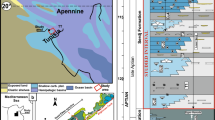
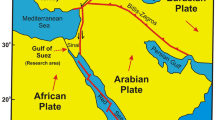
Abstract
Based on their facies characteristics and stratal geometries, the carbonate deposits of the Middle Eocene outcropping in the Tamerza area (Western Gafsa Basin) led to the recognition of nine facies that were deposited in shallow marine environment summarized in a carbonate ramp model: homoclinal ramp under an arid climate. The depiction of facies features and the sequential analysis help to determine the depositional environments and establish the linkage between facies evolution, eustasy, climate and tectonics. The vertical evolution of facies shows a regressive trend that records a transition from infratidal to supratidal environments. The stacking pattern revealed several kinds of meter-scale, shallowing-upward cycles. Each cycle starts with relatively open-marine deposits, which are overlain by shallower and more restricted facies (tidal flat progradation). The varied facies, which are described within the Kef Eddour Formation, compose seven depositional sequences, mainly made of carbonates, marls and phosphates. Fauna associations and sedimentary structures imply a shallow subtidal to intertidal, moderately to high-energy platform. Seven sequences are interpreted as depositional sequences showing retrogradational (lowstand systems tract), aggradational (transgressive systems tract) and progradational (highstand systems tract) packages of facies associations. The seven depositional sequences which show a hierarchical organization of many cycles, as described above, suggested that eustatic sea-level oscillations caused by cyclic perturbations of the Earth’s orbit played a fundamental role in determining the formation of hierarchical cyclic rhythmicity.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed AM, Werner S (1980) A general aspect in the genesis of nodular limestones documented by the upper cretaceous limestones of Jordan. Sed Geol 26(1980):329–335
Aigner T (1985a) Biofabrics as dynamic indications in nummulite accumulation. J Sedim Petrol 55(1):131–134
Aigner T (1985b) Storm depositional systems: dynamic stratigraphy in modern and ancient shallow marine sequences. Lecture notes in earth science, vol 3. Springer, Berlin, p 174
Amberg CE, Collart T, Salenbien W, Egger LM, Munnecke A, Nielsen AT, Vandenbroucke TR (2016) The nature of Ordovician limestone-marl alternations in the Oslo-Asker District (Norway): witnesses of primary glacio-eustasy or diagenetic rhythms? Sci Rep 20:6
Amri A, Ben Youssef M, Ghanmi M (2005) Enregistrement de phénomènes de resédimentation au cours du Maastrichtien supérieur et du Paléocène supérieur (J. Serj, Tunisie atlasique): apport micropaléontologique et signature tectono-eustatique. Comptes Rendus Geosci 20:1525–1531
Badenas B, Aurell M, Bosence D (2010) Continuity and facies heterogeneities of shallow carbonate ramp cycles (Sinemurian, Lower Jurassic, north-east Spain). Sedimentology 57:1021–1048
Ben Haj Ali M, Kadri A, Zagrarni MF, Gaied ME (2002) Les unités lithostratigraphiques de l’Eocène en Tunisie : evolution latérale et actualisation de la nomenclature. Notes serv géol Tunisie 69:60–63
Bishop WF (1975) Geology of Tunisia and adjacent parts of Algeria and Libya. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Bull 59:413–450
Bjorlykke K (1973) Origin of limestone nodules in the Lower Palaeozoic of the Oslo Region. Norsk Geol Tidsskr 53:419–431
Bosence D, Procter E, Aurell M, Bel Kahla A, Boudagher-Fadel M, Casaglia F, Cirilli S, Mehdie M, Nieto L, Rey J, Scherreiks R, Soussi M, Waltham D (2009) A dominant tectonic signal in high-frequency, peritidal carbonate cycles? A regional analysis of Liassic platforms from western Tethys. J Sedim Res 79:389–415
Brett C (1995) Sequence stratigraphy, biostratigraphy, and taphonomy in shallow marine environments. Palaios 10(6):597–616. https://doi.org/10.2307/3515097
Burgess PM (2001) Modeling carbonate sequence development without relative sea-level oscillations. Geology 29:1127–1130
Burgess PM, Wright VP, Emery D (2001) Numerical forward modeling of peritidal carbonate parasequence development: implication for outcrop interpretation. Basin Res 13:1–16
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. Ph.D. Thesis Paris. Annales des Mines et de la Géologie, Tunis, no. 18, p 350
Catuneanu O, Martins-Neto MA, Erikson PG (2005) Precambrian sequence stratigraphy. Sed Geol 176:67–95
Catuneanu O, Abreu V, Bhattacharya JP, Blum MD, Dalrymple RW, Eriksson PG, Fielding CR, Fisher WL, Galloway WE, Gibling MR, Giles KA, Holbrook JM, Jordan R, Kendall CGSTC, Macurda B, Martinsen OJ, Miall AD, Neal JE, Nummedal D, Pomar L, Posamentier HW, Pratt BR, Sarg JF, Shanley KW, Steel RJ, Strasser A, Tucker ME, Winker C (2009) Towards the standardization of sequence stratigraphy. Earth Sci Rev 92:1–33
Chaabani F (1995) Dynamique de la partie orientale du bassin de Gafsa au crétacé et au paléogène. Etude minéralogique et géochimique de la série phosphatée éocène-Tunisie Méridionale. Ph.D. Thesis, Manar II Univ. Tunisia
Chaabani F, Ounis A (2008) Sequence stratigraphy and depositional environment of phosphorite deposits evolution: case of the Gafsa Basin, Tunisia. In: Conference abstract at the international. Geological. Cong, Oslo
Chen D, Tucker ME, Jiang M, Zhu J (2001) Long-distance correlation between tectonic controlled, isolated carbonate platforms by cyclostratigraphy and sequence stratigraphy in the Devonian of South China. Sedimentology 48:57–78
De Wever P, Azéma J, Fourcade E (1994) Radiolaires et radiolarites: production primaire, diagenèse et paléogéographie. Bull Ctr Rech Expl Prod Elf Aquitaine 18:315–379
Dunham RJ (1962) Classification of carbonate rocks according to their depositional texture. In: Ham WE (ed) Classification of carbonate rocksda symposium, vol 1. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, Tulsa, OK, pp 108–121
Flügel E (2004) Microfacies of carbonate rocks: analysis, interpretation and application. Springer, Berlin, p 976
Folk RL (1959) Practical petrographic classification of limestones. Am Assoc Pet Geol 43(1):1–38
Fournie D (1978) Nomenclature lithostratigraphique des séries du crétacé supérieur au tertiaire de Tunisie. Bull Cent Rec Prod Elf Aquitaine 2(1):97–148
Galfati I, Sassi AB, Zaier A, Bouchardon JL, Bilal E, Joron JL, Sassi S (2010) Geochemistry and mineralogy of Paleocene–Eocene Oum El Khecheb phosphorites (Gafsa-Metlaoui Basin) Tunisia. Geochem J 44:189–210
Gourmelen C, Rigane A, Broquet P, Truillet R, Aite MR (2000) Caractères structuraux et dynamique d'un bassin en transtension: la plate-forme tunisienne a l'Yprésien terminal. Bull La Soc Geol 171(5):559–568
Haq BU, Schutter SR (2008) A chronology of Paleozoic sea-level changes. Science 322:64–68
Harwood CA (1985) Facies analysis of shale-nodular limestone cycles from the Upper Ordovician of the Oslo Region, Norway. PhD thesis, University of Liverpool, p 295
Henchiri M (2007) Sedimentation, depositional environment and diagenesis of Eocene biosiliceous deposits in Gafsa basin, southern Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 49:187–200
Henningsmoen GA (1974) Comment. Origin of limestone nodules in the Lower Palaeozoic of the Oslo Region. Norsk Geol Tidsskr 54:401–412
Hilgen FJ, Iaccarino S, Krijgsman W, Villa G, Langereis CG, Zachariasse WJ (2000) The global boundary stratotype and point (GSSP) of the Messinian Stage (Uppermost Miocene). Episodes 23:1–6
Hilgen FJ, Abdul Aziz H, Krijgsman W, Raffi I, Turco E (2003) Integrated stratigraphy and astrochronology of the Serravallian and lower Tortonian at Monte dei Corvi (Middle–Upper Miocene, Northern Italy). Paleogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 199:229–264
Hilgen F, Brinkhuis H, Zachariasse WJ (2006) Unit stratotypes for global stages: theNeogene perspective. Earth Sci Rev 74:113–125
Hüsing SK, Hilgen FJ, Aziz HA, Krijgsman W (2007) Completing the Neogene geological time scale between 8.5 and 12.5 Ma. Earth Planet Sci Lett 253:340–358
Jenkyns HC (1974) Origin of red nodular limestones (Ammonitico Rosso, Knollenkalke) in the Mediterranean Jurassic: a diagenetic model. Int Assoc Sedimentol Spec Publ 1:249–271
Kocsis L, Ounis A, Baumgartner C, Pirkenseer C, Harding I, Adatte A, Chaabani F, Salah MN (2014) Paleocene–Eocene palaeoenvironmental conditions of the main phosphorite deposits (Chouabine Formation) in the Gafsa Basin. Tunisia J Afr Earth Sci 100(2014):586–597
Lee HS, Chough SK (2011) Depositional processes of the Zhushadong and Mantou formations (early to Middle Cambrian), Shandong Province, China: roles of archipelago and mixed carbonate–siliciclastic sedimentation on cycle genesis during initial flooding of the North China platform. Sedimentology 58:1530–1572
Lourens LJ, Hilgen FJ, Laskar J, Shackleton NJ, Wilson D (2004) The Neogene period. In: Gradstein FM (eds) Ogg. Geol J Smith
Marie J, Trouvé P, Desforges G, Dufaure P (1982) Nouveaux éléments de la paléogéographie du Crétacé de la Tunisie. In: Notes Mémoires, no. 19, CFP-Total, Paris, pp 6–37
Mejri F, Burollet PF, Ben Ferjani A (2006) Petroleum geology of 815 Tunisia, a renewed synthesis. Entreprise tunisienne des activites 816 p etroli eres, Tunisia, p 230
Melas P (1982) Etude sédimentologique, paléogéographique et géochimique du Lias carbonaté du Nord- Lodévois. Application à la reconnaissance et à l'interprétation d'amas métallifères. Ph.D. Thesis, Montpellier 2 Univ, France
Messadi AM (2014) Caractères sédimentaires et stratigraphie évènementielle des dépôts de l'intervalle Paléocène-Eocène dans la région de Tamerza. Master, Manar II Univ., Tunisia
Messadi AM, Mardassi B, Ouali JA, Touir J (2016a) Sedimentology, diagenesis, clay mineralogy and sequential analysis model of Upper Paleocene evaporite-carbonate ramp succession from Tamerza area (Gafsa Basin: Southern Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 118:205–230 (ISSN 1464-343X)
Messadi AM, Mardassi B, Ouali JA, Touir J (2016) The undulate levels of Upper Paleocene–Lower Eocene in the Tamerza region: sedimentological characterization, geodynamic significance and contribution in sequential stratigraphy. In: The international symposium on georesources and the environment ISYGE-2016, the Khayam Garden Hotel, Nabeul, Tunisia, 09/2016, p 1
Messadi AM, Mardassi B, Ouali JA, Touir J (2017) Sedimentology, diagenesis, and sequential analysis of a carbonate series in shallow marine environments of the Middle Eocene deposits from Gafsa basin (Southern Tunisia). In: 1st Atlas georesources international congress, Hammamet-Tunisia; 03/2017, p 1
Messadi AM, Mardassi B, Ouali JA, Touir J (2018) Diagenetic process as tool to diagnose paleo-environment conditions, bathymetry and oxygenation during Late Paleocene–Early Eocene in the Gafsa basin. Carbon Evap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-018-0424-3
Messadi AM, Mardassi B, Ouali J, Touir J (2019) Sedimentology, sequential analysis and paleoclimate associations of the upper Paleocene–lower Eocene Chouabine Formation at the Oued Thelja section, Gafsa Basin, Southern Tunisia. Stratigraphy J 20:20
Moller NK, Kvingan K (1988) The genesis of nodular limestones in the Ordovician and Silurian of the OsloRegion (Norway). Sedimentology 35:405–420
Muller J, Fabricius F (1974) Magnesian–calcite nodules in the Ionian deep sea: an actualistic model for the formation of some nodular limestones. Int Assoc Sedimentol Spec Publ 1:235–247
Naish TR, Wehland F, Wilson GS, Browne GH, Cook RA, Morgans HEG, Rosenberg M, King PR, Smale D, Nelson CS, Kamp PJJ, Ricketts B (2005) An integrated sequence stratigraphic, palaeoenvironmental, and chronostratigraphic analysis of the Tangahoe Formation, southern Taranaki coast, with implications for mid-Pliocene (c.3.4–3.0 Ma) glacio-eustatic sea-level changes. J R Soc N Z 35(1–2):151–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/03014223.2005.9517780
Osleger D, Read JF (1991) Relation of eustasy to stacking patterns of meter-scale carbonate cycles, Late Cambrian, USA. J Sediment Petrol 61:1225–1252
Purser BH (1978) Early diagenesis and the preservation of porosity inJurassic limestones. J Pet Geol 1:83–94
Rigane A (1991) Les calcaires de l'Yprésien en Tunisie centro-septentrionale: cartographie, cinématique et dynamique des structures. PHD-Thesis. Franche-Comte Univ, Besançon
Rigane A, Gourmelen C (2011) Inverted intracontinental basin and vertical tectonics: the Saharan Atlas in Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sci 6(2):109–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2011.05.003(ISSN 1464-343X)
Rigane A, Gourmelen C, Broquet P, Truillet R (1994) Originalité des phénomènes tectoniques synsédimentaires fini-yprésiens en Tunisie Centro-septentrionale (région de Kairouan). Bull Soc Géol 156:27–35
Salaj J (1980) Microbiostratigraphie du Cretace et du Paleogene de la Tunisie septentrionale et orientale (Hypostratotypes tunisiens). Inst. Geol. Dionyz Stur, Bratislava, p 238
Sassi S (1974) La sédimentation phosphatée au Paléocène dans le Sud et le Centre Ouest de la Tunisie. Ph.D. Thesis, Paris Univ, France
Schweigl J, Neubauer F (1997) Structural evolution of the central Northern Calcareous Alps: significance for the Jurassic to Tertiary geodynamics in the Alps. Eclogae Geol Helv 90:303–323
Slansky M (1980) Géologie des phosphates sédimentaires. Mémoire du Bureau de recherches géologiques et Minières, p 92
Sramek J (1974) Discussion of Bjorrlykke, K. Origin of limestone nodules in the Lower Palaeozoic of the Oslo region (Nor. Geol. Tidsskr. (53) 419–431). Nor Geol Tidsskr 54:395–396
Strasser A (1991) Lagoonal-peritidal sequences in carbonate environments: autocyclic and allocyclic processes. In: Einsele G, Ricken W, Seo A (eds) Cycles and events in stratigraphy. Springer, Berlin, p 955
Strasser A, Pittet B, Hillgartner H, Pasquier JB (1999) Depositional sequences in shallow carbonate-dominated sedimentary systems: concepts for a high-resolution analysis. Sed Geol 128:201–221
Tucker M, Garland J (2010) High-frequency cycles and their sequence stratigraphic context: orbital forcing and tectonic controls on Devonian cyclicity Belgium. Geol Belg 13(3):213–240
Vail PR, Mitchum RMJR, Todd RJ, Thompson S, Sangrie JB, Bodd JN, Sarg JF (1977) In: Wilgus C (ed) Carbonate sequence stratigraphy in sea-level changes: an integrated approach. SEPM Special Publication No. 42, pp 155–181
Wilson JL (1975) Carbonate facies in geologic history. Springer, New York
Zaier A, Beji-Sassi A, Sassi S, Moody RTJ (1998) Basin evolution and deposition during the Early Paleogene in Tunisia. In: Maggregor DS, Moody RTJ, Clark-Lowes DD (eds) Petroleum geology of North Africa. Geological Society, London, pp 375–393
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the personnel of the Civil Engineering department at the National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS), the Physics Department of the Faculty of Sciences of Bizerte and the personnel of the Higher Institute of Biotechnology of Sfax for their technical support. The authors extend their thanks to Ms Ahmed Ben Rguiga, English professor at the FSEG (Faculty of Economics and Management of Sfax), for patiently proof reading the first version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messadi, A.M., Touir, J., Mardassi, B. et al. Factors controlling sedimentation and sequence stratigraphy evolution in shallow marine (carbonates) platform: example of Middle Eocene deposits from Gafsa Basin. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 58 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00593-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00593-6