Abstract
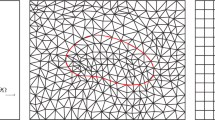
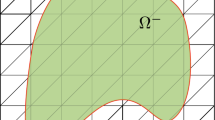
We propose an immersed hybrid difference (IHD) method for elliptic interface problems. An essential feature of the IHD method lies in the VR(virtual to real) transformation, which makes it possible to derive accurate finite difference approximations with functions of low regularity on interface cells. The VR transformation is consisting of the interface conditions in addition to the consistency equations, which are derived from the governing equation. The method is easy to be implemented and high order methods are conveniently derived. Numerical tests on several types of interfaces with low and high order methods are presented, which demonstrates efficiency of the IHD method. Numerical analysis for the one dimensional case is provided.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjerid, S., Ben-Romdhane, M., Lin, T.: Higher degree immersed finite element methods for second-order elliptic interface problems. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Modeling 11(2), 541–566 (2014)
Beale, A., Layton, A.T.: On the accuracy of finite difference methods for elliptic problems with interfaces. Comm. App. Math. Comp. 1, 91–119 (2006)
Bruno, O.P., Lyon, M.: High-order unconditionally stable fc-ad solvers for general smooth domains I. Basic elements. J. Comp. Phys. 229, 2009–2033 (2010)
Camp, B., Lin, T., Lin, Y., Sun, W.: Quadratic immersed finite element spaces and their approximation capabilities. Adv. Comp. Math. 24(4), 81–112 (2006)
Griffith, B.E., Peskin, C.S.: On the order of accuracy of the immersed boundary method: Higher order convergence rates for sufficiently smooth problems. J. Comp. Phys. 208(1), 75–105 (2005)
He, X.-M., Lin, T., Lin, Y.: A bilinear immersed finite volume element method for the diffusion equation with discontinuous coefficient. Comm. Comp. Phys. 6(1), 185–202 (2009)
Huang, H., Li, Z.: Convergence analysis of the immersed interface method. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 19(4), 583–608 (1999)
Huang, H., Li, Z.: Convergence analysis of theimmersed interface method. IMAJ. Numer. Anal. 19, 583? – 608 (1999)
Jeon, Y.: Hybrid difference methods for pdes. J. Sci. Comput. 64, 508–521 (2015)
Jeon, Y.: Hybrid spectral difference methods for elliptic equations on exterior domains with the discrete radial absorbing boundary condition. J. Sci. Comput. 75, 889–905 (2018)
Jeon, Y., Park, E.-J., Shin, D.-W.: Hybrid spectral difference methods for an elliptic equation. Comput. Meth. Appl. Math. 17, 253–267 (2017)
Jeon, Y., Sheen, D.: Upwind hybrid spectral difference methods for the steady-state navier-stokes equations. In: Dick, J., Kuo, F. (eds.) Contemporary Computational Mathematics-A Celebration of the 80th Birthday of Ian Sloan, pp. 632–641. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2018)
Jung, E., Peskin, C.S.: Two-dimensional simulations of valveless pumping using the immersed boundary method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 23(1), 19–45 (2001)
Kim, Y., Lai, M.-C., Peskin, C.S.: Numerical simulations of two-dimensional foam by the immersed boundary method. J. Comput. Phys. 229(13), 5194–5207 (2010)
Kwak, D.Y., Jin, S., Kyeong, D.H.: A stabilized P1-nonconforming immersed finite element method for the interface elasticity problems. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 51, 187–207 (2017)
Lai, M.-C., Peskin, C.S.: An immersed boundary method with formal second-order accuracy and reduced numerical viscosity. J. Comput. Phys. 160(2), 705–719 (2000)
Lee, L., LeVeque, R.: An immersed interface method for incompressible navier-stokes equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 25(3), 832–856 (2003)
LeVeque, R.J., Li, Z.: The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31(4), 1019–1044 (1994)
LeVeque, R.J., Li, Z.: Immersed interface methods for stokes flow with elastic boundaries or surface tension. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18(3), 709–735 (1997)
Li, Z.: On convergence of the immersed boundary method for elliptic interface problems. Math. Comp. 84, 1169–1188 (2015)
Li, Z., Ito, K.: The immersed interface method: Numerical solutions of PDEs involving interfaces and irregular domains, Frontiers in Applied Mathematics. SIAM Pub., (2006)
Li, Z., Lai, M.-C.: The immersed interface method for the navier-stokes equations with singular forces. J. Comp. Phys. 171(2), 822–842 (2001)
Li, Z., Lin, T., Lin, Y., Rogers, R.C.: An immersed finite element space and its approximation capability. Numer. Meth. PDEs 20(3), 338–367 (2004)
Lin, T., Sheen, D., Zhang, X.: A nonconforming immersed finite element method for elliptic interface problems. J. Sci. Comput. 79, 442–463 (2019)
Marques, A., Nave, J.-C., Rosales, R.R.: A correction function method for poisson problems with interface jump conditions. J. Comp. Phys. 230, 7567–7597 (2011)
Marques, A.N., Nave, J.-C., Rosales, R.R.: High order solution of poisson problems with piecewise constant coefficients and interface jumps. J. Comp. Phys. 335, 497–515 (2017)
Peskin, C.: The immersed boundary method. Acta Numer. 11, 479–517 (2002)
Stein, D.B., Guy, R.D., Thomases, B.: Immersed boundary smooth extension: A high-order method for solving pde on arbitrary smooth domains using fourier spectral methods. J. Comp. Phys. 304, 252–274 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The author would like express sincere thanks to Prof. Son-Young Yi at department of mathematics, UTEP for careful reading the manuscript and suggesting invaluable comments, which improved the early version of the manuscript a lot.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This author was supported by NRF 2018R1D1A1A09082082.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, Y. An immersed hybrid difference method for the elliptic interface equation. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 39, 669–692 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-022-00503-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-022-00503-4