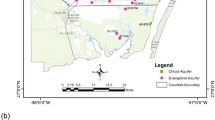
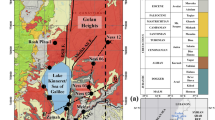
Abstract
Understanding the hydro-chemical evolution characteristics of groundwater is of great significance for the sustainable management and utilization of groundwater resources. In this study, the evolution characteristics of groundwater in northeast of Jianghan Plain were studied by hydro chemistry and isotope analysis, multivariate statistical analysis, and inverse geochemical modeling. First, a total of 130 groundwater samples were collected from three different aquifers for anion and cation analysis and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes analysis. Then the hydro-chemical type, composition, ion relationship, and evolution law of the three aquifers were discussed detailedly. Finally, inverse geochemical modeling and principal component analysis were carried out. The results show that the hydro-chemical types, anions and cations of the Holocene (Qhal) aquifer in the study area are more diverse. The inverse geochemical model indicates that water–rock interaction is one of the factors affecting the chemical evolution of groundwater. The relatively higher concentrations of Na+ and Cl− in Paleogene (Ey) aquifer may be originated from the dissolution of saline minerals in red sandstone. The evaporation intensities of the three aquifers are controlled by the depth of the aquifer. Anthropogenic activities might have a greater effect on the Qhal aquifer, but a less effect on the Ey aquifer. This work not only strengthens the understanding of groundwater evolution in this area, but also provides a reference for groundwater analysis in other similar areas.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All relevant data are included in the paper or Supplementary Information.
References
Adiya T, Johnson CL, Loewen MA, Ritterbush KA, Constenius KN, Dinter CM (2017) Microbial-caddisfly bioherm association from the lower cretaceous shinekhudag formation, Mongolia: earliest record of plant armoring in fossil caddisfly cases. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0188194. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188194
Al-Mashakbeh HM (2017) The influence of lithostratigraphy on the type and quality of stored water in Mujib Reservoir-Jordan. J Environ Prot 8(04):568–590. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2017.84038
Andersen MS, Nyvang V, Jakobsen R, Postma D (2005) Geochemical processes and solute transport at the seawater/freshwater interface of a sandy aquifer. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(16):3979–3994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.017
Aravena R, Suzuki O (1990) Isotopic evolution of river water in the northern Chile region. Water Resour Res 26(12):2887–2895. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR026i012p02887
Ayadi Y, Mokadem N, Besser H, Khelifi F, Harabi S, Hamad A, Boyce A, Laouar R, Hamed Y (2018) Hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (δ18O and δ2H) tools applied to the study of karst aquifers in southern mediterranean basin (Teboursouk area, NW Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 137:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.10.018
Barnes CJ, Allison GB (1988) Tracing of water movement in the unsaturated zone using stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. J Hydrol 100(1–3):143–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(88)90184-9
Blasch KW, Bryson JR (2007) Distinguishing sources of ground water recharge by using δ2H and δ18O. Ground Water 45(3):294–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2006.00289.x
Bretzler A, Osenbruck K, Gloaguen R, Ruprecht JS, Kebede S, Stadler S (2011) Groundwater origin and flow dynamics in active rift systems—a multi-isotope approach in the Main Ethiopian Rift. J Hydrol 402(3–4):274–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.022
Cates DA, Knox RC, Sabatini DA (1996) The impact of ion exchange processes on subsurface brine transport as observed on Piper diagrams. Ground Water 34(3):532–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1996.tb02035.x
Chadha DK (1999) A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrogeol J 7(5):431–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100400050216
Christophersen N, Hooper RP (1992) Multivariate analysis of stream water chemical data: the use of principal components analysis for the end-member mixing problem. Water Resour Res 28(1):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1029/91WR02518
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis, New York
Davis SN, Whittemore DO, Fabrykamartin J (1998) Uses of chloride/bromide ratios in studies of potable water. Ground Water 36(2):338–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb01099.x
Du Y, Ma T, Deng Y, Shen S, Lu Z (2017) Sources and fate of high levels of ammonium in surface water and shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Environ Sci-Process Impacts 19(2):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6em00531d
Du Y, Deng Y, Ma T, Lu Z, Shen S, Gan Y, Wang Y (2018a) Hydrogeochemical evidences for targeting sources of safe groundwater supply in arsenic-affected multi-level aquifer systems. Sci Total Environ 645:1159–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.173
Du Y, Ma T, Deng Y, Shen S, Lu Z (2018b) Characterizing groundwater/surface-water interactions in the interior of Jianghan Plain, central China. Hydrogeol J 26(4):1047–1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1709-7
Gan Y, Wang Y, Duan Y, Deng Y, Guo X, Ding X (2014) Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Jianghan Plain, central China. J Geochem Explor. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.12.013
Gan YQ, Zhao K, Deng YM, Liang X, Ma T, Wang YX (2018) Groundwater flow and hydro-geochemical evolution in the Jianghan Plain, central China. Hydrogeol J 26(5):1609–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1778-2
Gomaah M, Meixner T, Korany EA, Garamoon H, Gomaa MA (2016) Identifying the sources and geochemical evolution of groundwater using stable isotopes and hydrogeochemistry in the Quaternary aquifer in the area between Ismailia and El Kassara canals Northeastern Egypt. Arab J Geosci 9(6):437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2444-4
Halim MA, Majumder RK, Nessa SA, Hiroshiro Y, Sasaki K, Saha BB, Saepuloh A, Jinno K (2010) Evaluation of processes controlling the geochemical constituents in deep groundwater in Bangladesh: spatial variability on arsenic and boron enrichment. J Hazard Mater 180(1–3):50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.008
Harford CL, Sparks RSJ (2001) Recent remobilisation of shallow-level intrusions on Montserrat revealed by hydrogen isotope composition of amphiboles. Earth Planet Sci Lett 185(3–4):285–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00373-3
Huang P, Wang X (2018) Piper-PCA-fisher recognition model of water inrush source: a case study of the Jiaozuo Mining Area. Geofluids 2018:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9205025
Jiang X, Wan L, Wang X, Wang D, Wang H, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Zhao K (2018) A multi-method study of regional groundwater circulation in the Ordos Plateau NW China. Hydrogeol J 26(5):1657–1668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1731-4
Katz BU, Coplen TB, Sullen TD (1997) Use of chemical and isotopic tracers to characterize the interactions between ground water and surface water in Mantled Karst. Ground Water 35:1014–1028. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1997.tb00174.x
Kazakis N, Mattas C, Pavlou A, Patrikaki O, Voudouris K (2017) Multivariate statistical analysis for the assessment of groundwater quality under different hydrogeological regimes. Environ Earth Sci 76(9):349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6665-y
Khalil MM, Tokunaga T, Yousef AF (2015) Insights from stable isotopes and hydrochemistry to the Quaternary groundwater system, south of the Ismailia canal, Egypt. J Hydrol 527:555–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.05.024
Lecomte KL, Pasquini AI, Depetris PJ (2005) Mineral weathering in a semiarid mountain river: its assessment through PHREEQC inverse modeling. Aquat Geochem 11(2):173–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-004-3523-9
Lihe Y, Guangcai H, Zhengping T, Ying L (2010) Origin and recharge estimates of groundwater in the ordos plateau, People’s Republic of China. Environ Earth Sci 60(8):1731–1738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0310-3
McArthur JM, Sikdar PK, Hoque MA, Ghosal U (2012) Waste-water impacts on groundwater: Cl/Br ratios and implications for arsenic pollution of groundwater in the Bengal Basin and Red River Basin, Vietnam. Sci Total Environ 437:390–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.068
McGuire KJ, DeWalle DR, Gburek WJ (2002) Evaluation of mean residence time in subsurface waters using oxygen-18 fluctuations during drought conditions in the mid-Appalachians. J Hydrol 261(1–4):132–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00006-9
Mertler CA, Reinhart RV (2016) Advanced and multivariate statistical methods: practical application and interpretation, 6th edn. Routledge, New York
Mokadem N, Demdoum A, Hamed Y, Bouri S, Hadji R, Boyce AJ, Laouar R, Sâad A (2016) Hydrogeochemical and stable isotope data of groundwater of a multi-aquifer system: Northern Gafsa basin–Central Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 114:174–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.11.010
Momen B, Eichler LW, Boylen CW, Zehr JP (1996) Application of multivariate statistics in detecting temporal and spatial patterns of water chemistry in Lake George, New York. Ecol Model 91(1–3):183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(95)00189-1
Mountadar S, Younsi A, Hayani A, Siniti M, Tahiri S (2018) Groundwater salinization process in the coastal aquifer Sidi Abed-Ouled Ghanem (Province of El Jadida, Morocco). J Afr Earth Sci 147:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.06.025
Mukherjee A, Bhattacharya P, Shi F, Fryar AE, Mukherjee AB, Xie ZM, Jacks G, Bundschuh J (2009) Chemical evolution in the high arsenic groundwater of the Huhhot basin (Inner Mongolia, PR China) and its difference from the western Bengal basin (India). Appl Geochem 24(10):1835–1851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.06.005
Niu B, Wang H, Loáiciga HA, Hong S, Shao W (2017) Temporal variations of groundwater quality in the Western Jianghan Plain, China. Sci Total Environ 578:542–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.225
Qin D, Turner JV, Pang Z (2005) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater circulation in the Xi’an geothermal field. China Geotherm 34(4):471–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2005.06.004
Rodriguez M, Sfer A, Sales A (2016) Application of chemometrics to hydrochemical parameters and hydrogeochemical modeling of Calera River basin in the Northwest of Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 75(6):500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5328-8
Sharif MU, Davis RK, Steele KF, Kim B, Kresse TM, Fazio JA (2008) Inverse geochemical modeling of groundwater evolution with emphasis on arsenic in the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer, Arkansas (USA). J Hydrol 350(1–2):41–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.11.027
Shi D, Yin X, Sun J, Yin Z (1998) A simulation study on the evolution of groundwater circulation systems in Cenozoic basins of Northern China. Acta Geol Sin 72(1):100–107. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.1998.tb00737.x
Slimani R, Guendouz A, Trolard F, Moulla AS, Hamdi-Aïssa B, Bourrié G (2017) Identification of dominant hydrogeochemical processes for groundwaters in the Algerian Sahara supported by inverse modeling of chemical and isotopic data. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21(3):1669–1691. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-1669-2017
Van Geldern R, Baier A, Subert HL, Kowol S, Balk L, Barth JA (2014) Pleistocene paleo-groundwater as a pristine fresh water resource in southern Germany–evidence from stable and radiogenic isotopes. Sci Total Environ 496:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.011
Verma S, Mukherjee A, Mahanta C, Choudhury R, Mitra K (2016) Influence of geology on groundwater–sediment interactions in arsenic enriched tectono-morphic aquifers of the Himalayan Brahmaputra River basin. J Hydrol 540:176–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.05.041
Weyhenmeyer CE, Burns SJ, Waber HN, Macumber PG, Matter A (2002) Isotope study of moisture sources, recharge areas, and groundwater flow paths within the eastern Batinah coastal plain Sultanate of Oman. Water Resour Res 38(10):21–222. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000WR000149
Williams AE, Rodoni DP (1997) Regional isotope effects and application to hydrologic investigations in southwestern California. Water Resour Res 33(7):1721–1729. https://doi.org/10.1029/97WR01035
Yang N, Wang G, Shi Z, Zhao D, Jiang W, Guo L, Liao F, Zhou P (2018) Application of multiple approaches to investigate the hydrochemistry evolution of groundwater in an Arid Region: Nomhon Northwestern China. Water 10(11):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111667
Yang J, Ye M, Tang Z, Jiao T, Song X, Pei Y, Liu H (2020) Using cluster analysis for understanding spatial and temporal patterns and controlling factors of groundwater geochemistry in a regional aquifer. J Hydrol 583:124594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124594
Yangui H, Zouari K, Trabelsi R, Rozanski K (2011) Recharge mode and mineralization of groundwater in a semi-arid region: Sidi Bouzid plain (central Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 63(5):969–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0771-4
Ye C, Zheng M, Wang Z, Hao W, Wang J, Lin X, Han J (2015) Hydrochemical characteristics and sources of brines in the Gasikule salt lake, Northwest Qaidam Basin China. Geochem J 49(5):481–494. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.2.0372
Yidana SM, Ophori D, Banoeng-Yakubo B (2008) A multivariate statistical analysis of surface water chemistry data—the Ankobra Basin Ghana. J Environ Manage 86(1):80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.11.023
Zeng Z (1997) The background features and formation of chemical elements of groundwater in the region of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Geol Sin 71(1):80–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.1997.tb00348.x
Zhang Y, Tian Y, Shen M, Zeng G (2018) Heavy metals in soils and sediments from Dongting Lake in China: occurrence, sources, and spatial distribution by multivariate statistical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):13687–13696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1590-5
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Zwahlen F, Boillat J (2013) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of central Jianghan Plain China. Environ Earth Sci 68(3):765–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1778-9
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2007AA06Z418), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20577036, 20777058, 20977070), the National Natural Science Foundation of Hubei province in China (No. 2015CFA137), China Geological Survey (DD20160290), and the Open Fund of Hubei Biomass-Resource Chemistry and Environmental Biotechnology Key Laboratory, and the Fund of Eco-environment Technology R&D and Service Center (Wuhan University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, M., Zhou, P. Hydro-geochemical evolution characteristics of shallow groundwater in northeast of Jianghan Plain, China. Carbonates Evaporites 36, 71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00739-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00739-0