Abstract
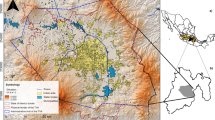
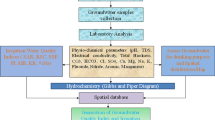
This study aims to assess the groundwater status of a basin in a semi-arid climate, based on the hydrogeochemical, piezometric, statistical and geographic information system (GIS) approach. The region held as an example is the upstream part of the Essaouira basin (Morocco). Analysis of the evolution of the rainfall series by applying the Pettitt and Mann–Kendall tests shows a rainfall deficit of around 14% for the study period (1940–2015). For temperatures and with the application of both tests, an upward trend was observed with a warming of about 2.3 °C for the period 1987–2014. The same trend was observed for ETP, with an increase of around 5 mm for the period 1987–2014. The piezometric study shows a general decrease in the piezometric level over the last 24 years, as a result of the rainfall deficit. The hydrogeochemical approach shows (1) the dominance of the mixed Ca–Mg–Cl and Ca–Cl facies and that by passing from one campaign to another, groundwater generally keeps the same facies; (2) groundwater mineralization is controlled by the phenomenon of dissolution of evaporite and carbonate minerals and by the phenomenon of reverse ion exchange; (3) water quality index (WQI) values show that groundwater quality is becoming increasingly poor from each year to the next. However, the results obtained could be a reference to decision makers to protect this vital resource.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abutaleb KAA, Mohammed AHES, Ahmed MHM (2018) Climate change impacts, vulnerabilities and adaption measures for Egypt’s Nile Delta. Earth Syst Environ 2:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-018-0047-9
Ambrouggi R (1963) Etude géologique du versant méridional du Haut Atlas occidental et de la plaine de Souss. Notes Mém Serv Géol Maroc 157:322
Assani AA (1999) Analyse de la variabilité temporelle des précipitations (1916–1996) à Lubumbashi (Congo-Kinshasa) en relation avec certains indicateurs de la circulation atmosphérique (oscillation australe) et océanique (El Niño/La Niña). Sécheresse 10:245–252
Bahir M, Ouhamdouch S, Carreira PM (2016) La ressource en eau au Maroc face aux changements climatiques; cas de la nappe Plio-Quaternaire du bassin synclinale d’Essaouira. Comun Geol 103(1):35–44
Bahir M, Ouazar D, Ouhamdouch S (2019) Hydrogeochemical investigation and groundwater quality in Essaouira region, Morocco. Mar Freshw Res. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF18319 (article in press)
Boughariou E, Bouri S, Khanfir H, Zarhloule Y (2014) Impacts of climate change on water resources in arid and semi-arid regions: Chaffar sector, eastern Tunisia. Desalin Water Treat 52:2082–2093
Boyacioglu H (2007) Development of a water quality index based on a European classification sheme. Afr J Online (AJOL) 33:101–106
Brown RM, McClelland NI, Deininger RA, Tozer RG (1970) A water quality index: do we dare? Water Sew Works 117:339–343
Duffaud F (1960) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique du bassin secondaire du Haut Atlas occidental (Sud-Ouest du Maroc). Bull Soc Geol Fr 7:728–734
Duffaud F, Brun L, Planchot B (1966) Bassin du Sud-Ouest Marocain (SW Morocco Basin). In: Reyre (ed) Bassin sédimentaire du littoral Africain, partie I, Paris, pp 5–12
El Gayar A, Hamed Y (2018) Climate change and water resources management in Arab countries. In: Kallel A et al. (eds), Recent advances in environmental science from the Euro Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation, pp 89–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70548-4-31
Hamlat A, Guidoum A (2018) Assessment of groundwater quality in a semiarid region of northwestern Algeria using water quality index (WQI) A. Appl Water Sci 8:220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0863-y
Horton RK (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. J Water Pollut Control Feder 37:300–306
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013, the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, TF Stocker, D Qin, GK Plattner, M Tignor, SK Allen, J Boschung, A Nauels, Y Xia, V Bex and PM Midgley (eds). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535
Jalal M, Blavoux B, Bahir M, Bellion Y, Laftouhi N, Puig JM, Mennani A, Daniel M (2001) Etude du fonctionnement du système aquifère karstique cénomano-turonien de l’oued Igrounzar (Bassin d’Essaouira, Maroc). J Afr Earth Sci 32:803–817
Kammoun S, Trabelsi R, Re V, Zouari K, Henchiri J (2018) Groundwater quality assessment in semi-arid regions using integrated approaches: the case of Grombalia aquifer (NE Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 190:87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6469-x
Kendall MG (1975) Multivariate nonparametric tests for trend in water quality. Water Resour Bull 24:505–512
Latha SP, Rao NK (2010) Assessment and spatial distribution of quality of groundwater in zone-II and III, greater Visakhapatnam, India using water quality index (WQI) and GIS. Int J Environ Sci 1:198–212
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrical 13:245–259
Mousannif A (1976) Inventaire et évaluation des ressources en eau du synclinal d’Essaouira-Chechaoua (Maroc). Thèse de doctorat, Université des Sciences et Techniques Languedoc, France
Nicholson SE (1986) The spatial coherence of African rainfall anomalies: interhemispheric teleconnections. J Clim Appl Meteorol 25:1365–1381
Ouhamdouch S, Bahir M, Carreira P (2018a) Impact du changement climatique sur la ressource en eau en milieu semi-aride: exemple du bassin d’Essaouira (Maroc). RSE 31:13–27
Ouhamdouch S, Bahir M, Carreira PM (2018b) Impact du changement climatique sur la ressource en eau en milieu semi-aride : exemple du bassin d'Essaouira (Maroc). RSE 31(1):13–27
Ouhamdouch S, Bahir M, Ouazar D, Zouari K, Carreira PM (2019) Evaluation of climate change impact on groundwater from semi-arid environment (Essaouira Basin, Morocco) using integrated approaches. Environ Earth Sci 78(15):449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8470-2
Pettitt AN (1979) A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. Appl Stat 28:126–135
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Rao NS (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur district Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 49:413–429
Ravikumar P, Mehmood MA, Somashekar RK (2013) Water quality index to determine the surface water quality of Sankey tank and Mallathahalli Lake, Bangalore urban district, Karnataka. India Appl Water Sci 3(1):247–261
Rodier J, Legube B, Merlet N, et al (2009) L’Analyse de l’eau. 9e édition, Dunod, p 1203. ISBN 978-2-10-054179-9
Srinivas Y, Hudson Oliver D, Stanley Raj A, Chandrasekar N (2013) Evaluation of groundwater quality in and around Nagercoil town, Tamil Nadu, India: an integrated geochemical and GIS approach. Appl Water Sci 3:631–651
Tiwari AK, Singh AK, Mahato MK (2018) Assessment of groundwater quality of Pratapgarh district in India for suitability of drinking purpose using water quality index (WQI) and GIS technique. Sustain Water Resour Manag 4:601–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0144-1
Trabelsi N, Triki I, Hentati I, Zairi M (2016) Aquifer vulnerability and seawater intrusion risk using GALDIT, GQISWI and GIS: case of a coastal aquifer in Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 75:669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5459-y
Tyagi S, Sharma B, Singh P, Dobhal R (2013) Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am J Water Resour 1(3):34–38
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editor-in-chief, the associate editor who handled this manuscript and the anonymous reviewers who greatly improved an early version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahir, M., Ouhamdouch, S., Ouazar, D. et al. Assessment of groundwater quality from semi-arid area for drinking purpose using statistical, water quality index (WQI) and GIS technique. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00564-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00564-x