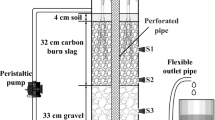
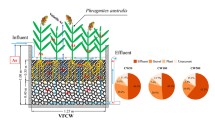
Abstract
A vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland (VF wetland) treating wastewater of a touristically used lodge was studied over a period of eight years. The study aim was to investigate if the design and the operation of VF wetlands can be adjusted to the seasonal loading of recreation facilities. Compared to standard VF wetlands, the plant was designed with a lower specific surface area. The operation was divided into a high load phase during the season and a non-loaded regeneration phase after the season. A further object of the study resulted from the operation of the VF wetland. Since the wetland is located in an area with sulfate-rich drinking water, high sulfide concentrations occur in the wastewater resulting from sulfate-reducing bacteria. While the COD and BOD5 effluent concentrations always stayed within the permissible values, ammonia oxidation was incomplete for several years. The results show the different short- and long-term effects of sulfide on ammonium and nitrite oxidation and their influences on plant operations. It is concluded that nitrite oxidizers are sensitive to sulfide during short-time observations but less sensitive than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria over long periods. Furthermore, the effect of a completely inhibited nitrification on phosphorous removal was studied.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
AbwV (1997) Ordinance on requirements for the discharge of waste water into waters (waste water ordinance - AbwV). Federal Ministry for the Environment. Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, Germany
Æsøy A, Ødegaard H, Bentzen G (1998) The effect of sulphide and organic matter on the nitrification activity in a biofilm process. Water Science and Technology 37(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00760-9
ATV-DVWK (2000) German standard ATV-DVWK-A 131 (withdrawn in 2016): Bemessung von einstufigen Belebungsanlagen (dimensioning of single-stage activated sludge plants). German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA). ISBN 3-933707-41-2
Benndorf J (2005) Ecotechnology: basis of a new immission concept in water pollution control. Water Science and Technology 52(5):17–24. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2005.0099
Beristain-Cardoso R, Gómez J, Méndez-Pampín R (2010) The behavior of nitrifying sludge in presence of sulfur compounds using a floating biofilm reactor. Bioresource Technology 101(22):8593–8598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.084
Boutin C, Prost-Boucle S (2015) Vertical flow constructed wetlands subject to load variations: an improved design methodology connected to outlet quality objectives. Water Science and Technology 72(5):817–823. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.271
Boutin C, Prost-Boucle S, Boucher M (2010) Robustness of vertical reed bed filters facing loads variations: the particular case of campsites. Proceedings of the 12th Int. Conf. On wetland Systems for Water Pollution Control, pp. 177-185, Venice, Italy
Brandenburg FS (2003) Richtlinie über den Einsatz von Kleinkläranlagen (directive on the use of small sewage treatment plants). Ministry of rural development. Environment and Agriculture of the Federal State of Brandenburg. Amtsblatt für Brandenburg 14(17):467–483
Chen KY, Morris JC (1972) Kinetics of oxidation of aqueous sulfide by O2. Environmental Science & Technology 6(6):529–537. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60065a008
Cooper P (1999) A review of the design and performance of vertical-flow and hybrid reed bed treatment systems. Water Science and Technology 40(3):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00414-X
Cooper P (2001) Constructed wetlands and reed beds: mature technology for the treatment of wastewater from small populations. Water and Environment Journal 15(2):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-6593.2001.tb00310.x
DIN (2010) Standard DIN 4261–1: Kleinkläranlagen – Teil 1: anlagen zur Schmutzwasservorbehandlung (small sewage treatment plants - part 1: plants for waste water pretreatment). DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V, Berlin
Dotro G, Langergraber G, Molle P, Nivala J, Puigagut J, Stein O, von Sperling M (2017) Treatment wetlands. Biological wastewater treatment series, Vol. 7, IWA publishing, London, UK. https://doi.org/10.2166/9781780408774
DWA (2006) Standard DWA-A 262: Grundsätze für Bemessung, Bau und Betrieb von Pflanzenkläranlagen mit bepflanzten Bodenfiltern zur biologischen Reinigung kommunalen Abwassers (DWA principles for design, construction and operation of constructed wetlands with reedbeds for the biological treatment of municipal wastewater), German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA). ISBN 978-3-939057-12-3
DWA (2016) Standard DWA-A 131: Bemessung von einstufigen Belebungsanlagen (dimensioning of single-stage activated sludge plants). German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA). ISBN 978-3-88721-331-2
DWA (2017) German standard DWA-A 262: Grundsätze für Bemessung, Bau und Betrieb von Kläranlagen mit bepflanzten und unbepflanzten Filtern zur Reinigung häuslichen und kommunalen Abwassers (DWA principles for dimensioning, construction and operation of wastewater treatment plants with planted and unplanted filters for treatment of domestic and municipal wastewater). German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA). ISBN 978-3-88721-547-7
DWA (2018) German standard DWA-A 262E: principles for dimensioning, construction and operation of wastewater treatment plants with planted and unplanted filters for treatment of domestic and municipal wastewater. German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA). ISBN 978-3-88721-641-2
Erguder TH, Boon N, Vlaeminck SE, Verstraete W (2008) Partial nitrification achieved by pulse sulfide doses in a sequential batch reactor. Environmental Science & Technology 42(23):8715–8720. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801391U
Foladori P, Ortigara ARC, Ruaben J, Andreottola G (2012) Influence of high organic loads during the summer period on the performance of hybrid constructed wetlands (VSSF + HSSF) treating domestic wastewater in the Alps region. Water Science and Technology 65(5):890–897. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.932
Füssel J, Lücker S, Yilmaz P, Nowka B, van Kessel MAHJ, Bourceau P, Hach PF, Littmann S, Berg J, Spieck E, Daims H, Kuypers MMM, Lam P (2017) Adaptability as the key to success for the ubiquitous marine nitrite oxidizer Nitrococcus. Science Advances. 3:e1700807. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700807
García J, Rousseau DPL, Morató J, Lesage E, Matamoros V, Bayona JM (2010) Contaminant removal processes in subsurface-flow constructed wetlands: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 40:561–661. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380802471076
Haaijer SCM, van der Welle MEW, Schmid MC, Lamers LPM, Jetten MSM, Op den Camp HJM (2006) Evidence for the involvement of betaproteobacterial thiobacilli in the nitrate-dependent oxidation of iron sulfide minerals. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 58(3):439–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00178.x
Hagendorf U, Bartocha W, Diehl K, Feuerpfeil I, Hummel A, Lopez-Pila J, Szewzyk R (2002) Mikrobiologische Untersuchungen zur seuchenhygienischen Bewertung naturnaher Abwasserbehandlungsanlagen (microbiological research for an epidemic-hygienic assessment of constructed wetlands). WaBoLu-Hefte, (3-02), Umweltbundesamt (German environment agency), Dessau-Roßlau (Germany)
Hayakawa A, Hatakeyama M, Asano R, Ishikawa Y, Hidaka S (2013) Nitrate reduction coupled with pyrite oxidation in the surface sediments of a sulfide-rich ecosystem. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 118(2):639–649. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrg.20060
Lewis WM, Morris DP (1986) Toxicity of nitrite to fish: a review. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 115(2):183–195. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8659(1986)115<183:TONTF>2.0.CO;2
Lucassen ECHET, Smolders AJP, van der Salm AL, Roelofs JGM (2004) High groundwater nitrate concentrations inhibit eutrophication of sulphate-rich freshwater wetlands. Biogeochemistry 67(2):249–267. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOG.0000015342.40992.cb
Lützner K, Kühn V, Müller V (1998) Pflanzenkläranlagen im Freistaat Sachsen - Leistungsfähigkeit, Betriebssicherheit und langfristige Entwicklung (constructed wetlands in the Free State of Saxony – performance, reliability, long-term trend). Report to the Department for Environment and Agriculture of the Free State of Saxony, Germany. Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Urban and Industrial Water Management, Germany
Lützner K, Müller V, Giese R, Swaboda D (2001) Sauerstoffhaushalt und Einlagerung von Feststoffen in Pflanzenbeeten – langfristige Entwicklung von Pflanzenkläranlagen (oxygen balance and solids incorporation in constructed wetlands – long term performance of constructed wetlands). Report to the Department for Environment and Agriculture of the Free State of Saxony, Germany. Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Urban and Industrial Water Management, Germany
Martinez-Guerra E, Jiang Y, Lee G, Kokabian B, Fast S, Truax DD, Martin JL, Magbanua BS, Gude VG (2015) Wetlands for wastewater treatment. Water Environment Research 87(19):1095–1126. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143015X14338845155426
Masi F, Martinuzzi N, Bresciani R, Giovannelli L, Conte G (2007) Tolerance to hydraulic and organic load fluctuations in constructed wetlands. Water Science and Technology 56(3):39–48. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2007.507
McBride GB, Tanner CC (2000) Modelling biofilm nitrogen transformations in constructed wetland mesocosms with fluctuating water levels. Ecological Engineering 14(1–2):93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(99)00022-1
Nielsen AH, Vollertsen J, Hvitved-Jacobsen T (2006) Kinetics and stoichiometry of aerobic sulfide oxidation in wastewater from sewers - effects of pH and temperature. Water Environment Research 78(3):275–283. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143005X94367
Nivala J, van Afferden M, Hasselbach R, Langergraber G, Molle P, Rustige H, Nowak J (2018) The new German standard on constructed wetland systems for treatment of domestic and municipal wastewater. Water Science and Technology 78(11):2414–2426. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.530
O’Brian DJ, Birkner FB (1977) Kinetics of oxygenation of reduced sulfur species in aqueous solution. Environmental Science & Technology 11(12):1114–1120. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60135a009
Ortiz DIB, Thalasso F, Lopez FDC, Texier AC (2013) Inhibitory effect of sulfide on the nitrifying respiratory process. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology 88(7):1344–1349. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.3982
Rao PSC, Jessup RE (1984) Simulation of nitrogen dynamics in flooded soils. Soil Science 138(1):64–62. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-198407000-00009
Schalk T (2017) Möglichkeiten zur Behandlung saisonal anfallender Abwässer in ländlich strukturierten Gebieten durch Anpassung der Bemessungsgrundlagen und temporäre Aktivierung interner Reserven (Treatment of seasonal generated wastewater in rural areas by adjusting the design criterions and activation of internal buffers). PhD thesis, Technische Unversität Dresden, Institute of Urban and Industrial Water Management, Germany
Sears K, Alleman JE, Barnard JL, Oleszkiewicz JA (2004) Impacts of reduced sulfur components on active and resting ammonia oxidizers. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 31(8):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-004-0157-2
Sikora FJ, Tong Z, Behrends LL, Steinberg SL, Coonrod HS (1995) Ammonium removal in constructed wetlands with recirculating subsurface flow: removal rates and mechanisms. Water Science and Technology 32(3):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1223(95)00620-6
Smolders AJP, Lucassen ECHET, Bobbink R, Roelofs JGM, Lamers LPM (2010) How nitrate leaching from agricultural lands provokes phosphate eutrophication in groundwater fed wetlands: the Sulphur bridge. Biogeochemistry 98(1–3):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9387-8
TrinkwV (2001) Ordinance on the quality of water intended for human consumption (Trinkwasserverordnung – TrinkwV). Federal Ministry of Health, Germany
Vasudevan P, Griffin P, Warren A, Thapliyal A, Tandon M (2011) Localized domestic wastewater treatment: part I – constructed wetlands (an overview). Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research 70:583–594
von Felde K, Kunst S (1997) N- and COD-removal in vertical-flow systems. Water Science and Technology 35(5):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00055-3
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment 380(1–3):48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.09.014
Wiessner A, Kuschk P, Jechorek M, Seidel H, Kästner M (2007) Sulphur transformation and deposition in the rhizosphere of Juncus effusus in a laboratory-scale constructed wetland. Environmental Pollution 155(1):125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.10.027
Wiessner A, Rahman KZ, Kuschk P, Kästner M, Jechorek M (2010) Dynamics of Sulphur compounds in horizontal sub-surface flow laboratory-scale constructed wetlands treating artificial sewage. Water Research 44(20):6175–6185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.07.044
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt DBU (German Federal Environmental Foundation) for financing the projects with the grant numbers AZ 27143/1, AZ 27143/2, and AZ 32535/01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schalk, T., Marx, C., Haupt, A. et al. Long-Term Effects of Sulfide on Ammonia Oxidation and Nitrite Accumulation in a Seasonally Loaded Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland. Wetlands 40, 205–222 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-019-01185-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-019-01185-4