Abstract
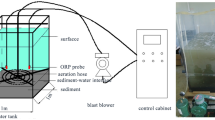
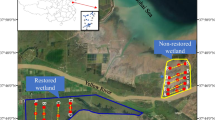
Surface waters in Taihu Basin, China are increasingly threatened by phosphorus (P) related eutrophication. This study investigated the temporal-spatial status of P in sediment-water in riparian wetlands located in the southern region of Taihu Basin. Two sets of laboratory simulation study, 1) static columns and 2) steady-flow flumes representing wetland in both dry and rainy seasons, were carried out to understand the characteristics and mechanisms of P interaction between sediment and overlying water. In wetland sediments, significant increases in total P (TP) and NaHCO3 (pH = 8.5) extractable P (Olsen-P) occurred with the increase of NaOH + EDTA extractable P (NaOH + EDTA-P). After comparing the P adsorption capacity (Q max ) with TP in the sediment, there could be a risk of P export from the sediment. In the static column experiment, dynamic characteristics of dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP) in the overlying water can be divided into buffer reaction, rapid adsorption, and slow adsorption. A quasi U-pattern curve was observed in the steady-flow flume experiment, i.e., DRP in the overlying water decreased initially and then increased. Because upstream water with high P concentration flowed over the test wetland during rainy seasons, the ecological role of P interception by the sediment could be weakened.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren J, Tranvik L, Gogoll A, Waldeback M, Markides K, Rydin E (2005) Sediment depth attenuation of biogenic phosphorus compounds measured by 31P NMR. Environmental Science and Technology 39:867–872
Bao SD (2000) Agro-chemical analysis of soil. China Agricultural, Beijing
Cade-Menun BJ, Preston CM (1996) A comparison of soil extraction procedures for 31P NMR spectroscopy. Soil Science 161:770–785
Carpenter SR (2005) Eutrophication of aquatic ecosystems: bistability and soil phosphorus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102:10002–10005
EPA China (2002) Analysis methods of water and wastewater. China Environmental Science, Beijing
Dunne EJ, Reddy R, Clark MW (2006) Biogeochemical indices of phosphorus retention and release by wetland soils and adjacent stream sediments. Wetlands 26:1026–1041
Elser JJ, Bracken MES, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters 10:1135–1142
Fink DF, Mitsch WJ (2007) Hydrology and biogeochemistry in a created river diversion oxbow wetland. Ecological Engineering 30:93–102
Groffman P, Baron J, Blett T, Gold A, Goodman I, Gunderson L, Levinson B, Palmer M, Paerl H, Peterson G, Poff N, Rejeski D, Reynolds J, Turner M, Weathers K, Wiens J (2006) Ecological thresholds: the key to successful environmental management or an important concept with no practical application? Ecosystems 9:1–13
Haygarth PM, Jarvis SC (1997) Soil derived phosphorus in surface runoff from grazed grassland lysimeters. Water Research 31:140–148
Hooda PS, Moynagh M, Svoboda IF, Edwards AC, Anderson HA, Sym G (1999) Phosphorus loss in drainflow from intensively managed grassland soils. Journal of Environmental Quality 28:1235–1242
House WA, Denison FH (2002) Exchange of inorganic phosphate between river waters and bed-sediments. Environmental Science and Technology 36:4295–4301
Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Jensen JP, Havens KE, Anneville O, Carvalho L, Coveney MF, Deneke R, Dokulil MT, Foy B, Gerdeaux D, Hampton SE, Hilt S, Kangur K, Kohler J, Lammens EHHR, Lauridsen TL, Manca M, Miracle MR, Moss B, Noges P, Persson G, Phillips G, Portielje R, Romo S, Schelske CL, Straile D, Tatrai I, Willen E, Monika W (2005) Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading–an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology 50:1747–1771
Jin XC, Wang SR, Pang Y, Wu FC (2006) Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution 139:288–295
Koopmans GF, Chardon WJ, McDowell RW (2007) Phosphorus movement and speciation in a sandy soil profile after long-term animal manure applications. Journal of Environmental Quality 36(1):305–315
Li M, Wei HP, Wang GQ, Ni JR (2004) Study on the distribution and different forms of phosphorus in sediments from the Changjiang Estuary and the Hangzhou Bay. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 26(2):125–131
Li T, Wang DS, Zhang B, Liu HJ, Tang HX (2006) Characterization of the phosphate adsorption and morphology of sediment particles under simulative disturbing conditions. Journal of Hazardous Material 137:1624–1630
May RM (1977) Thresholds and breakpoints in ecosystems with a multiplicity of stable states. Nature 269:471–477
McDowell R, Sharpley A, Withers P (2002) Indicator to predict the movement of phosphorus from soil to subsurface flow. Environmental Science and Technology 36:1505–1509
Mitsch WJ, Zhang L, Anderson CJ, Altor A, Hernandez M (2005) Creating riverine wetlands: ecological succession, nutrient retention, and pulsing effects. Ecological Engineering 25:510–527
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphorus in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27(31e):3631–3636
Nairn RW, Mitsch WJ (2000) Phosphorus removal in created wetland ponds receiving river overflow. Ecological Engineering 14:107–126
Pant HK, Reddy KR (2003) Potential internal loading of phosphorus in a wetland constructed in agricultural land. Water Research 37:965–972
Peng JF, Wang BZ, Song YH, Yuan P, Liu ZH (2007) Adsorption and release of phosphorus in the surface sediment of a wastewater stabilization pond. Ecological Engineering 31:92–97
Qin BQ, Xu PZ, Wu QL, Luo LC, Zhang YL (2007) Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581:3–14
Scheffer M, Carpenter S, Foley JA, Folke C, Walker B (2001) Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 413:591–596
Selig U, Hübener T, Michalik M (2002) Dissolved and particulate phosphorus forms in a eutrophic shallow lake. Aquatic Science 64:97–105
Shao ZC, Zhao MZ (2002) Activation kinetics of accumulative phosphorus in soils: I. the effects of organic matter. Acta Pedologica Sinica 39:318–325
Sharpley AN, Chapra SC, Wodepohl R (1994) Managing agriculture phosphorus protection of floodwaters: issues and options. Journal of Environmental Quality 23:437–451
Sondergaard M, Jensen JP, Jeppesen E (2003) Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506–509:135–145
Song ZG, Gao XJ, Zhang C (2007) Distribution, existed forms and ecological significance of phosphorus in tide-beach surface sediments of the Hangzhou Bay. Chinese Journal of Ecology 26:853–858
Tian JR, Zhou PJ (2007) Phosphorus fractions of floodplain sediments and phosphorus exchange on the sediment–water interface in the lower reaches of the Han River in China. Ecological Engineering 30:264–270
Turner BJ, Newman S (2005) Phosphorus cycling in wetland soils: the importance of phosphate diesters. Journal of Environmental Quality 34:1921–1929
Verhoeven JTA, Arheimer B, Yin CQ, Hefting MM (2006) Regional and global concerns over wetlands and water quality. Trends of Ecology and Evolution 21:96–103
Wang SR, Jin XC, Zhao HC, Zhou XN, Wu FC (2007) Effect of organic matter on the sorption of dissolved organic and inorganic phosphorus in lake sediments. Colloid Surface A 297:154–162
Weilhoefer CL, Pan YD, Eppard S (2008) The effects of river floodwaters on floodplain wetland water quality and diatom assemblages. Wetlands 28:473–486
Yin CQ, Shao X, Wang X (1999) Retention capacity of phosphorus and nitrogen by land/water ecotone soil in Lake Baiyangdian. Chinese Journal of Ecology 18:7–11
You BS, Zhong JC, Fan CX, Wang TC, Zhang L, Ding SM (2007) Effects of hydrodynamics processes on phosphorus fluxes from sediment in large, shallow Taihu Lake. Journal of Environmental Science-China 19:1055–1060
Zhang MK, Zhou C, Fang LP (2006) Environmentally sensitive thresholds of phosphorus of paddy soils. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 25:170–174
Zhang ZJ, Zhang JY, He R, Wang ZD, Zhu YM (2007) Phosphorus interception in floodwater of paddy field during the rice-growing season in Taihu Lake Basin. Environmental Pollution 145:425–433
Zhu GW, Qin BQ, Gao G, Zhang L, Fan CX (2004) Fractionation of phosphorus in sediments and its relation with soluble phosphorus contents in shallow lakes located in the middle and lower reaches of Changjiang River, China. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 24:381–388
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Project of China (2007CB109305), and Natural Science Foundation of China (40701162, Y506215). We thank anonymous reviewers for assistance in improving English usage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yao, J., Li, S. et al. Spatial Status and Retention Potential of Phosphorus in Riparian Wetlands of the Southern Taihu Basin, China. Wetlands 30, 149–157 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-009-0006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-009-0006-1