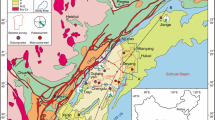
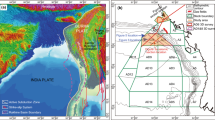
Abstract
The recognition of incised valleys and the reconstruction of their filling history are significant for defining unconformity surfaces and their stratigraphic framework, particularly when detailed petrographic data are missing. However, little of such research is published so far on the characterization and factors influencing the development of incised valleys using three-dimensional seismic and well data. Thus, this work aims to examine and analyze the geometry and factors controlling the formation and sediments filling of an Eocene incised valley in a sequence stratigraphic frame using an integration of three-dimensional seismic and well data from NE Sirte Basin, Libya. The Eocene incised valley is defined by an unconformable sequence boundary underneath and contains sediments of the lowstand systems tract of Sequence 6. The incision deposits are thick limestones intercalated by thin shales and show a low-order stacking of serrated log motif. The thickness of the incised valley is 118 m and has an aerial extension of ~ 3.2 km in a southwest-northeast direction. Its uppermost width was found to be ranging between 950 and 1100 m and displays a moderately sinuous geometry with asymmetrical meanders occurring each 1 to 1.8 km. The amplitude of these meanders ranges from 500 to 700 m. No distinguishable tributaries are observed in the studied incised valley, indicating the formation of a singular stream or possibly the seismic data resolution not capable to identify small size tributaries. The geometry and stratigraphic architecture of the incised valley suggest a fluvial rather than tidal incisions. The incision primarily formed as a result of a falling sea-level that led to a subaerial exposure, while a successive rising sea-level caused the development of the lowstand deposits and infilling of the incised valley.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Abadi AM, Van Wees JD, Van Dijk PM, Cloetingh SA (2008) Tectonics and subsidence evolution of the Sirte Basin, Libya. AAPG Bull 92(8):993–1027
Abdalla M (2021) Seismic Attributes Aided Characterization of Margin Backstepping and Advance Along Carbonate Sequences, Sirte Basin, Libya. Al-Mukhtar Journal of Sciences. 36 (4): 280–287, 2021
Abdalla M, Yang W (2021) Progradation of a middle Eocene carbonate slope system, Assamoud Field, Sirte Basin, north central Libya – implications on the dynamics of lateral growth of isolated carbonate platforms. Mar Pet Geol, 105119
Abdalla M, Yang W (2022) Characterization and evolution of a carbonate basin floor fan on a leeward side of an isolated carbonate platform, Sirte Basin, Libya. J Afr Earth Sc 196:104675
Abdalla M, Yang W, El Ebaidi S (2023a) Sequence stratigraphic architecture, evolution, and geological controls of an Eocene isolated carbonate platform, NE Sirte Basin, Libya. J Afr Earth Sc 201:104884
Abdalla M, Yang W, Shaniba S (2023b) Growth and demise of a Paleocene isolated carbonate platform, northwest Sirte Basin, Libya: sequence stratigraphic architecture and controlling factors. AAPG Bull 107(10):1723–1752
Allan JR, Matthews RK (1982) Isotope signatures associated with early meteoric diagenesis: Sedimentology, v. 29, p. 797–817
Ambrose G (2000) The geology and hydrocarbon habitat of the Sarir Sandstone, SE Sirte Basin, Libya. J Pet Geol 23(2):165–192
Asquith GB, Daniel Krygowski, Charles Gibson R (2004) Basic well log analysis, vol 16. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa
Asquith GB, Gibson CR (1982) Basic well log analysis for geologists AAPG methods in exploration series. Am Association Petroleum Geol Okla 216p
Baird WD, Aburawi RM, and, Bailey JN (1996) Geohistory and petroleum in the central Sirte Basin, in Salem M. J., Busrewil M. T., Misallati A. A., & Sola M. A., eds., The geology of the Sirte Basin: Amsterdam, Elsevier, vol. 3, pp. 3–56
Barr FT, Weegar AA (1972) Stratigraphic nomenclature of the Sirte Basin, Libya. Petroleum Exploration Society of Libya, pp 1–179
Boardman MR, Carney C (1991) Origin and accumulation of lime mud in ooid tidal channels, Bahamas. J Sediment Petrol v 61:p661–680
Catuneanu O (2006) Principles of sequence stratigraphy. Elsevier
El-Ghoul A (1996) An approach to locate subtle Waha structural traps on the Zelten Platform: geology and geophysics
Ferreri V, Weissert H, D’argenio B, Buonocunto FP (1997) Carbon isotope stratigraphy: a tool for basin to carbonate platform correlation, vol 9. Terra Nova, pp 57–61
Gomez-Perez I, Fernandez-Mendiola PA, Garcia-Mondejar J (1998) In: Wright VP, Burchette TP (eds) Constructional dynamics for a lower cretaceous carbonate ramp. Special Publication, vol 149. Geological Society of London, Carbonate Ramps, pp 229–252
Grélaud C, Razin P, Homewood P, Schwab A (2006) Development of incisions on a periodically emergent carbonate platform (natih formation, late cretaceous, Oman). J Sediment Res 76:647–669
Grélaud C, Razin P, Homewood P (2010) Channelized systems in an inner carbonate platform setting: differentiation between incisions and tidal channels (natih formation, late cretaceous, Oman). Geol Soc Lond Special Publications 3291:163–186
Haq B (1981) Paleogene paleoceanography: early cenozoic oceans revisited. Oceanol Acta Special Issue 4:71–82
Hassan S, Zafir A, Ibrahem A, Abdalla M (2022) Microfacies and depositional environment of the Lower Oligocene Al Bayda formation, N Cyrenaica Promontory, NE Libya. Libyan J Basic Sci 17(1):56–71
Miller KG, Kominz MA, Browning JV, Wright JD, Mountain GS, Katz ME, Pekar SF (2005) The phanerozoic record of global sea-level change. Science 310(5752):1293–1298
Mitchum RM Jr, Vail PR, Iii T, S (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level: Part 2. The depositional sequence as a basic unit for stratigraphic analysis: Sect. 2. Application of seismic reflection configuration to stratigraphic interpretation
Mohammed A, Nassar A, Aboharara A, Abdalla M (2022) Sedimentary facies, Depositional Environment, and high-resolution sequence stratigraphy of Dernah formation, N Cyrenaica Promontory, NE Libya. Libyan J Basic Sci 16:12
Mouzughi AJ, Taleb TM (1981) Tectonic elements of Libya (1: 2,000,000). National Oil Corporation of Libya
Rankey EC, Bachtel SL, Kaufman J (1999) Controls on stratigraphic architecture of icehouse mixed carbonate–siliciclastic systems: a case study from the holder formation (Pennsylvanian, Virgilian), Sacramento Mountains, New Mexico. In: Harris PM, Saller AH, Simo JAT (eds) Recent advances in Carbonate sequence stratigraphy: applications to reservoirs. SEPM, Outcrops, and Models, pp 127–150. Special Publication 63
Roohi M (1996) A geological view of source-reservoir relationships in the western Sirte Basin. Geol Sirte Basin: Amsterdam Elsevier 2:323–336
Sarg JF (1988) Carbonate sequence stratigraphy, in Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.S., Kendall, C.G.St.C., Posamentier, H.W., Ross, C.A., and Van Wagoner, J.C., eds., Sea-Level Changes: An Integrated Approach: SEPM, Special Publication 42, pp. 155–182
Sattler U, Immenhauser A, Hillga¨ Rtner H, Esteban M (2005) Characterization, lateral variability and lateral extent of discontinuity surfaces on a carbonate platform (Barremian to Lower Aptian, Oman). Sedimentology v 52:p339–361
Schlager W, Reijmer JJ, Droxler A (1994) Highstand shedding of carbonate platforms. J Sediment Res 64(3b):270–281
Scotese CR, Paleogeography PALEOMAP, Project (2001) Arlington, Texas. Atlas Earth History, 1, 52
Signell RP, Carniel S, Cavaleri L, Chiggiato J, Doyle J, Pullen J, Sclavo M (2005) Assessment of wind quality for oceanographic modeling in semi-enclosed basins. J Mar Syst 53(1–4):217–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marsys.2004.03.006
Tucker ME (1993) In: Wright P (ed) Carbonate diagenesis and sequence stratigraphy. Glasgow, Blackwell Science, Sedimentology Review I, pp 5l–72
Wilson JL, Cyclic and reciprocal sedimentation in Virgilian strata of southern New Mexico: Geological Society of America, Bulletin, v. 78, pp. 805–818., Wright VP (1967) 1994, Paleosols in shallow marine carbonate sequences: Earth-Science Reviews, v. 35, pp. 367–395
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully thank the Sirte Oil Company in Libya for the datasets utilized in this research. We also thank Omar Al-Mukhtar University for providing the software and machines used in this study. The authors gratefully thank the editor and reviewers for their suggestions and comments in the early version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A wrote the main manuscript. B supervising. C helped with used softwares. D helped with the 3D seismic interpretation. E organising manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdalla, M., Yang, W., Ibrahem, A. et al. Creation and fill of an Eocene incision on a leeward margin of an isolated carbonate platform, northeast Sirte Basin, Libya. Carbonates Evaporites 39, 54 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-024-00969-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-024-00969-y