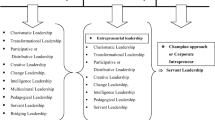
Abstract
There is considerable confusion about what constitutes servant leadership. This paper outlines an approach to guide empirical investigation, while also addressing current inexact specifications of servant leadership, the issue of the unique dimensions of the construct, and distinctive characteristics of servant leadership considering other leadership styles. With knowledge of the abundance of servant leadership domain elements from the literature as a background, we provide a conceptually distinct approach to studying servant leadership to advise future measurement of the construct. Additionally, we discuss the convoluted state of the conceptual and empirical attributes that currently comprise the dimensions of servant leadership in relation to those proposed in existing definitions. Likewise, we delineate the challenges of empirically parsing out distinctive servant leadership traits in search of an operational definition, identifying traits that might be distinct to servant leaders, and discuss the implications from both theoretical and managerial perspectives; also, we provide directions for future research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahearne, M., MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, P. M., Mathieu, J. E., & Lam, S. K. (2010). The role of consensus in sales team performance. Journal of Marketing Research, 47(3), 458–469.
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1982). Some methods for respecifying measurement models to obtain unidimensional construct measurement. Journal of Marketing Research, 19(4), 453–460.
Andrich, D. (1988). Rasch models for measurement (Vol. 68). Newbury Park: Sage.
Ashill, N. J., Carruthers, J., & Krisjanous, J. (2006). The effect of management commitment to service quality on frontline employees’ affective and performance outcomes: an empirical investigation of the New Zealand public healthcare sector. International Journal of Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Marketing, 11(4), 271–287.
Avolio, B. J. (2007). Promoting more integrative strategies for leadership theory-building. American Psychologist, 62(1), 25.
Avolio, B. J., & Gardner, W. L. (2005). Authentic leadership development: getting to the root of positive forms of leadership. Leadership Quarterly, 16, 315–338.
Awee, A., Cheah, W. Y., Cheng, C. N., Hong, K. S., Ling, L. B., & Tan, M. C. (2014). Effect of servant leadership on affective commitment among hotel employees. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 4(November), 1–7.
Bande, B., Fernández-Ferrín, P., Varela, J. A., & Jaramillo, F. (2014). Emotions and salesperson propensity to leave: The effects of emotional intelligence and resilience. Industrial Marketing Management, forthcoming.
Barbuto, J. E., & Wheeler, D. W. (2006). Scale development and construct clarification of servant leadership. Group and Organization Management, 31(3), 300–326.
Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership and Performance Beyond Expectations. Philadelphia: Lawrence Ernbaum Associates.
Bass, B. M. (2000). The future of leadership in learning organizations. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 7(3), 18–40.
Bass, B. M., & Avolio, B. J. (1990). Multifactor leadership questionnaire-MLQ. Center for Leadership Studies, Binghamton: School of Management SUNY.
Bass, B. M., & Avolio, B. J. (1995). Improving organizational effectiveness through transformational leadership. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Bearden, W. O., & Netmeyer, R. G. (1999). Handbook of Marketing Scales. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Bearden, W. O., & Teel, J. E. (1983). Selected determinants of consumer satisfaction and complaint reports. Journal of Marketing Research, 20(1), 21–28.
Bollen, K. A., & Lennox, R. (1991). Conventional wisdom on measurement: a structural equation perspective. Psychological Bulletin, 110(2), 305–314.
Bond, T. G., & Fox, C. M. (2001). Applying the Rasch model: Fundamental measurement in the human sciences. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Brown, M. E., & Gioia, D. A. (2002). Making things click: distributive leadership in an online division of an offline organization. Leadership Quarterly, 13(4), 397–414.
Brown, M. E., & Trevino, L. K. (2006). Socialized charismatic leadership, values congruence, and deviance in work groups. Journal of Applied Psychology, 91(4), 954--962.
Bruner, G. C. B., James, K. E., & Hensel, P. E. (2001). Marketing Scales Handbook. Chicago: American Marketing Association.
Buchen, I. H. (1998). Servant leadership: a model for future faculty and future institutions. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 5(1), 125–134.
Buckley, P. J., & Chapman, M. (1996). Theory and method in international business research. International Business Review, 5(3), 233–245.
Butler, J. K., Jr., & Reese, R. M. (1991). Leadership style and sales performance: a test of the situational leadership® model. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 11(3), 37–46.
Cadogan, J. W., Kuivalainen, O., & Sundqvist, S. (2009). Export market-oriented behavior and export performance: quadratic and moderating effects under differing degrees of market dynamism and internationalization. Journal of International Marketing, 17(4), 71–89.
Carmeli, A., Schaubroeck, J., & Tishler, A. (2011). How CEO empowering leadership shapes top management team processes: implications for firm performance. The Leadership Quarterly, 22(2), 399–411.
Carnap, R. (1953). Testability & Meaning. In H. Feigel & M. Brodbeck (Eds.), Readings in the Philosophy of Science. New York: Appleton-Century Crofts.
Carson, J. B., Tesluk, P. E., & Marrone, J. A. (2007). Shared leadership in teams: an investigation of antecedent conditions and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 50(5), 1217–1234.
Cherry, J., & Fraedrich, J. (2000). An empirical investigation of locus of control and the structure of moral reasoning: examining the ethical decision-making processes of sales managers. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 20(3), 173–188.
Choudhary, A. I., Akhtar, S. A., & Zaheer, A. (2013). Impact of transformational and servant leadership on organizational performance: a comparative analysis. Journal of Business Ethics, 116(2), 433–440.
Churchill, G. A., Jr. (1979). A paradigm for developing better measures of marketing constructs. Journal of Marketing Research, 16(1), 64–73.
Colbert, A. E., Kristof-Brown, A. L., Bradley, B. H., & Barrick, M. R. (2008). CEO transformational leadership: the role of goal importance congruence in top management teams. Academy of Management Journal, 51(1), 81–96.
Covey, S. R. (1996). Three roles of the leader in the new paradigm. The leader of the future, 149–160.
Cummings, B. (2007). Group Dynamics. Sales and Marketing Management, 159(1), 8.
D’Innocenzo, L., Mathieu, J. E., & Kukenberger, M. R. (2015). A meta-analysis of different forms of shared leadership – team performance relations. Journal of Management, forthcoming.
Dannhauser, Z., & Boshoff, A. B. (2006). The relationships between servant leadership, trust, team commitment and demographic variables. In Servant leadership Research Roundtable Proceedings.
Day, D. V., Gronn, P., & Salas, E. (2006). Leadership in team –based organizations: on the threshold of a new era. The Leadership Quarterly, 17(3), 211–216.
De Pree, M., & Pree, M. (1997). Leading without Power: Finding Hope in Serving Community, 99. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
de Waal, A., & Sivro, M. (2012). The relation between servant leadership, organizational performance, and the high-performance organization framework. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 19(2), 173–190.
Del, M. R. A., & Akbarpour, M. (2011). The relationship between servant leadership of managers and employees trust. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 3(6), 525–535.
Dennis, R. S. (2004). Servant leadership theory: Development of the servant leadership assessment instrument. Doctoral dissertation, Regent University.
Dennis, R. S., & Bocarnea, M. (2005). Development of the servant leadership assessment instrument. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 26(8), 600–615.
Dennis, R. S., & Winston, B. E. (2003). A factor analysis of Page and Wong’s servant leadership instrument. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 24(8), 455–459.
DeRue, D. S., Nahrgang, J. D., Wellman, N. E. D., & Humphrey, S. E. (2011). Trait and behavioral theories of leadership: an integration and meta‐analytic test of their relative validity. Personnel Psychology, 64(1), 7–52.
Dubinsky, A. J., Yammarino, F. J., Jolson, M. A., & Spangler, W. D. (1995). Transformational leadership: an initial investigation in sales management. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 15(2), 17–29.
Ehrhart, M. G. (2004). Leadership and procedural justice climate as antecedents of unit-level organizational citizenship behavior. Personnel Psychology, 57(1), 61–94.
Fairholm, G. W. (1997). Capturing the Heart of Leadership: Spirituality and Community in the New American Workplace. Westport: Praeger.
Fairholm, G. W. (1998). Leadership as an exercise in virtual reality. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 19(4), 187–193.
Farling, M. L., Stone, A. G., & Winston, B. E. (1999). Servant leadership: setting the stage for empirical research. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 6(1–2), 49–72.
Ferch, S. R., & Mitchell, M. M. (2001). Intentional forgiveness in relational leadership: a technique for enhancing effective leadership. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 7(4), 70–83.
Focht, A., & Ponton, M. (2015). Identifying primary characteristics of servant leadership: Delphi study. International Journal of Leadership Studies, 9(1), 44–60.
Gil Saura, I. G., Contrí, G. B., Taulet, A. C., & Velázquez, B. M. (2005). Relationships among customer orientation, service orientation, and job satisfaction in financial services. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 16(5), 497–525.
Gnoth, J., & Zins, A. H. (2013). Developing a tourism cultural contact scale. Journal of Business Research, 66(6), 738–744.
Graham, J. W. (1991). Servant-leadership in organizations: inspirational and moral. The Leadership Quarterly, 2(2), 105–119.
Graham, J. W. (1995). Leadership, moral development, and citizenship behavior. Business Ethics Quarterly, 5(1), 43–54.
Greenleaf, R. K. (1970). The Servant leadership. Indianapolis: Greenleaf Center.
Greenleaf, R. K., & Spears, L. E. (1977). Servant leadership: A Journey into the Nature of Legitimate Power & Greatness. Mahwah: Paulist Press.
Greenleaf, R. K., & Spears, L. E. (2002). Servant leadership: A journey into the nature of legitimate power and greatness (25th Annual Edition). Mahwah: Paulist Press.
Grisaffe, D. B., & Jaramillo, F. (2007). Toward higher levels of ethics: preliminary evidence of positive outcomes. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 27(4), 355–371.
Gunnarsdottir, S. (2014). Is Servant leadership useful for sustainable nordic health care? Nursing Science, 112(34), 53–55.
Guttman, L. L. (1950). The basis for scalogram analysis. In S. A. Stouffer, et al. Measurement & Prediction, Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Hall, A. S. (1991). Why a great leader. In K. Hall (Ed.), Living Leadership: Biblical Leadership Speaks to Our Day. Anderson: Warner Press.
Houghton, J. D., Pearce, C. L., Manz, C. C., Courtright, S., & Stewart, G. L. (2014). sharing is caring: toward a model of proactive caring through shared leadership. Human Resource Management Review.
House, R. J. (1971). A path-goal theory of leader effectiveness. Administrative Science Quarterly, 16(3), 321–329.
Hoveida, R., Salari, S., & Asemi, A. (2011). A study of the relationship among servant leadership and organization commitment: a case study. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business, 3(3), 499–509.
Hu, J., & Liden, R. C. (2011). Antecedents of team potency and team effectiveness: an examination of goal and process clarity and servant leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(4), 851–862.
Hunt, S. D. (1976). The nature and scope of marketing. Journal of Marketing, 40(July), 17–28.
Hunter, E. M., Neubert, M. J., Perry, S. J., Witt, L. A., Penney, L. M., & Weinberger, E. (2013). Servant leaders inspire servant followers: antecedents and outcomes for employees and the organization. The Leadership Quarterly, 24(2), 316–331.
Ingram, T. N., LaForge, R. W., Locander, W. B., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, P. M. (2005). New directions in sales leadership research. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 25(2), 137–154.
Ingram, T. N., LaForge, R. W., & Schwepker, C. H. (2007). Salesperson ethical decision making: the impact of sales leadership and sales management control strategy. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 27(4), 301–315.
Jacobs, G. A. (2006). Servant leadership and follower commitment. In Proceedings of the 2006 Servant leadership Research Roundtable.
Jaramillo, F. (2015). Servant leadership and ethics: a dyadic examination of supervisor behaviors and salesperson perceptions. Journal of Personal selling & Sales Management, forthcoming.
Jaramillo, F., & Noboa, F. (2012). Impact of servant leadership on ethical climate, and organizational outcomes. Proceedings of the Academy of Marketing Science.
Jaramillo, F., Grisaffe, D. B., Chonko, L. B., & Roberts, J. A. (2009a). Examining the impact of servant leadership on sales force performance. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 29(3), 257–276.
Jaramillo, F., Grisaffe, D. B., Chonko, L. B., & Roberts, J. A. (2009b). Examining the impact of servant leadership on salesperson’s turnover intention. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 29(4), 351–366.
Jenkins, M., & Stewart, A. C. (2010). The importance of a servant leader orientation. Health Care Management Review, 35(1), 46–54.
Joseph, E. E., & Winston, B. E. (2005). A correlation of servant leadership. leader trust and organizational trust. Leadership and Organizational Development Journal, 26(1), 6–22.
Kamakura, W. A., Ramaswami, S. N., & Srivastava, R. K. (1991). Applying latent trait analysis in the evaluation of prospects for cross-selling of financial services. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 8(4), 329–349.
Koyunco, M., Burke, R. J., & Astakhova, M. (2014). Servant leadership and perceptions of service quality produced by front line service workers in hotels: achieving competitive advantage. International Journal of Contemporary Hospital Management, 20(7), 1083–1092.
Kuhn, T. S. (1962). The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Lambe, C. J., Webb, K. L., & Ishida, C. (2009). Self-managing selling teams and team performance: the complementary roles of empowerment and control. Industrial Marketing Management, 38(1), 5–16.
Laub, J. A. (1999). Assessing the servant organization: development of the organizational leadership assessment (OLA) instrument. Dissertation Abstracts Online, 60(2), 308A.
Laub, J. A. (2003). From paternalism to the servant organization: expanding the organizational leadership assessment (OLA) model. In Proceedings of the Servant leadership Research Roundtable.
Levering, R., & Moskowitz, M. (2000). The 100 best companies to work for in America. Fortune, 141(1), 82–110.
Liden, R. C., Wayne, S. J., Zhao, H., & Henderson, D. (2008). Servant leadership: development of a multidimensional measure and multi-level assessment. The Leadership Quarterly, 19(2), 161–177.
Liden, R. C., Wayne, S. J., Liao, C., & Meuser, J. D. (2014). Servant leadership and serving culture: influence on individual and unit performance. Academy of Management Journal, 57(5), 1434–1452.
Liden, R. C., Wayne, S. J., Meuser, J. D., Hu, J., Wu, J., & Liao, C. (2015). Servant leadership: validation of a short form of the SL-28. The Leadership Quarterly, 26(2), 254–269.
Lytle, R. S., & Timmerman, J. E. (2006). Service orientation and performance: an organizational perspective. Journal of Services Marketing, 20(2), 136–147.
MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, P. M., & Rich, G. A. (2001). Transformational and transactional leadership and salesperson performance. Academy of Marketing Science Journal, 29(2), 115–134.
MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakopf, P. M., & Jarvis, C. B. (2005). The problem of measurement model misspecification in behavioral and organizational research and some recommended solutions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(4), 710–730.
McCann, J. T., Graves, D., & Cox, L. (2014). Servant leadership, employee satisfaction, and organizational performance in rural community hospitals. International Journal of Business and Management, 9(10), 28–38.
McGee-Cooper, A., & Looper, G. (2001). The Essentials of Servant leadership: Principles in Practice. Dallas: Pegasus Communications.
Mengue, B., Auh, S., & Uslu, A. (2013). Customer knowledge creation capability and performance in sales teams. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 41(1), 19–39.
Miao, Q., Newman, A., Schwarz, G., & Xu, L. (2014). Servant leadership, trust, and the organizational commitment of public sector employees in china. Public Administration, 2(3), 727–743.
Mittal, R., & Dorfman, P. W. (2012). Servant leadership across cultures. Journal of World Business, 47(4), 555–570.
Moorman, M. B., & Albrecht, C. (2009). Tea selling: getting incentive compensation right. Velocity, 10(2), 33–37.
Narayandas, D. (1998). Measuring and managing the benefits of customer retention an empirical investigation. Journal of Service Research, 1(2), 108–128.
Nath, P., & Harbib, J. P. (2011). Marketing in the C-suite: a study of chief marketing officer power in firms’ top management teams. Journal of Marketing, 75(1), 60–77.
Nath, P., & Mahajan, V. (2008). Chief marketing officers: a study of their presence in firms’ top management teams. Journal of Marketing, 72(1), 65–81.
Neubert, M. J., Kacmar, K. M., Carlson, D. S., Chonko, L. B., & Roberts, J. A. (2008). Regulatory focus as a mediator of the influence of initiating structure and servant leadership on employee behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(6), 1220–1233.
Nuitjen, I. (2009). Servant leadership: Paradox or diamond in the rough? A multidimensional measure and empirical evidence. Dissertation, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam.
Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994). Psychometric Theory (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of Marketing, 63, 33–44.
Oner, Z. H. (2012). Servant leadership and paternalistic leadership styles in the Turkish business context. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 33(3), 300–316.
Page, D., & Wong, T. P. (2000). A conceptual framework for measuring servant leadership. The human factor in shaping the course of history and development, 69--110.
Page, D., & Wong, T. P. (2002). Conceptual framework for measuring servant leadership. In The Human Factor in Shaping the Course of History & Development. Lanham: University Press of America.
Parolini, J. L. (2004) Effective servant leadership: a model incorporating servant leadership and the competing values framework. In Proceedings of the Servant leadership Research Roundtable.
Parolini, J. L., Patterson, K., & Winston, B. (2009). Distinguishing between transformational and servant leadership. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 30(3), 274–291.
Parris, D. L., & Peachey, J. W. (2013). A systematic literature review of servant leadership theory in organizational contexts. Journal of Business Ethics, 113(3), 377–393.
Patterson, K. A. (2003). Servant leadership: A Theoretical Model (Doctoral Dissertation, Regent University).
Peterson, S. J., Galvin, B. M., & Lange, D. (2012). CEO servant leadership: exploring executive characteristics and firm performance. Personnel Psychology, 65(3), 565–596.
Rafferty, A. E., & Griffin, M. A. (2006). Refining individualized consideration: distinguishing developmental leadership and supportive leadership. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 79(1), 37–61.
Rapp, A., Ahearne, M., Mathieu, J., & Rapp, T. (2010). Managing sales teams in a virtual environment. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 27(3), 213–224.
Reed, L. L., Vidaver-Cohen, D., & Colwell, S. R. (2011). A new scale to measure executive servant leadership: development, analysis, and implications for research. Journal of Business Ethics, 101(3), 415–434.
Reinke, S. J. (2004). Service before self: towards a theory of servant leadership. Global Virtue Ethics Review, 5(3), 30–57.
Rindflesch, A., Malter, A. J., Ganesan, S., & Moorman, C. (2008). Cross-sectional versus longitudinal survey research: concepts, findings, & guidelines. Journal of Marketing Research, 45(3), 261–279.
Rowald, J., & Borgman, L. (2013). Are leadership constructs really independent? Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 34(1), 20–43.
Russell, R. F. (2001). The role of values in servant leadership. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 22(2), 76–84.
Russell, R. F., & Stone, A. G. (2002). A review of servant leadership attributes: developing a practical model. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 23(3), 145–157.
Schneider, S. K., & George, W. M. (2011). Servant leadership versus transformational leadership in voluntary service organizations. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 32(1), 60–77.
Schwab, D. P. (1980). Construct validity in organizational behavior. In L. L. Cummings & B. M. Staw (Eds.), Research in organizational behavior. Greenwich: JAI Press.
Schwepker, C. H. (2015). Influence of the ethical servant leader and ethical climate on customer value enhancing sales performance. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, forthcoming.
Schwepker, C. H., & Good, D. J. (2010). Transformational leadership and its impact on sales force moral judgment. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 30(4), 299–317.
Sendjaya, S. (2003). Development and validation of a servant leadership scale. Regent University Servant Leadership Roundtable Proceedings.
Sendjaya, S., Sarros, J. C., & Santora, J. C. (2008). Defining and measuring servant leadership behaviour in organizations. Journal of Management Studies, 45(2), 402--424.
Sendjaya, S., & Pekerti, A. (2010). Servant leadership as antecedent of trust in organizations. Leadership and Organizational Development Journal, 31(7), 643–663.
Shaffer, J. A., DeGeest, D., & Li, A. (2016). Tackling the problem of construct proliferation: a guide to assessing the discriminant validity of conceptually related constructs. Organization Research Methods, 9(1), 80–110.
Shahzad, A., Rizvi, R. A., Waheed, A., Khan, I., Usman, S. M., Nazier, N., Amin, G., & Kiyani, T. M. (2013). Linking servant leadership with organizational citizenship behavior through trust: an embryonic structural modeling approach. European Journal of Social Science, 39(2), 273–284.
Shannahan, K., Bush, A., & Shannahan, R. (2013). Are your salespeople coachable? How salesperson coachability, trait competitiveness, and transformational leadership enhance sales performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 41(1), 40–54.
Simon, C. H. L., & Mali, W. (2014). The impact of servant leadership on organizational tenure and trust in leaders and attitudes. Personnel Review, 43(2), 272–287.
Singhapakdi, A., & Vitell, S. J. (1992). Marketing ethics: sales professionals versus other marketing professionals. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 12(2), 27–38.
Southey, R. (1837). The Doctor. United Kingdom: Longman Press.
Spears, L. C. (1995). Servant leadership and the Greenleaf legacy. In L. C. Spears (Ed.), Reflections on Leading: How R. K. Greenleaf’s Theory of Servant Leadership Influenced Today’s Top Management Thinkers. New York: Wiley.
Spears, L. C. (1998). Creating caring leadership for the 21st century. The Non-for-Profit CEO, 5(9), 1–3.
Spears, L. C., & Lawrence, M. (Eds.). (2002). Focus on Leadership: Servant leadership for the 21st Century. New York: Wiley.
Stewart, D. W., & Zinkhan, G. M. (2006). From the Editors: enhancing marketing theory in academic research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 34(4), 477.
Stone, G. A., Russell, R. F., & Patterson, K. (2004). Transformational versus servant leadership: a difference in leader focus. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 25(4), 349–361.
van Dierendonck, D. (2011). Servant leadership: a review and synthesis. Journal of Management, 37(4), 1228–1261.
van Dierendonck, D., & Nuijten, I. (2011). The servant leadership survey: development and validation of a multidimensional measure. Journal of Business Psychology, 26(3), 249–267.
van Dierendonck, D., & Patterson, K (2014). Compassionate love as a cornerstone of servant leadership: an integration of previous theorizing and research. Journal of Business Ethics, 1–13.
Vidic, Z., & Burton, D. (2011). Developing effective leaders: motivational correlates of leadership styles. Journal of Applied Sports Psychology, 23(3), 277–291.
Walumbwa, F. O., Hartnell, C. A., & Oke, A. (2010). Servant leadership, procedural justice climate, service climate, employee attitudes, and organization citizenship behavior: a cross-level investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 9(3), 517–529.
Wang, D., Waldman, D. A., & Zhang, Z. (2014). A meta-analysis of shared leadership and team effectiveness. Journal of Applied Psychology, 74, 259–264.
Washington, R. R., Sutton, C. D., & Feild, H. S. (2006). Individual differences in servant leadership: the roles of values and personality. Leadership and Organizational Development Journal, 27(8), 700–716.
Wei, L. S., & Desa, N. M. (2013). Servant leadership and organizational commitment: An empirical evidence from banking industry in Malaysia. In 4th International conference on business & economic research (4th ICBER 2013).
Weick, K. E. (1999). Theory construction as disciplined reflexivity: tradeoffs in the 90s. Academy of Management Review, 24(4), 797–806.
Winston, B. E. (2002). Be A Leaders for God’s Sake: From Values to Behaviors. Regent University, School of Leadership Studies.
Winston, B., & Fields, D. (2015). Seeking and measuring the essential behaviors of servant leadership. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 36(4), 413–434.
Wong, P. T. P. (2004). The paradox of servant leadership. Leadership Link, Spring, 2004, 3–5.
Wong, P. T. P., & Page D. (2003). An Opponent Process Model and the Revised Servant Leadership Profile. Regent University: School of Leadership Studies.
Yammarino, F. J., & Dansereau, F. (2002). Individualized leadership. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 9(1), 90--99.
Yukl, G. A. (2002). Leadership in Organizations. National College for School Leadership: Prentice Hall.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VanMeter, R., Chonko, L.B., Grisaffe, D.B. et al. In search of clarity on servant leadership: domain specification and reconceptualization. AMS Rev 6, 59–78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13162-016-0075-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13162-016-0075-2