Abstract
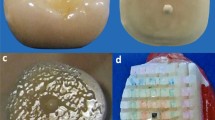
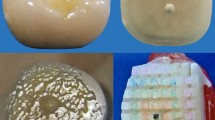
Retention of fixed partial dentures is mostly dependent upon the bond between metal and cement as well as cement and tooth structure. However, most of the time clinical failure of bond has been observed at metal and cement interface. The treatment of metal surface, prior to luting, plays a crucial role in bonding cement with the metal. This study is conducted to evaluate and compare the effect of different surface preparations on the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement with nickel–chromium metal ceramic alloy. Fifty caries-free extracted molar teeth were made flat until the dentin of the occlusal surface was exposed. After fabrication of the wax patterns and subsequent castings, the castings were subjected to porcelain firing cycles. The nickel–chromium metal ceramic alloy discs were also divided into five groups and subjected to various surface treatments: (1) Unsandblasted (U), (2) sandblasted (S), (3) sandblasted and treated with 10% aqueous solution of KMnO4 (SK), (4) unsandblasted and roughened with diamond abrasive points (UD) and (5) unsandblasted and roughened with diamond abrasive points and treated with 10% aqueous solution of KMnO4 (UDK). After surface treatments, the castings were cemented using Fuji PLUS encapsulated resin-modified glass ionomer cement. The obtained values of all the groups were subjected to statistical analysis for Tensile and Shear bond strength. Different surface treatments of the metal affects the bond strength values of resin-modified glass ionomer cement when used as luting agent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rubo JH, Pegoraro LF (1995) Tensile bond strength of a composite resin cement for bonded prosthesis to various dental alloys. J Prosthet Dent 74:230–234
Kolodney H, Puckett AD, Breazeale MS, Patterson KL, Lentz DL (1992) Shear bond strengths of prosthodontic adhesive systems to a nickel–chromium–beryllium alloy. Quintessence Int 23:65–69
Rubo JH, Pegoraro LF, Marolato F, Rubo MHM (1998) The effect of tin-electroplating on the bond of four dental alloys to resin cement: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent 80:27–31
Imbery TA, Davis RD (1993) Evaluation of tin plating systems for a high-noble alloy. Int J Prosthodont 6:55–59
Kohli S, Levine WA, Grisius RJ, Fenster RK (1990) The effect of three different surface treatments on the tensile strength of the resin bond to nickel chromium beryllium alloy. J Prosthet Dent 63:4–8
Re GJ, Kaiser DA, Malone WFP (1988) Shear bond strengths and scanning electron microscope evaluation of three different retentive methods for resin-bonded retainers. J Prosthet Dent 59:568–573
Anusavice KJ (2003) Phillips science of dental materials, 12th edn. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia
Rosenstiel S, Land MF, Fujimoto J (2001) Contemporary fixed prosthodontics, 3rd edn. Mosby, St. Louis
Coehlo CMP, Rubo JH, Pegoraro LF (1996) Tensile bond strength of a resinous cement to a nickel chromium alloy modified with five surface treatments. J Prosthet Dent 76:246–249
Campbell SD, Pelletier LB (1992) Thermal cycling distortion of metal ceramics: part I—metal collar width. J Prosthet Dent 67:603–608
Nomoto R, Komoriyama M, McCabe JF, Hirano S (2004) Effect of mixing method on the porosity of encapsulated glass ionomer cement. Dent Mater 20:972–978
GC Fuji PLUS. Product and Instruction manual
Livaditis GJ (1986) A chemical etching system for creating micromechanical retention in resin bonded retainers. J Prosthet Dent 86:181–188
Livaditis GJ, Tate DL (1988) Gold plating etched metal surfaces of resin bonded retainers. J Prosthet Dent 59(2):153–158
Tanaka T, Atsuta M, Nakabayashi N, Masuhara E (1988) Surface treatment of gold alloys for adhesion. J Prosthet Dent 60(3):271–279
Wilson AD (1990) Resin modified glass ionomer cements. Int J Prosthodont 3:425–429
Tanaka T (1981) 4-META opaque resin—a new resin strongly adhesive to nickel–chromium alloy. J Prosthet Dent
Tanaka T, Fujiyama E, Shimizu H, Takaki A, Atsuta M (1986) Surface treatment of nonprecious alloys for adhesion fixed partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent 55(4):456–462
Ishijima T, Caputo AA, Mito R (1992) Adhesion of resin to casting alloys. J Prosthet Dent 67:445–449
Ergin S, Gemalmaz D (2002) Retentive properties of five different luting cements on base and noble metal copings. J Prosthet Dent 88:491–497
Mota CS, Demarco FF, Camacho GB, Powers JM (2003) Tensile bond strength of four resin luting agents bonded to bovine enamel and dentin. J Prosthet Dent 89:558–564
Acknowledgment
The author acknowledges Dr. Anurag Hasti, Mr. Monal Hasti and Dr. Nidhi Gupta for their help during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasti, K., Jagadeesh, H.G. & Patil, N.P. Evaluation and Comparison of the Effect of Different Surface Preparations on Bond Strength of Glass Ionomer Cement with Nickel–Chrome Metal–Ceramic Alloy: A Laboratory Study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc 11, 14–19 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13191-011-0043-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13191-011-0043-3