Abstract
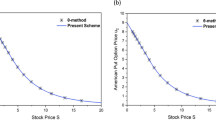
When solving the American options with or without dividends, numerical methods often obtain lower convergence rates if further treatment is not implemented even using high-order schemes. In this article, we present a fast and explicit fourth-order compact scheme for solving the free boundary options. In particular, the early exercise features with the asset option and option sensitivity are computed based on a coupled of nonlinear PDEs with fixed boundaries for which a high order analytical approximation is obtained. Furthermore, we implement a new treatment at the left boundary by introducing a third-order Robin boundary condition. Rather than computing the optimal exercise boundary from the analytical approximation, we simply obtain it from the asset option based on the linear relationship at the left boundary. As such, a high order convergence rate can be achieved. We validate by examples that the improvement at the left boundary yields a fourth-order convergence rate without further implementation of mesh refinement, Rannacher time-stepping, and/or smoothing of the initial condition. Furthermore, we extensively compare the performance of our present method with several 5(4) Runge–Kutta pairs and observe that Dormand and Prince and Bogacki and Shampine 5(4) pairs are faster and provide more accurate numerical solutions. Based on numerical results and comparison with other existing methods, we can validate that the present method is very fast and provides more accurate solutions with very coarse grids.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
The data could be shared at a reasonable request.
References
Ballestra, L.V.: Fast and accurate calculation of American option prices. Decisions Econ. Finan. 41, 399–426 (2018)
Bhatt, H.P., Khaliq, A.Q.M.: Fourth-order compact schemes for the numerical simulation of coupled Burgers’ equation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 200, 117–138 (2016)
Bogacki, P.: A family of Parallel Runge-Kutta Pairs. Comput. Math. Appl. 31, 23–31 (1996)
Bogacki, P., Shampine, L.F.: An efficient Runge-Kutta (4,5) pair. Comput. Math. Appl. 32, 15–28 (1996)
Brennan, M., Schwartz, E.: The valuation of American put options. J. Fin. 32, 449–462 (1997)
Cash, R.J., Karp, A.H.: A variable order Runge-Kutta for initial value problems with rapidly varying right-hand sides. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 16, 201–222 (1990)
Cen, Z., Chen, W.: A HODIE finite difference scheme for pricing American options. Adv. Differ. Equ. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-018-1917-z
Chen, X., Chadam, J.: A mathematical analysis of the optimal exercise boundary American put options. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 38, 1613–1641 (2006)
Christara, C.C., Dang, D.M.: Adaptive and high-order methods for valuing American options. J. Comput. Fin. 14, 73–113 (2011)
Company, R., Egorova, V.N., Jódar, L.: A positive, stable, and consistent front-fixing numerical scheme for American options. In: Russo G., Capasso V., Nicosia G., Romano V. (eds) Progress in Industrial Mathematics at ECMI 2014. Mathematics in Industry, 22, 57–64 (2016)
Company, R., Egorova, V.N., Jódar, L.: Solving American option pricing models by the front fixing method: numerical analysis and computing. Abstract Appl. Anal. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/146745
Cox, J.C., Ross, S.A., Rubinstein, M.: Option pricing: a simplified approach. J. Financ. Econ. 7, 229–263 (1979)
Dormand, J.R., Prince, J.P.: A family of embedded Rung-Kutta formulae. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6, 19–26 (1980)
Egorova, V.N., Company, R., Jódar, L.: A new efficient numerical method for solving American option under regime switching model. Comput. Math. Appl. 71, 224–237 (2016)
Fehlberg, E.: Low-order classical Runge-Kutta formulas with step size control and their application to some heat transfer problems. NASA Tech. Rep. 315 (1969)
Forsyth, P.A., Vetzal, K.R.: Quadratic convergence of a penalty method for valuing American options. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 23, 2096–2123 (2002)
Goodman, J., Ostrov, D.N.: On the early exercise boundary of the American put option. J. SIAM Appl. Math. 62, 1823–1835 (2002)
Hajipour, M., Malek, A.: Efficient high-order numerical methods for pricing option. Comput. Econ. 45, 31–47 (2015)
Han, H., Wu, X.: A fast numerical method for the Black-Scholes equation for American options. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41, 2081–2095 (2003)
Holmes, A.D., Yang, H.: A front-fixing finite element method for the valuation of American options. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 30, 2158–2180 (2008)
Hoover, W.G., Sprot, J.C., Hoover, C.G.: Adaptive Runge-Kutta integration for stiff systems: comparing Nose and Nose-Hoovers dynamics for the harmonic oscillator. Am. J. Phys. 84, 786 (2016)
Ikonen, S., Toivanen, J.: Operator splitting methods for American option pricing. Appl. Math. Lett. 17, 809–814 (2004)
Ketcheson, D.I., Mortenson, M., Parsani, M., Schilling, N.: More efficient time integration for Fourier pseudospectral DNS of incompressible turbulence. Int. J. Numer. Method. Fluids 92, 79–93 (2020)
Kim, B.J., Ma, Y., Choe, H.J.: A simple numerical method for pricing an American put option. J. Appl. Math. 2013, 128025 (2013)
Kim, B.J., Ma, Y., Choe, H.J.: Optimal exercise boundary via intermediate function with jump risk. Jpn. J. Ind. Appl. Math. 34, 779–792 (2017)
Leisen, D., Reimer, M.: Binomial models for option valuation—examining and improving convergence. Appl. Math. Fin. 3, 319–346 (1996)
Macdougall, T., Verner, J.H.: Global error estimators for 7, 8 Runge-Kutta pairs. Numer. Algorithm 31, 215–231 (2002)
Mallier, R.: Evaluating approximations to the optimal exercise boundary for American options. J. Appl. Math. 2, 71–92 (2002)
Muthuraman, K.A.: moving boundary approach to American option pricing. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 32, 3520–3537 (2008)
Nielsen, B.F., Skavhaug, O., Tveito, A.: A penalty and front-fixing methods for the numerical solution of American option problems. J. Comput. Fin. 5, 69–97 (2002)
Oosterlee, C.W., Leentvaar, C.C.W., Huang, X.: Accurate American option pricing by grid stretching and high order finite differences. Working Papers, DIAM. Delft University of Technology, Delft (2005)
Papakostas, S.N., Papageorgiou, G.: A family of fifth-order Runge-Kutta pairs. Math. Comput. 65, 1165–1181 (1996)
Pooley, D.M., Vetzal, K.R., Forsyth, P.A.: Convergence remedies for non-smooth payoffs in option pricing. J. Comput. Fin. 6, 25–40 (2003)
Simos, T.E.: A Runge-Kutta Fehlberg method with phase-lag of order infinity for initial-value problems with oscillation solution. Comput. Math. Appl. 25, 95–101 (1993)
Simos, T.E., Papakaliatakis, G.: Modified Runge-Kutta Verner methods for the numerical solution of initial and boundary-value problems with engineering application. Appl. Math. Model. 22, 657–670 (1998)
Simos, T.E., Tsitouras, C.: Fitted modifications of classical Runge-Kutta pairs of orders 5(4). Math. Method Appl. Sci. 41, 4549–4559 (2018)
Song, H., Zhang, K., Li, Y.: Finite element and discontinuous Galerkin methods with perfect matched layers for American options. Numer. Math. Theory Methods Appl. 10, 829–521 (2017)
Tangman, D.Y., Gopaul, A., Bhuruth, M.: A fast high-order finite difference algorithm for pricing American options. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 222, 17–29 (2008)
Tsitouras, C.: A parameter study of explicit Runge-Kutta pairs of orders 6(5). Appl. Math. Lett. 11, 65–69 (1998)
Wilkie, J., Cetinbas, M.: Variable-stepsize Runge-Kutta for stochastic Schrodinger equations. Phys. Lett. A 337, 166–182 (2005)
William, H.P., Saul, A.T.: Adaptive stepsize Runge-Kutta Integration. Comput. Phys. 6, 188 (1992)
Wu, L., Kwok, Y.K.: A front-fixing method for the valuation of American options. J. Fin. Eng. 6, 83–97 (1997)
Yan, Y., Dai, W., Wu, L., Zhai, S.: Accurate gradient preserved method for solving heat conduction equations in double layers. Appl. Math. Comput. 354, 58–85 (2019)
Zhang, K., Song, H., Li, J.: Front-fixing FEMs for the pricing of American options based on a PML technique. Appl. Anal.: Int. J. 94, 1–29 (2014)
Zhao, J.: Highly accurate compact mixed method for two point boundary value problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 188, 1402–1418 (2007)
Zhao, J., Davidson, M., Corless, R.M.: Compact finite difference method for American option pricing. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 206, 306–321 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their invaluable comments and suggestions.
Funding
No funding was received from any resource.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Nwankwo, C., Dai, W. On the efficiency of 5(4) RK-embedded pairs with high order compact scheme and Robin boundary condition for options valuation. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 39, 753–775 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-022-00507-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-022-00507-0