Abstract
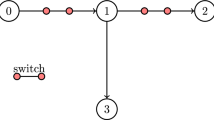
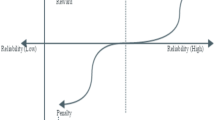
Power system failures are random events and their prevention can be managed by the regulatory agencies through pre-established performance targets. Once a standard or target is established for a certain performance index, it is assumed to be the limit value that must not be overstepped or it may cause penalties for the utility. Penalty based schemes, although very popular among regulatory agencies, are very limited to provide efficient economic signals for investments in reliability. This work discusses, firstly, how reliability indices can be fully used through performance-based mechanisms to establish contracts that reward a utility for providing good reliability and/or penalize it for poor services in electric power distribution systems. These contracts can be established between the regulatory agencies and the utilities in the form of performance-based rates (PBR) and between a utility and a customer in the form of customer service disruption payments. Such mechanisms must provide incentives for those utilities that invest in improvements of their system reliability and penalize the ones that do not act the same way. This discussion is extended to cope with tariffs and possible insurances based on reliability performance, so that consumers may share the risks with utilities by paying differentiated price services. The proposed concepts, PBR methodologies, and assessment tools are applied to a small test system (IEEE-RBTS) and the results are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan RN, da Silva MG (1995) Evaluation of reliability indices and outage costs in distribution systems. IEEE Trans Power Syst 10(1):413–419
Allan RN, Billinton R, Sjarief I, Goel L, So KS (1991) A reliability test system for educational purposes—basic distribution system data and results. IEEE Trans Power Syst 6(2):813–820
ANEEL—Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica (2000) Resolução 024. Diário Oficial da União, Brazil
Billinton R, Allan RN (1996) Reliability evaluation of power systems, 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York
Billinton R, Wang P (1998) Distribution system reliability cost/worth analysis using analytical and sequential simulation techniques. IEEE Trans Power Syst 13(4):1245–1250
Billinton R, Wenyuan L (1994) Reliability assessment of electric power systems using Monte Carlo methods. Plenum Press, New York
Billinton R, Cui L, Pan Z (2002) Quantitative reliability considerations in the determination of performance-based rates and customer service disruption payments. IEE Proc Gener Transm Distrib 149(6):640–644
Brown RE, Burke JJ (2000) Managing the risk of performance based rates. IEEE Trans Power Syst 15(2):893–898
Fumagalli E, Black JW, Vogelsang I, Ilic M (2004) Quality of service provision in electric power distribution systems through reliability insurance. IEEE Trans Power Syst 19(3):1286–1293
IEEE PES Transmission and Distribution Committee (2004) IEEE guide for electric power distribution reliability indices (IEEE Std 1366-2003). The IEEE Inc., USA
Leite da Silva AM, Manso LAF, Mello JCO, Billinton R (2000) Pseudo-chronological simulation for composite reliability analysis with time varying loads. IEEE Trans Power Syst 15(1):73–80
Leite da Silva AM, Cassula AM, Billinton R, Manso LAF (2002a) Integrated reliability evaluation of generation, transmission and distribution systems. IEE Proc Gener Transm Distrib 149(1):1–6
Leite da Silva AM, Cassula AM, Sacramento CE (2002b) Reliability evaluation of distribution systems under load transfer restrictions. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on PMAPS—probabilistic methods applied to power systems, vol 1, pp 9–14, Sept 2002
Leite da Silva AM, Schmitt WF, Cassula AM, Sacramento CE (2005) Analytical and Monte Carlo approaches to evaluate probability distributions of interruption duration. IEEE Trans Power Syst 20(3):1341–1348
Leite da Silva AM, Cassula AM, Nascimento LC, Freire JC Jr, Sacramento CE, Guimarães ACR (2006) Chronological Monte Carlo-based assessment of distribution system reliability. In: PMAPS 2006—international conference on probability methods applied to power systems, 11–15 June, Stockholm, Sweden
Manso LAF, Leite da Silva AM, Mello JCO (1999) Comparison of alternative methods for evaluating loss of load costs generation and transmission systems. Electr Power Syst Res 50(2):107–114
Rubinstein RY, Kroese DP (2007) Simulation and the Monte Carlo method, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Weddendorf WA (1968) Reliability insurance—when it is practical. IEEE Trans Ind Gen Appl IGA-4(4):375–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leite da Silva, A.M., Nascimento, L.C., Guimarães, A.C.R. et al. Reliability indices applied to performance-based mechanisms in electric power distribution systems. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 1, 105–112 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-010-0019-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-010-0019-4