Abstract
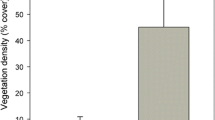
The Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) is an exotic benthivorous fish that can have negative impacts in aquatic ecosystems. This study examines the direct and indirect ecological impacts of Common Carp on water column nutrient concentrations, suspended solids, sedimentation, and submersed macrophytes in large (5–7 ha) experimental wetlands in Delta Marsh, Manitoba, Canada. In general, the effects of Common Carp on water quality were similar to those encountered in systems undergoing cultural eutrophication. With increasing densities of Common Carp, water column nutrient concentrations, suspended solids, and chlorophyll a increased while dissolved oxygen concentrations, submersed macrophyte density, and photic depth decreased. The wetlands did not become noticeably more turbid, contrary to our expectation, probably due to the mitigating effects of dense submersed macrophyte beds, and to high water color that likely prevented phytoplankton from flourishing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson G, Berggren H, Cronberg G, Gelin C (1978) Effects of planktivorous and benthivorous fish on organisms and water chemistry in eutrophic lakes. Hydrobiologia 59:9–15
Angeler DG, Alvarez-Cobelas M, Sanchez-Carrillo S, Rodrigo MA (2002) Assessment of exotic fish impacts on water quality and zooplankton in a degraded semi-arid floodplain wetland. Aquatic Science 64:76–86
Atton FM (1959) The invasion of Manitoba and Saskatchewan by carp. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 88:203–205
Barton DR, Kelton N, Eedy RI (2000) The effects of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) on sediment export from a small urban impoundment. Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress and Recovery 8:155–159
Breukelaar AW, Lammens EHRR, Klein Breteler JGP, Tátrai I (1994) Effects of benthivorous bream (Abramis brama) and carp (Cyprinus carpio) on sediment resuspension and concentrations of nutrients and chlorophyll a. Freshwater Biology 32:113–121
Carlson RE (1977) A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 22:361–369
Cline JM, East TL, Threkeld ST (1994) Fish interaction with the sediment-water interface. Hydrobiologia 275(276):301–311
Cooper EL (1987) Carp in North America. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda
Environment Canada (2003) Canadian guidance framework for the management of phosphorus in freshwater systems. Environment Canada, National Guidelines and Standards Office, Water Policy and Coordination Directorate, Gatineau, Québec, Canada
Havens KE (1991) Fish-induced sediment resuspension: effects on phytoplankton biomass and community structure in a shallow hypereutrophic lake. Journal of Plankton Research 13:1163–1176
Hnatiuk S (2006) Experimental manipulation of ponds to determine the impact of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) in Delta Marsh, Manitoba: Effects on water quality, algae, and submersed vegetation. MSc Thesis, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada
Jeppesen E, Jensen JP, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen T, Pedersen LJ, Jensen L (1997) Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submersed macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia 342(343):151–164
Kadlec JA (1986) Effects of flooding on dissolved and suspended nutrients in small diked marshes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 43:1999–2008
Keen WH, Gagliardi J (1981) Effect of brown bullheads on release of phosphorus, in sediment and water systems. The Progressive Fish-Culturist 43:183–185
King AJ, Robertson AI, Healey MR (1997) Experimental manipulations of the biomass of introduced carp (Cyprinus carpio) in billabongs. I. Impacts on water-column properties. Marine and Freshwater Research 48:435–443
Koehn JD (2004) Carp (Cyprinus carpio) as a powerful invader in Australian waterways. Freshwater Biology 49:882–894
Kolterman BF (1990) Effects of Common Carp and black bullheads on sago pondweed. MS Thesis. South Dakota State University, Brookings, USA
Lougheed VL, Crosbie B, Chow-Fraser P (1998) Predictions on the effects of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) exclusion on water quality, zooplankton, and submergent vegetation in a Great Lakes wetland. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 55:1189–1197
Lougheed VL, Theÿsmeÿer T, Smith T, Chow-Fraser P (2004) Carp exclusion, food-web interactions, and the restoration of Cootes Paradise Marsh. Journal of Great Lakes Research 30:44–57
Marker AFH, Nusch EA, Rai H, Riemann B (1980) The measurement of photosynthetic pigments in freshwaters and standardization of methods: conclusions and recommendations. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Beiheft: Ergebnisse der Limnologie 14:91–106
Meijer ML, Raat AJP, Doef RW (1989) Restoration of Lake Bleiswijkse Zoom (The Netherlands): first results. Hydrobiology Bulletin 23:49–57
Murkin HR, Batt BDJ, Caldwell PJ, Kadlec JA, van der Valk AG (2000) Introduction to the marsh ecology research program. In: Murkin HR, van der Valk AG, Clark WR (eds) Prairie wetland ecology: the contribution of the marsh ecology research program. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 3–6
Newcombe CP, MacDonald DD (1991) Effects of suspended sediments on aquatic ecosystems. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 11:72–82
Parkos JJ, Santucci VJ, Wahl DH (2003) Effects of adult Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) on multiple trophic levels in shallow mesocosms. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60:182–192
Robel RJ (1961) The effects of carp populations on the production of waterfowl food plants on a western waterfowl marsh. Transactions of the North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference 26:147–159
Roberts J, Chick A, Oswald L, Thompson P (1995) Effect of carp, Cyprinus carpio L., an exotic benthivorous fish, on aquatic plants and water quality in experimental ponds. Marine and Freshwater Research 46:1171–1180
Robertson AI, Healey MR, King AJ (1997) Experimental manipulations of the biomass of introduced carp (Cyprinus carpio) in billabongs. II. Impacts on benthic properties and processes. Marine and Freshwater Research 48:445–454
Sager EPS, Whillans TH, Fox MG (1998) Factors influencing the recovery of submersed macrophytes in four coastal marshes of Lake Ontario. Wetlands 18:256–265
Scheffer M (1998) Ecology of shallow lakes. Chapman & Hall, Toronto
Scheffer M (1999) The effect of aquatic vegetation on turbidity; how important are the filter feeders? Hydrobiologia 408(409):307–316
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer M-L, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 8:275–279
Shormann DE, Cotner JB (1997) The effects of benthivorous smallmouth buffalo (Ictiobus bubalus) on water quality and nutrient cycling in a shallow floodplain lake. Journal of Lake Research Management 13:270–278
Smil V (2000) Phosphorus in the environment: natural flows and human interferences. Annual Review of Energy and Environment 25:53–88
Stainton MP, Capel MJ, Armstrong FAJ (1977) The chemical analysis of fresh water, 2nd edn. Canadian Fisheries and Marine Service Miscellaneous Special Publication 25
Timms RM, Moss B (1984) Prevention of growth of potentially dense phytoplankton populations by zooplankton grazing, in the presence of zooplanktivorous fish, in a shallow wetland ecosystem. Limnology and Oceanography 29:472–486
Wainright SC (1987) Stimulation of heterotrophic microplankton production by resuspended marine sediments. Science 238:1710–1712
Zambrano L, Perrow M, Macías-García C, Aguirre-Hidalgo V (1999) Impact of introduced carp (Cyprinus carpio) in subtropical shallow ponds in Central Mexico. Journal of Aquatic and Ecosystem Stress and Recovery 6:281–288
Zambrano L, Scheffer M, Martinez-Ramos M (2001) Catastrophic response of lakes to benthivorous fish introduction. Oikos 94:344–350
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by Ducks Unlimited Canada and a Discovery Grant to Gordon Goldsborough from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and logistically by the Delta Marsh Field Station (University of Manitoba). We thank Dan Leitch, Andrea Patenaude, and Birte Gerdes for help in the field, Llwellyn Armstrong for statistical advice, and Vania Nunes-Halldorson for her assistance in assembling this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badiou, P.H.J., Goldsborough, L.G. Ecological Impacts of an Exotic Benthivorous Fish in Large Experimental Wetlands, Delta Marsh, Canada. Wetlands 30, 657–667 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-010-0071-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-010-0071-5