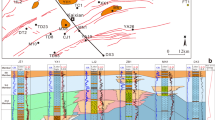
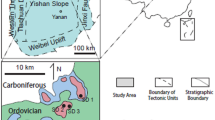
Abstract
Great breakthroughs have been recently made in exploring oil and gas in the Middle Permian Qixia Formation, the southwestern Sichuan Basin, China. These discoveries in dolomitic reservoirs revealed abundant hydrocarbon reserves, agreeing on traditional predictions associated with dolomite prospect, which also left the controversy about the nature of dolomitization. Therefore, it is particularly important to research dolomite reservoirs characteristics and their genesis. In this study, comprehensive analyses, including pore-casted thin-section observation, scanning electron microscopy, physical property analysis, mercury injection measurement, fluid inclusion test, and isotopic measurement, are carried out to characterize Qixia Formation dolomites that are sampled from five outcrop sections and nine wells, followed by an investigation into controlling factors of these characteristics and establishment of pore evolution models. Granular dolomites, especially fine-grained and coarser dolomites, are demonstrated to be the best reservoir rocks, with their reservoir capacity positively related to dolomite grain sizes. There are mainly four types of pore-throat structures, namely large pores with wide throats, medium pores with medium throats, small pores with narrow throats, and fracture pore-throat structure. Dolomite reservoirs in the study area have experienced complex diagenetic changes, including the meteoric water dissolution in the penecontemporaneous stage, dolomitization in the shallow-burial stage, and hydrothermal- and formation water-related dissolution during the middle-deep burial stage. High-quality reservoirs are mainly distributed in the shoal facies deposits, especially where both dolomitization and multi-stage dissolution have occurred.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JE, Rhodes ML (1960) Dolomitization by seepage refluxion. AAPG Bull 44:1912–1920
Amthor J, Mountjoy E, Machel H (1994) Regional-scale porosity and permeability variations in Upper Devonian Leduc buildups: implications for reservoir development and prediction in carbonates. AAPG Bull 78(10):1541–1559
Azmy K, Lavoie D, Knight I, Chi GX (2008) Dolomitization of the Lower Ordovician Aguathuna Formation carbonates, Port au Port Peninsula, western Newfoundland, Canada: implications for a hydrocarbon reservoir. Can J Earth Sci 45(8):795–813
Baker PA, Kastner M (1981) Constraints on the formation of sedimentary dolomite. Science 213(4504):214–216
Chen MQ (1989) A discussion of the origin of Yangxin dolomite of Lower Permian in Southwest Sichuan. Acta Sedimentol Sin 7(2):45–50
Chen DZ, Qian YX (2017) Deep or super-deep dolostone reservoirs: opportunities and challenges. J Palaeogeogr 19(2):187–196
Choquette P, Hiatt E (2008) Shallow-burial dolomite cement: a major component of many ancient sucrosic dolomites. Sedimentology 55(2):423–460
Daives GR, Smith LB (2011) Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: an overview. AAPG Bull 90(11):1641–1690
Deng HC, Zhou W, Guo R (2014) Pore structure characteristics and control factors of carbonate reservoirs: the Middle-Lower Cretaceous formation, AI Hardy cloth Oilfield, Iraq. Acta Petrol Sin 30(3):801–812
Denison RE, Kirkland DW, Evans R (1998) Using strontium isotopes to determine the age and origin of gypsum and anhydrite beds. J Geol 106:1–17
Dolomieu D, Lettre ÀMP (1796) Professeur de physique à Genève et membre de la Société royale de Londres, sur la chaleur des laves et sur les concrétions quartzeuses. J Mines IV(22):53–72
Friedman I, Sanders JE (1967) Origin and occurrence of dolostone. In: Chilingar GV, Bissel HJ, Fairbridge RW (eds) Carbonate rocks. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 267–348
Halley RB, Schmoker J (1983) High porosity Cenozoic carbonate rocks of south Florida: progressive loss of porosity with depth. AAPG Bull 67(2):191–200
Hao Y, Zhou JG, Zhang JY, Ni C, Gu MF, Xin YG (2013) The dolostone reservoirs from the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin: characteristics and controlling factors. Sedim Geol Tethyan Geol 33(1):68–74
Huang SJ, Qing HR, Hu ZW (2007) Closed-system dolomitization and the significance for petroleum and economic geology: An example from Feixianguan carbonates, Triassic, NE Sichuan Basin of China. Acta Petrol Sin 23(11):2955–2962
Huang D, Wang H, Chen LM, Yuan XL, Shi XW (2012a) Geologic origin of aquifer with high resistivity in the carbonate reservoirs in South China: a case study from the Lower Permian Qixia Formation in West Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind 32(11):22–26
Huang SJ, Li XN, Huang KK, Lan Y, Jie L (2012b) Authigenic noncarbonate minerals in hydrothermal dolomite of Middle Permian Qixia Formation in the west of Sichuan Basin. J Chengdu Univ Technol (Science & Technology Edition) 4:343–352
Huang SJ, Huang KK, Lü J, Lan YF (2014) The relationship between dolomite textures and their formation temperature: a case study from the Permian-Triassic of the Sichuan Basin and the Lower Paleozoic of the Tarim Basin. Petrol Sci 11(1):39–51
Huang QY, Liu W, Zhang YQ, Shi SY, Wang K (2015) Progress of research on dolomitization and dolomite reservoir. Adv Earth Sci 30(5):539–551
Huang KK, Zhong YJ, Li XN, Hu ZW (2016) Oxygen and carbon isotopic composition of carbonate rocks of the Permian Qixia formation, Sichuan basin: thermal effects of Emeishan basalt. Earth Sci Res J 20(1):1–9
Hung SJ (1997) A study on carbon and strontium isotopes of Late Paleozoic carbonate rocks in the Upper Yangtze platform. Acta Geol Sin 71(1):45–53
Jones B (2013) Microarchitecture of dolomite crystals as revealed by subtle variations in solubility: implications for dolomitization. Sed Geol 288:66–80
Kırmacı M, Yıldız M, Kandemir R, Eroğlu-Gümrük T (2018) Multistage dolomitization in Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous platform carbonates (Berdiga Formation), Başoba Yayla (Trabzon), NE Turkey: implications of the generation of magmatic arc on dolomitization. Mar Pet Geol 89:515–529
Koehrer BS, Heymann C, Prousa F, Aigner T (2010) Multiple-scale facies and reservoir quality variations within a dolomite body–outcrop analog study from the Middle Triassic, SW German Basin. Mar Pet Geol 27(2):386–411
Kyser TK, James NP, Bone Y (2002) Shallow burial dolomitization and dedolomitization of Cenozoic coolwater limestones, southern Australia: geochemistry and origin. J Sedim Res 2(1):146–157
Lucia FJ, Major RP (1994) Porosity evolution through hypersaline reflux dolomitization//Purser B, Tucker M, Zenger D, eds. Dolomites: A Volume in Honor of Dolomieu. International Association of Sedimentologists Special Publication 21, pp 325–341
Luczaj JA, Harrison WB, Smith WN (2006) Fractured hydrothermal dolomite reservoirs in the devonian dundee formation of the central michigan basin. AAPG Bull 90(11):1787–1801
Machel HG, Buschkuehle BE (2008) Diagenesis of the devonian southesk-cairn carbonate complex, Alberta, Canada: Marine cementation, burial dolomitization, thermochemical sulfate reduction, anhydritization, and squeegee fluid flow. J Sedim Res 78(5):366
McArthur JM (1994) Recent trends in strontium isotope stratigraphy. Terra Nova 6:331–358
Menke HP, Andrew MG, Blunt MJ, Bijeljic B (2016) Reservoir condition imaging of reactive transport in heterogeneous carbonates using fast synchrotron tomography—effect of initial pore structure and flow conditions. Chem Geol 428:15–26
Murray RC (1960) Origin of porosity in carbonate rocks. J Sedim Res 30(1):59–84
Ni ZY, Chen ZH, Li MJ, Yang CY, Wen L, Hong HT, Luo B (2020) Trace element characterization of bitumen constraints on the hydrocarbon source of the giant gas field in Sichuan Basin, South China. Geol J 55:317–329
Rezaee MR, Jafari A, Kazemzadeh E (2006) Relationships between permeability, porosity and pore throat size in carbonate rocks using regression analysis and neural networks. J Geophys Eng 3(4):370–376
Schmoker JW, Halley RB (1982) Carbonate porosity versus depth: a predictable relation for south Florida. AAPG Bull 66(12):2561–2570
Shen P, Zhang J, Song J, Hong H, Tang D, Wang X, Luo W (2015) Significance of new breakthrough in and favorable targets of gas exploration in the Middle Permian system, Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind B 2(5):391–398
Slater BE, Smith LB (2012) Outcrop analog for Trenton-Black River hydrothermal dolomite reservoirs, Mohawk Valley, New York Hydrothermal Dolomite Outcrop, Mohawk Valley, New York. AAPG Bull 96(7):1369–1388
Smith LB Jr (2006) Origin and reservoir characteristics of Upper Ordovician Trenton-Black River hydrothermal dolomite reservoirs in New York. AAPG Bull 90(11):1691–1718
Tan XC, Liu H, Luo B, Liu XG, Mou XH (2011) Primary intergranular pores in oolitic shoal reservoir of lower triassic Feixianguan formation, Sichuan Basin, Southwest China: fundamental for reservoir formation and retention diagenesis. J Earth Sci 22(1):101–114
Vasconcelos C, Mc Kenzie JA, Bernasconi S, Grujic D, Tiens AJ (1995) Microbial mediation as a possible mechanism for natural dolomite formation at low temperature. Nature 377(6546):220–222
Wang YG, Yu XG, Yang Yu, Zhang J (1998) Applications of fluid inclusions in the study of paleo-geotemperature in Sichuan basin. Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci 23(3):285–288
Warren J (2000) Dolomite: occurrence, evolution and economically important associations. Earth-Sci Rev 52(1–3):1–81
Weger RJ, Eberli GP, Baechle GT, Massaferro JL, Sun YF (2009) Quantification of pore structure and its effect on sonic velocity and permeability in carbonates. AAPG Bull 93(10):1297–1317
Weyl PK (1960) Porosity through dolomitization-conservation of mass requirements. AAPG Bull 30(1):85–90
Wierzbicki R, Davis JJ, Al-Aasm I, Harland N (2006) Burial dolomitization and dissolution of Upper Jurassic Abenaki platform carbonates, Deep Panuke reservoir, Nova Scatia, Canada. AAPG Bull 90(11):1843–1861
Yang TB, He ZL, Jin ZK, Zhan JT, Li SN (2020) Pore structure and controlling factors of the ultra-deep Middle Permian dolomite reservoirs, northwestern Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol 41(1):116–131
Zhang YB (1982) Dolomitization in Permian rocks in Sichuan basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica 3(1):29–33
Zhang YF, Tan F, Qu HZ, Zhong ZQ, Liu Y, Luo XS, Wang ZY, Qu F (2017) Karst monadnock fine characterization and reservoir control analysis: a case from Ordovician weathering paleokarst reservoirs in Lungu area, Tarim Basin, NW China. Petrol Explor Dev 44(5):758–769
Zhang BJ, Xie JR, Yin H, Hu X, Wang YF, Yang X, Pei SQ (2018a) Characteristics and exploration direction of the Middle Permian carbonate reservoirs in the Longmenshan mountain areas, western Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind 38(2):33–42
Zhang YF, Tan F, Sun YB, Wang ZY, Yang HQ, Zhao JX (2018b) Differences between reservoirs in the intra-platform and platform margin reef-shoal complexes of the Upper Ordovician Lianglitag Formation in the Tazhong oil field, NW China, and corresponding exploration strategies. Mar Pet Geol 98(12):66–78
Zhang BJ, Yin H, Li RR, Xie C, Wang XX, Pei SQ, Hu X, Yang H, Deng B, Chen X, Li XC (2020) New breakthrough of natural gas exploration in the Qixia Formation of Middle Permian by Well Pingtan 1 in the southwestern Sichuan Basin and its implications. Nat Gas Ind 40(7):34–41
Zhao WZ, Shen AJ, Hu SY, Zhang B, Wang Z (2012) Geological conditions and distributional features of large-scale carbonate reservoirs onshore China. Petrol Explor Dev 39(1):1–12
Zhou JG, Hao Y, Deng HY et al (2019) Genesis and distribution of vuggy dolomite reservoirs of the Lower Permian Qixia Formation and Maokou Formation, western-central Sichuan Basin[J]. Mar Orig Petrol Geol 24(4):67–78
Zou CN, Du JH, Xu CC, Wang ZC, Zhang BM, Wei GQ, Wang TS, Yao GS, Deng SH, Liu JJ, Zhou H, Xu AA, Yang Z, Jiang H, Gu ZD (2014) Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petrol Explor Dev 41(3):278–293
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a science and technology project granted by PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gas Field Company, which is entitled "Research on Oil and Gas Enrichment Conditions of the Lower Permian in Southwestern Sichuan Basin and Evaluation of Exploration Targets" (no. 20170301-03-02) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 41702122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, S., Wang, X., Hu, X. et al. Characteristics and diagenetic evolution of dolomite reservoirs in the Middle Permian Qixia Formation, southwestern Sichuan Basin, China. Carbonates Evaporites 37, 17 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00678-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00678-w