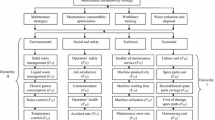
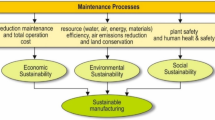
Abstract
Diverse maintenance performance models have been previously proposed in literature. However, many of these frameworks perform inefficiently or are not applicable in real-world problems due to their over-simplified assumptions. Such models do not take into account peculiarities of the maintenance situation in which multiple factors need to be prioritised under uncertain conditions. Keeping the above issues in mind, this communication proposes a framework for ranking maintenance performance systems using integrated fuzzy entropy weighting method, grey relational analysis (GRA) and weighted aggregate sum product assessment (WASPAS). The values of criteria weights were determined using fuzz entropy weighting method. Ranking was carried out using GRA and WASPAS methods. GRA ranking considered a criterion, while WASPAS method considered multi-criteria. It is the belief of the authors that merging these three mentioned tools generates synergy. The synergic advantage of the fusion is that these tools interact to create the combined results of ability to handle logic decisions, or partial information and choice among complex alternatives, demonstrated in this paper. The built-up frame-work was illustrated with practical data from five manufacturing companies operating in Nigeria with information gathered through the questionnaire approach to show that the approach can be effectively implemented in practice. Based on the proposed framework’s results, the highest ranked maintenance system belongs to companies 4 and 5, while the lowest ranked maintenance system belongs to company 5. TOPSIS method was used to determine the best performing maintenance function of the companies. It was observed that maintenance system of company 4 was the highest ranked system. The results from model testing confirmed that the presented scheme is feasibility in industrial settings, efficient and capable of revealing the best company in performance according to certain six input criteria. The novelty of this approach is its uniqueness of the combined frameworks’ structures in achieving the highest accuracy of estimation, introduced for the first time in maintenance performance assessment in a multi-criteria framework.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afkhama L, Abdia F, Komijanb AR (2012) Evaluation of service quality by using fuzzy MCDM: a case study in Iranian health-care centre. Manag Sci Lett 2:291–300
Alsyouf I (2006) Measuring maintenance performance using a balanced scorecard approach. J Qual Maint Eng 12(2):133–149
Arts RHPM, Knapp GM, Mann L Jr (1998) Some aspects of measuring maintenance performance in the process industry. J Qual Maint Eng 4(1):6–11
Azadeh A, Gaeini Z, Moradi B (2014a) Optimisation of HSE in maintenance activities by integration of continuous improvement cycle and fuzzy multivariate approach: a gas refinery. J Loss Prev Process Ind 32:415–427
Azadeh A, Madine M, Haghighi SM, Rad EM (2014b) Continuous performance assessment and improvement of integrated HSE and maintenance systems by multivariate analysis in gas transmission units. J Loss Prev Process Ind 27:32–41
Bashiri M, Badri H, Hejazi TH (2011) Selecting optimum maintenance strategy based on fuzzy interactive linear assignment method. Appl Math Model 42(1):152–164
Chakraborty S, Zavadskas EK (2014) Application of WASPAS method in manufacturing decision making. Informatica 25(1):1–20
Chen SH, Hsieh CH (2000) Representation, ranking, distance, and similarity of L-R type fuzzy number and application. Aust J Int Inf Process Syst 6(4):217–229
Chopu-inwai R, Diaotrakun R, Thaiupathump T (2013) Key indicators for maintenance performance measurement: The aircraft galley and associated equipment manufacturer case study. In: 2013 10th International conference Service systems and service management (ICSSSM), 17–19 July, pp 844–849
De Groote P (1995) Maintenance performance analysis: a practical approach. J Qual Maint Eng 1(2):4–24
Duran C (2011) Computer-aided maintenance management systems selection based on fuzzy AHP approach. Adv Eng Softw 42(10):821–829
Ertugrul D, Karakasoglu N (2009) Performance evaluation of Turkish cement firms with fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and TOPSIS methods. Expert Syst Appl 36(1):702–715
Famurewa SM, Parida A, Kumar U (2015a) Application of maintenance performance measurement for continuous improvement in railway infrastructure management. Int J COMADEM 18(1):49–58
Famurewa SM, Asplund M, Rantatalo M, Parida A, Kumar U (2015b) Maintenance analysis for continuous improvement of railway infrastructure performance. Struct Infrast Eng 11(7):957–969
Gecevska MM, Radovanovic V, Petkovic O (2014) Multi-criteria economic analysis of machining processes using the WASPAS method. J Prod Eng 17(2):79–82
Gustafson A, Suhunnession H, Galar D, Kumar U (2013) Production and maintenance performance analysis: manual versus semi-automatic LHDs. J Qual Maint Eng 19(1):74–88
Hasani H, Tabatabaei SA, Amiri G (2012) Grey relational analysis to determine the optimum process parameters for open-end spinning yarns. J Eng Fiber Fabr 7(2):81–86
Hashemkhani ZS, Aghdaie MH, Derakhti A, Zavadskas EK, Morshed VMH (2013) Decision making on business issues with foresight perspective: an application of new hybrid MCDM model in shopping mall locating. Expert Syst Appl 40(17):7111–7121
Horenbeek AV, Pintelon L (2014) Development of a maintenance performance measurement framework—using the analytic network process (ANP) for maintenance performance indicator selection. Omeg 42(1):33–46
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple Attribute Decision Making Methods and Applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Juuso E, Lahdelma S (2013) Intelligent performance measures for condition based maintenance. J Qual Maint Eng 19(3):278–294
Kabir G, Hasin MAA (2012) Comparative analysis of TOPSIS and fuzzy TOPSIS for the evaluation of travel website service quality. Int J Qual Res 6(3):169–185
Khanlari A, Mohammadi K, Sohrabi B (2008) Prioritising equipment for preventive maintenance (PM) activities using fuzzy rules. Comput Ind Eng 54(2):169–184
Kothamasu R, Huang SH (2007) Adaptive mamdani fuzzy model for condition-based maintenance. Fuzzy Sets Syst 158(24):2715–2733
Kumar G, Maiti J (2012) Modelling risk based maintenance using fuzzy analytic network process. Expert Syst Appl 39(11):9946–9954
Kumar U, Parida A, (2006) Maintenance performance measurement: The need of the hour for the mechanized mining industry, Proceedings of the 1st Asian Mining Congress. Kolkata, India
Kumar U, Galar D, Parida A, Stunstrom C, Berges L (2013) Maintenance performance metrics: a state-of-the-art review. J Qual Maint Eng 19(3):233–277
Lashgari S, Antuchericiene J, Delavari A, Kheirkhah O (2014) Using QSPM and WASPAS methods for determining outsourcing strategies. J Bus Econ Manag 15(4):729–743
Lin MC, Wang CC, Chen MS, Chang CA (2008) Using AHP and TOPSIS approaches in customer-driven product design process. Comput Ind 59(1):17–31
Liyanage JP, Kumar U (2001a) Rephrasing the strategy significance of asset maintenance from a cost centre to a value driver: a case inferred from the petroleum industry. J Maint Asset Manag 16(1):3–12
Liyanage JP, Kumar U (2001b) An adaptive performance measurement system using the balanced scorecard. J Maint Asset Manag 16(1):13–21
Liyanage JP, Kumar U (2003) Towards a value-based view on operation and maintenance performance management. J Qual Maint Eng 9(4):333–350
Lu K-Y, Sy C-C (2009) A real-time decision-making of maintenance using fuzzy agent. Expert Syst Appl 36(2):2691–2698
Madi EN, Tap AOM (2011). Fuzzy TOPSIS method in the selection of investment boards by incorporating operational risks. In: Proceedings of the world congress on engineering 2011 (WCE 2011), Vol 1 July 6–8, 2011, London, U.K
Maletic D, Maletic M, Gomiscek B (2012) The relationship between continuous improvement and maintenance performance. J Qual Maint Eng 18(1):30–41
Moazami D, Behbahani H, Muniandy R (2011) Pavement rehabilitation and maintenance prioritisation of urban roads using fuzzy logic. Experts Syst Appl 38(10):12869–12879
Narayan V (2012) Business performance and maintenance: how are safety, quality, reliability, productivity and maintenance related? J Qual Maint Eng 18(2):183–195
Oke SA, Oluleye AE (2005) Tracking distortions in holistic maintenance measures: A framework. S Afr J Ind Eng 16(1):83–93
Parida A, Chattopadhyay G (2007) Development of a multi-criteria hierarchical framework for maintenance performance measurement (MPM). J Qual Maint Eng 13(3):241–258
Parida A, Kumar U (2006) Maintenance performance measurement: issues and challenges. J Qual Maint Eng 12(3):239–251
Parida A, Kumar U (2009) Maintenance productivity and performance measurement. In: Ben-Daya M, Duffuaa SO, Raouf A, Knezevic J (Eds) Handbook of maintenance management and engineering. Springer, London. pp 17–41
Parida A, Åhren T, Kumar U (2003) Integrating maintenance performance with corporate balanced scorecard, Proceedings of the 16th International Congress. Växjö, Sweden, pp 53–59
Parida A, Kumar U, Galar D, Stenström C (2015) Performance measurement and management for maintenance: a literature review. J Qual Maint Eng 21(1):2–33
Salonen A, Deleryd M (2011) Cost of poor maintenance: a concept for maintenance performance improvement. J Qual Maint Eng 4(2):87–94
Sari E, Shaharoun AM, Ma’aram A, Yazid AM (2015a) Sustainable maintenance measures: a pilot survey in Malaysian automotive companies. Proced CRIP 26:443–448
Sari E, Shaharoun AM, Ma’aram A, Yazid AM (2015b) Sustainable maintenance performance measures: a pilot survey in Malaysian automotive companies. Proced CIRP 26:443–448
Shemshadi A, Shirazi H, Toreihi M, Tarokh MJ (2011) A fuzzy VIKOR method for supplier selection based on entropy measure for objective weighting. Expert Syst Appl 38:12160–12167
Solderholm P, Norrbin P (2013) Risk based dependability approach to maintenance performance measurement. J Qual Maint Eng 19(3):316–326
Staniunas M, Medineckiene M, Zavadskas EK, Kalibatas D (2013) To modernise or not: ecological-economical assessment of multi-dwelling houses modernisation. Arch Civ Mech Eng 13(1):88–98
Stefanovic M, Nestic S, Djurovic A, Macuzic I, Tadic D, Gacic M (2015) An assessment of maintenance performance indicator using the fuzzy sets approach and genetic algorithm. J Eng Manuf. doi:10.1177/0954405415572641
Sun Q, Ouyang J (2015) Hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute decision making based on TOPSIS with entropy-weighted method. Manag Sci Eng 9(3):1–6
Tsang AHC (1998) A strategic approach to managing maintenance performance. J Qual Maint Eng 4(2):87–94
Wang L, Chu J, Wu J (2008) Selection of optimum maintenance strategies base on a fuzzy analytic network process. Int J Prod Econ 107(1):151–163
Zavadskas EK, Turskis Z, Antucheviciene J, Zakarevicius A (2012) Optimization of weighted aggregated sum product assessment. Elektronika ir elektrotechnika 122(6):3–6
Zavadskas EK, Antucheviciene J, Saparauskas J, Turskis Z (2013) MCDM methods WASPAS and MULTIMOORA: verification of robustness of methods when assessing alternative solutions. Econ Comput Econ Cybern Stud Res 47(2):5–20
Zavadskas EK, Turskis Z, Antucheviciene J, Hajiagha SHR, Hashemi SS (2014) Extension of weighted aggregate sum product assessment with interval-valued intuition fuzzy numbers (WASPAS-IVIF). Appl Soft Comput 24:1013–1021
Zavadskas EK, Baušys R, Stanujkic D, Magdalinovic-Kalinovic M (2016) Selection of lead-zinc flotation circuit design by applying WASPAS method with single-valued neutrosophic set. Acta Montanistica Slovaca 21(2):85–92
Zhou D, Zhang H, Weng S (2014) A novel prognostic model of performance degradation trend for power machinery maintenance. Ener 78:740–746
Acknowledgements
The insightful comments from the reviewers of this manuscript are greatly appreciated. Their comments helped in improving the quality of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ighravwe, D.E., Oke, S.A. A fuzzy-grey-weighted aggregate sum product assessment methodical approach for multi-criteria analysis of maintenance performance systems. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8 (Suppl 2), 961–973 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0554-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-016-0554-8