Abstract
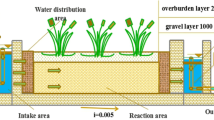
An integrated constructed wetland (ICW) with six subsystems has been operated for six years (60,000 Ton day−1) and exhibited strong stability and high efficiency for removing conventional pollutants in tail water. This study was aimed to characterize the removal efficiency of antibiotics in relation to bacterial community structure and composition in this integrated constructed wetland. Water samples were taken from different ICW sites in two distinct seasons (i.e. winter and summer). The results showed that concentrations of antibiotics in ICW decreased from influent to effluent with varying removal rates among the different antibiotics (quinolones, ulfonamides and macrolides). The pyrosequencing of 16S ribosomal DNA revealed that the composition of dominant phyla could be grouped into four bacterial clusters and the key discriminant phyla, family or genera from each cluster was strongly associated with the specific physicochemical parameters of water or type of antibiotics. Members of the key phyla (Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Parcubacteria, and Actinobacteria) appeared to play an important role in antibiotics removal. In general, both the concentration of antibiotics and physicochemical parameters of water shaped the bacterial communities. These results improve our understanding of the interactions between antibiotics or water physiochemical parameters and bacterial communities in the integrated constructed wetland.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpine wetlands in the Lhasa River Basin, China
Ansola G, Arroyo P, Saenz De Miera LE (2014) Characterisation of the soil bacterial community structure and composition of natural and constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment 473:63–71
Arroyo P, Saenz De Miera LE, Ansola G (2015) Influence of environmental variables on the structure and composition of soil bacterial communities in natural and constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment 506:380–390
Berglund B, Khan GA, Weisner SEB, Ehde PM, Fick J, Lindgren P (2014) Efficient removal of antibiotics in surface-flow constructed wetlands, with no observed impact on antibiotic resistance genes. Science of the Total Environment 476:29–37
Boonsaner M, Hawker DW (2013) Evaluation of food chain transfer of the antibiotic oxytetracycline and human risk assessment. Chemosphere 93:1009–1014
Brown KD, Kulis J, Thomson B, Chapman TH, Mawhinney DB (2006) Occurrence of antibiotics in hospital, residential, and dairy, effluent, municipal wastewater, and the Rio Grande in New Mexico. Science of the Total Environment 366:772–783
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods 7:335–336
Carvalho PN, Basto MCP, Almeida CMR (2012) Potential of Phragmites australis for the removal of veterinary pharmaceuticals from aquatic media. Bioresource Technology 116:497–501
Carvalho PN, Araujo JL, Mucha AP, Basto MCP, Almeida CMR (2013) Potential of constructed wetlands microcosms for the removal of veterinary pharmaceuticals from livestock wastewater. Bioresource Technology 134:412–416
Chen J, Wei X, Liu Y, Ying G, Liu S, He L, Su H, Hu L, Chen F, Yang Y (2016) Removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from domestic sewage by constructed wetlands: optimization of wetland substrates and hydraulic loading. The Science of Total Environment 565:240–248
Cheng C, Xie H, Yang E, Shen X, Dai P, Zhang J (2016) Nutrient removal and microbial mechanisms in constructed wetland microcosms treating high nitrate/nitrite polluted river water. RSC Advances 6:70848–70854
Dordio AV, Carvalho AJP (2013) Organic xenobiotics removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of the support matrix. Journal of Hazardous Materials 252:272–292
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Garcia-Rodriguez A, Matamoros V, Fontas C, Salvado V (2014) The ability of biologically based wastewater treatment systems to remove emerging organic contaminants-a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 21:11708–11728
Gillings M, Boucher Y, Labbate M, Holmes A, Krishnan S, Holley M, Stokes HW (2008) The evolution of class 1 integrons and the rise of antibiotic resistance. Journal of Bacteriology 190:5095–5100
Goebel A, McArdell CS, Joss A, Siegrist H, Giger W (2007) Fate of sulfonamides, macrolides, and trimethoprim in different wastewater treatment technologies. The Science of Total Environment 372:361–371
Guan W, Yin M, He T, Xie S (2015) Influence of substrate type on microbial community structure in vertical-flow constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22:16202–16209
Hijosa-Valsero M, Matamoros V, Sidrach-Cardona R, Martin-Villacorta J, Becares E, Bayona JM (2010) Comprehensive assessment of the design configuration of constructed wetlands for the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from urban wastewaters. Water Research 44:3669–3678
Huang X, Liu C, Wang Z, Gao C, Zhu G, Liu L (2013) The effects of different substrates on ammonium removal in constructed wetlands: a comparison of their physicochemical characteristics and ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotic communities. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 41:283–290
Kim SD, Cho J, Kim IS, Vanderford BJ, Snyder SA (2007) Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in south Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters. Water Research 41:1013–1021
Kosma CI, Lambropoulou DA, Albanis TA (2014) Investigation of PPCPs in wastewater treatment plants in Greece: occurrence, removal and environmental risk assessment. The Science of Total Environment 466:421–438
Kuemmerer K (2009) Antibiotics in the aquatic environment – a review – part II. Chemosphere 75:435–441
Li Y, Zhu G, Ng WJ, Tan SK (2014) A review on removing pharmaceutical contaminants from wastewater by constructed wetlands: design, performance and mechanism. The Science of Total Environment 468:908–932
Liu L, Liu Y, Liu C, Wang Z, Dong J, Zhu G, Huang X (2013) Potential effect and accumulation of veterinary antibiotics in Phragmites australis under hydroponic conditions. Ecological Engineering 53:138–143
Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhao L, Li Y, Dai Y, Xie S (2015) Distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in plateau freshwater lakes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 99:4435–4444
Liu A, Cao H, Yang Y, Ma X, Liu X (2016) Combinational effects of sulfomethoxazole and copper on soil microbial community and function. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 23:4235–4241
Lofmark S, Jernberg C, Jansson JK, Edlund C (2006) Clindamycin-induced enrichment and long-term persistence of resistant Bacteroides spp. and resistance genes. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 58:1160–1167
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Mathews S, Reinhold D (2013) Biosolid-borne tetracyclines and sulfonamides in plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 20:4327–4338
Nedashkovskaya OI, Balabanova LA, Zhukova NV, Kim S, Bakunina IY, Rhee S (2014) Flavobacterium ahnfeltiae sp nov., a new marine polysaccharide-degrading bacterium isolated from a Pacific red alga. Archives of Microbiology 196:745–752
Nicola Segata, Jacques Izard, Levi Waldron, Dirk Gevers, Larisa Miropolsky, Wendy S Garrett, Curtis Huttenhower, (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology 12 (6):R60
Papaevangelou VA, Gikas GD, Tsihrintzis VA, Antonopoulou M, Konstantinou IK (2016) Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in HSF and VF pilot-scale constructed wetlands. Chemical Engineering Journal 294:146–156
Ramond J, Welz PJ, Cowan DA, Burton SG (2012) Microbial community structure stability, a key parameter in monitoring the development of constructed wetland mesocosms during start-up. Research in Microbiology 163:28–35
Song K, Lee S, Kong H (2011) Denitrification rates and community structure of denitrifying bacteria in newly constructed wetland. European Journal of Soil Biology 47:24–29
Sorokin DY, Luecker S, Vejmelkova D, Kostrikina NA, Kleerebezem R, Rijpstra WIC, Damste JSS, Le Paslier D, Muyzer G, Wagner M, van Loosdrecht MCM, Daims H (2012) Nitrification expanded: discovery, physiology and genomics of a nitrite-oxidizing bacterium from the phylum Chloroflexi. The ISME Journal 6:2245–2256
Su H, Ying G, Tao R, Zhang R, Zhao J, Liu Y (2012) Class 1 and 2 integrons, sul resistance genes and antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from Dongjiang River, South China. Environmental Pollution 169:42–49
Truu M, Juhanson J, Truu J (2009) Microbial biomass, activity and community composition in constructed wetlands. The Science of Total Environment 407:3958–3971
Underwood JC, Harvey RW, Metge DW, Repert DA, Baumgartner LK, Smith RL, Roane TM, Barber LB (2011) Effects of the antimicrobial Sulfamethoxazole on groundwater bacterial enrichment. Environmental Science & Technology 45:3096–3101
Vanier SM, Dahab MF (2001) Start-up performance of a subsurface-flow constructed wetland for domestic wastewater treatment. Environmental Technology 22:587–596
Vymazal J (2011) Long-term performance of constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow: ten case studies from the Czech Republic. Ecological Engineering 37:54–63
Wagner M, Loy A (2002) Bacterial community composition and function in sewage treatment systems. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 13:218–227
Wang Z, Dong J, Liu L, Zhu G, Liu C (2013) Screening of phosphate-removing substrates for use in constructed wetlands treating swine wastewater. Ecological Engineering 54:57–65
Weber KP, Legge RL (2011) Dynamics in the bacterial community-level physiological profiles and hydrological characteristics of constructed wetland mesocosms during start-up. Ecological Engineering 37:666–677
Wu X, Xiang L, Yan Q, Jiang Y, Li Y, Huang X, Li H, Cai Q, Mo C (2014) Distribution and risk assessment of quinolone antibiotics in the soils from organic vegetable farms of a subtropical city, Southern China. The Science of Total Environment 487:399–406
Yan Q, Stegen JC, Yu Y, Deng Y, Li X, Wu S, Dai L, Zhang X, Li J, Wang C, Ni J, Li X, Hu H, Xiao F, Feng W, Ning D, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Wu L, Zhou J (2017) Nearly a decade-long repeatable seasonal diversity patterns of bacterioplankton communities in the eutrophic Lake Donghu (Wuhan, China). Molecular Ecology 26:3839–3850
Yang Q, Tam NFY, Wong YS, Luan TG, Su WS, Lan CY, Shin PKS, Cheung SG (2008) Potential use of mangroves as constructed wetland for municipal, sewage treatment in Futian, Shenzhen, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 57:735–743
Yang J, Ying G, Zhao J, Tao R, Su H, Liu Y (2011) Spatial and seasonal distribution of selected antibiotics in surface waters of the Pearl Rivers, China. Journal of Environmental Science Health Part B 46:272–280
Zhang Q, Ying G, Pan C, Liu Y, Zhao J (2015) Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environmental Science & Technology 49:6772–6782
Zhang H, Zheng S, Ding J, Wang O, Liu F (2017) Spatial variation in bacterial community in natural wetland-river-sea ecosystems. Journal of Basic Microbiology 57:536–546
Zhang S, Zhou Q, Xu D, et al. Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands Applied in a Recirculating Aquaculture System for Channel Catfish Culture: Effects on Water Quality and Zooplankton (vol 19, pg 1063, 2010)[J]. POLISH JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES, 2010, 19(6).
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by key program from Zhejiang Science & Technology Bureau (#2015C03007; #2018C02029); the key research and development projects from of Ministry of Science and Technology, China (#2016YFD0800805; #2019YFD0120801), and The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5048 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, A., Wang, W., Kang, K.J. et al. The Removal of Antibiotics in Relation to a Microbial Community in an Integrated Constructed Wetland for Tail Water Decontamination. Wetlands 40, 993–1004 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-019-01262-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-019-01262-8