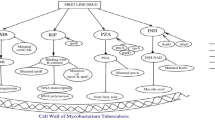
Abstract
The Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis occurs due to resistivity towards First-Line Drugs involved in Tuberculosis treatment. In present recorded data Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis is increasing in Tuberculosis patients as the diagnosis of resistivity of drugs is delaying than usual. This result also increases the resistivity towards Second-Line Drugs which results in Extensively-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis. This high-level Tuberculosis infection can be controlled by studying the molecular mechanism pathways involved in drugs involved in Tuberculosis treatment. The pathways in resistivity and susceptibility of drugs depend on the mutation of the responsible genes, which can be better studied using mathematical modeling. In this paper, a Discrete Driven System Petri net is being used to analyze the structural and behavioral properties of the modeled pathways. Petri net modeling can provide beneficiary results like Liveness, Boundedness, Safeness, and many more which other mathematical modeling tools lagged off. This type of modeling help to find the target to develop an early prediction method and also helps in new drug designing considering the mutation behavior of certain genes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afreen R, Tyagi S, Singh GP, Singh M (2021) Challenges and perspectives of polyhydroxyalkanoate production from microalgae/cyanobacteria and bacteria as microbial factories: an assessment of hybrid biological system. Front Bioeng Biotech 9:109
Brauer W, Reisig W (2009) Carl adam petri and “petri nets”. Fund Concepts Comp Sci 3(5):129–139
Dholakia YN, Shah DP (2013) Clinical profile and treatment outcomes of drug-resistant tuberculosis before directly observed treatment strategy plus: lessons for the program. Lung India: Official Organ Indian Chest Soc 30(4):316
Eckleder A, Freytag T (2008) WoPeD 2.0 goes BPEL 2.0. AWPN 380:75–80
Gupta, S., Kumawat, S., & Singh, G.P. (2019). Fuzzy Petri Net Representation of Fuzzy Production Propositions of a Rule-Based System. In: International Conference on Advances in Computing and Data Sciences. Springer, Singapore, pp. 197–210
Gupta S, Singh GP, Kumawat S (2019b) Petri Net recommender system to model metabolic pathway of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Int Knowl Syst Sci (IJKSS) 10(2):42–59
Heiner, M., Herajy, M., Liu, F., Rohr, C., & Schwarick, M. (2012, June). Snoopy—a unifying Petri net tool. In: International Conference on Application and Theory of Petri Nets and Concurrency (pp. 398–407). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Ibargüen-Mondragón E, Romero-Leiton JP, Esteva L, Burbano-Rosero EM (2016) Mathematical modeling of bacterial resistance to antibiotics by mutations and plasmids. J Biol Syst 24(01):129–146
Jensen K, Rozenberg G (eds) (2012) High-level Petri nets: theory and application. Springer
Kansal, S., Acharya, M., & Singh, G. P. (2010). Boolean Petri nets. In: Petri Nets-Manufacturing and Computer Science. IntechOpen.
Kansal S, Singh GP, Acharya M (2010b) On Petri nets generating all the binary n-vectors. Sci Math Japon 71(2):209–216
Murata T (1989) Petri nets: Properties, analysis, and applications. Proc IEEE 77(4):541–580
Olszak J, Radom M, Formanowicz P (2018) Some aspects of modeling and analysis of complex biological systems using time Petri nets. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Tech Sci 66(1):67–78
Peterson JL (1977) Petri Nets. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 9(3):223–252
Rivers EC, Mancera RL (2008) New anti-tuberculosis drugs in clinical trials with novel mechanisms of action. Drug Discovery Today 13(23–24):1090–1098
Rovetto, C., Cano, E., Ojo, K., Tuon, M., & Montes, H. (2018, September). Coloured petri net model for remote monitoring of cardiovascular dysfunction. In: Memorias de Congresos UTP, pp. 405–411.
Singh, G. P. (2016). Applications of Petri nets in electrical, electronics and optimizations. In: International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques (ICEEOT) IEEE, pp. 2180–2184.
Singh, G. P., & Gupta, A. (2019, March). A Petri net analysis to study the effects of diabetes on cardiovascular diseases. In: 2019 6th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom) . IEEE, pp. 481–488
Singh GP, Jha M, & Singh M (2021) Applications of Petri Net Modeling in Diverse Areas. In: Mathematical Modeling, Computational Intelligence Techniques and Renewable Energy: Proceedings of the First International Conference, MMCITRE 2020 Springer Nature, p. 437
Singh GP, Jha M, Singh M, Naina (2020) Modeling the mechanism pathways of first line drug in Tuberculosis using Petri nets. Int J Syst Assurance Eng Managet 11(2):1–12
Singh GP, Jha M, & Singh M (2020) Petri net Modeling of Clinical Diagnosis path in Tuberculosis. In: Proceedings of Springer in Asset Analytics—Performance and Safety Management. (Accepted). (b)
Singh GP, Kansal S, & Acharya M (2013) Construction of a crisp Boolean Petri net from a 1-safe Petri net. Int J Comp Appl 73(17):1–4
Singh GP, Kansal S (2016) Basic results on crisp boolean petri nets. modern mathematical methods and high-performance computing in science and technology. Springer, Singapore, pp 83–88
Singh GP, Kansal S, Acharya M (2013b) Embedding an arbitrary 1-safe petri net into a boolean petri net. Int J Comp Appl 70(6):7–9
Singh GP, Singh SK (2019) Petri net recommender system for generating of perfect binary tree. Int J Knowl Syst Sci (IJKSS) 10(2):1–12
Singh GP, Singh SK, Jha M (2019) Existence of forbidden digraphs for crisp boolean petri nets. Int J Math Eng Manage Sci 5:83–95. https://doi.org/10.33889/IJMEMS.2020.5.1.008
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST)-Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) project (Id: File No- ECR/2017/003480/PMS) and Department of Biotechnology, Ministtry of Science & Technology, Govt. of India (Project id BT/PR40251/BITS/137/11/2021) for funding to carriedout this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All three authors contributed equally to the conception and writing of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, M., Singh, M. & Singh, G.P. Modeling of second-line drug behavior in the treatment of tuberculosis using Petri net. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 13 (Suppl 2), 810–819 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01320-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01320-7