Abstract
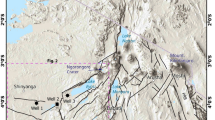
Kuhe-Lar sedimentary phosphate deposit is a major phosphate prospect located in Zagros folded basin in the flank of the Kuhe-Lar-anticline in the southeast of Iran. Phosphate deposits in the Middle East extend in Neo-Tethys basin rim through several countries from North Africa, Syria, Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Oman. The sedimentary phosphate mineralization occurred in the Pabdeh Formation, which is comprised of a marl, limestone, and shale sequence. Based on comprehensive field and laboratory studies, facies zones, standards microfacies, and standard ramp microfacies were recognized in the Pabdeh Formation. Sedimentary features such as tempestite, hummocky cross stratification, ripple marks, couplets of fine and coarse laminae, erosional surface, graded bedding, and shell lag features strongly supported a high-energy storm and shallow water depositional conditions. The main evidence of storm origin for the Pabdeh Formation is the occurrence of sandstones interbedded with bioturbated mudstones commonly as upward fine grade forms. Negative carbon isotopic composition (δ13C, − 1.85 to − 4.89) of bulk phosphatic rock shows that it may be formed within the suboxic-to-anoxic zone, almost 100-cm depths (under seafloor). These values are within the range of recent and ancient phosphorites, suggesting their good preservation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adabi MH, Kakemem U, Sadeghi A (2016) Sedimentary facies depositional environment and sequence stratigraphy of oligocene–miocene shallow water carbonate from the rig mountain, Zagros basin (SW Iran). Carbonates Evaporites 31:69–85
Al-Bassam KS (1980) Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of some marine sedimentary apatites from Iraq. Econ Geol 75:1231–1233
Al-Bassam KS, Al-Dahan AA, Jamil AK (1983) Campanian-Maastrichtian phosphorites of Iraq, Petrology, geochemistry and genesis. Miner Depos 18:215–233
Aba-Hussain AA, Al-Bassam KS, Al-Rawi YT (2010) Rare earth elements geochemistry of some paleocene carbonate fluorapatites in Iraq. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 6(1):81–94
Al-Sharhan AS, Nairn AEM (1997) Sedimentary basins and petroleum geology of the middle east. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 843
Asadi Mehmandousti E, Adabi MH, Bowden SA, Alizadeh B (2015) Geochemical investigation, oil–oil and oil–source rock correlation in the Dezful Embayment, Marun Oilfield, Zagros, Iran, Marine and Petroleum Geology, vol 68
Asfahani J, Aissa M, Al-Hent R (2005) Statistical factor analysis of aerial spectrometric data, Al-Awabed area, Syria: a useful guide for phosphate and uranium exploration. Appl Radiat Isot 62:649–661
Barber DA (1974) The absorption of ions by microorganisms and excised roots. New Phytol 73:91–96
Benni T (2013) Phosphate deposits of Iraq, Geological Survey of Iraq. In: UNFC workshop, Santiago, Chile, (July 9–12, 2013), pp 1–18. (https://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/energy/se/pp/unfc_egrc/unfc_ws_IAEA_CYTED_UNECE_Santiago_July2013/12_July/4_Benni_Iraq_PhosDepos.pdf). Accessed 12 July 2013
Berberian M, King G (1981) Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18:210–265
Burnett WC (1980) Apatiteglauconite associations off Peru and Chile: palaeooceanographic implication. J Geol Soc London 137:757–764
Bolourchifard F, Memar A (2015) The study of phosphate rock forming minerals (francolite) of Iran through the EDX-SEM to assessment of compositions in nano-scale. Proc Mater Sci 11:108–113
Brookfield MN, Hemmings DP, Van Straaten P (2009) Paleoenvironments and origin of the sedimentary phosphorites of the Napo Formation (Late Cretaceous, Oriente Basin, Ecuador). J S Am Earth Sci 28:180–192
Burchette T, Wright V (1992) Carbonate ramp depositional systems. Sed Geol 79:3–57
Compton JS, Hodell DA, Garrido JR, Mallinson DJ (1993) Origin and age of phosphorite from the south-central Florida Platform: Relation of phosphogenesis to sea-level fluctuation 13C excursion. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:131–146
Darvishzad B, Ghasemi-Nejad E, Ghourchaei S, Keller G (2007) Planktonic foraminiferal biostratigraphy and faunal turnover across the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary in southwestern Iran. J Sci Iran 18:139–149
Dehghani G, Makris J (1984) The gravity field and crustal structure of Iran. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie 168:215–229
Diaz J, Ellery I, Benitez-Nelson C, Paterson D, de Jonge MD, McNulty I, Brandes JA (2008) Marine polyphosphate: a key player in geologic phosphorus sequestration. Science 320(2008):652–655
Dickson J (1965) A modified staining technique for carbonates in thin section. Nature 205:587
Dumas S, Arnott R (2006) Origin of hummocky and swaley cross-stratification—the controlling influence of unidirectional current strength and aggradation rate. Geology 34:1073–1076
Dunham RJ (1962) Classification of carbonate rocks according to their depositional texture. In: Ham WE (Ed) Classification of carbonate rocks—a symposium. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, Tulsa, Ok, vol 1, pp 108–121
Flügel E (2010) Integrated facies analysis. Microfacies of carbonate rocks. Springer, Berlin, pp 641–656
Gerhard E (2000) Sedimentary Basins evolution, facies and sediment budget, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Guilbert JM, Park CF (2007) The geology of ore deposits. Waveland Press, Long Grove
Haq BU (2009) Sequence stratigraphy, sea-level change, and significance for the deep sea. Sedimentation, Tectonics and Eustasy. Int Assoc Sedimentol Spec Publ 12:3–39
Heydari E (2008) Tectonics versus eustatic control on supersequences of the Zagros Mountains of Iran. Tectonophysics 451:56–70
Jarvis I (1980) Geochemistry of phosphatic chalks and hardgrounds from the Santonian to early Campanian (Cretaceous) of northern France. J Geol Soc 137:705–721
Jarvis I (1992) Sedimentology, geochemistry and origin of phosphatic chalks: the upper cretaceous deposits of NW Europe. Sedimentology 39:55–97
John CM, Mutti M, Adatte T (2003) Mixed carbonate-siliciclastic record on the North African margin (Malta)—coupling of weathering processes and mid Miocene climate. Geol Soc Am Bull 115:217–229
Joudaki M, Baghbani D (2018) Biostratigraphy of Oligocene and Lower Miocene deposits, Anneh Anticline, Folded Zagros, SW of Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 33:509–515
Leturmy P, Robin C (2010) Tectonic and stratigraphic evolution of Zagros and Makran during the Mesozoic–Cenozoic: introduction. Geol Soc Lond Special Publ 330:1–4
McArthur JM (1980) Post-depositional alteration of the carbonate-flourapatite phase of Moroccan phosphates. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Special Publ 29:53–60
McArthur JM (1985) Francolite geochemistry-compositional controls during formation, diagenesis, metamorphism, and weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:23–35
McArthur JM, Benmore RA, Coleman ML, Soldi C, Yeh HW, O‘Brien, GW (1986) Stable isotopic characterization of francolite formation. Sci Lett 77:20–34
McArthur JM, Hamilton PJ, Greensmith JT, Boyce AJ, Fallick AE, Birch G, Walsh JN, Benmore RA, Coleman ML (1987) Phosphorite geochemistry: isotopic evidence for meteoric alteration of francolite on a local scale. Chem Geol (Isotopic Geoscience Section) 65:415–425
McCrory VL, Walker RG (1986) A storm and tidally-influenced prograding shoreline—upper cretaceous milk river formation of Southern Alberta, Canada. Sedimentology 33:47–60
Mohajjel M, Fergusson CL, Sahandi MR (2003) Cretaceous-Tertiary convergence and continental collision, Sanandaj-Sirjan Zone, western Iran. J Asian Earth Sci 21:379–412
Mohseni H, Al-Aasm I (2004) Tempestite deposits on a storm-influenced carbonate ramp: an example from the Pabdeh Formation (Paleogene), Zagros Basin, SW Iran. J Pet Geol 27:163–178
Motiei H (2003) Stratigraphy of Zagros, treatise on the geology of Iran. Geology Survey Press, Tehran, p 583
Nathan Y, Nielsen H (1980) Sulfur isotopes in phosphorites. In: Bentor Y, Marine phosphorites. The Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEPM) (Special Publications), vol 29, pp 73–78
Navabpour P, Barrier E (2012) Stress states in the Zagros fold-andthrust belt from passive margin to collisional tectonic setting. In: Gudmundsson A, Bergerat F, Crustal stresses, fractures, and fault zones: the Legacy of Jacques Angelier, Tectonophysics, vol 581, pp 76–83
Notholt A, Sheldon R, Davidson D (2005) Phosphate deposits of the world: volume 2, phosphate rock resources. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Özgüner AM, Varol B (2009) The genesis, mineralization, and stratigraphic significance of phosphatic/glauconitic condensed limestone unit in the Manavgat Basin, SW Turkey. Sediment Geol 221:40–56
Parrish JT (1987) Lithology, geochemistry, and depositional environment of the Shublik Formation (Triassic), northern Alaska. In: Tailleur IL, Weimer P (eds) Alaskan north slope geology, volume 1: Pacific section. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists and Alaska Geological Society, vol 50, pp 391–396
Parrish JT (1990) Paleoceanographic and paleoclimatic setting of the Miocene phosphogenic episode. Phosphate Depos Filipelli Delaney Phosphorus Continent Weather World 3:223–240
Parrish JT, Curtis RL (1982) Atmospheric circulation, upwelling, and organic-rich rocks in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 40:3–66
Parrish JT, Droser ML, Bottjer DJ (2001) A Triassic upwelling zone: the Shublik formation. Arctic Alaska, USA. J Sediment Res 71:272–285
Rees A, Thomas A, Lewis M, Hughes H, Turner P (2014) Lithostratigraphy and palaeoenvironments of the Cambrian in SW Wales. Geol Soc Lond Mem 42:33–100
Sadaqah RM, Abed AM, Grimm KA, Pufahl PK (2007) Oxygen and carbon isotopes in Jordanian phosphorites and associated fossils. Sci Direct J Asian Earth Sci 29:803–812
Şengör A (1990) A new model for the late Palaeozoic–Mesozoic tectonic evolution of Iran and implications for Oman. Geol Soc Lond Special Publ 49:797–831
Sepehr M, Cosgrove J (2004) Structural framework of the Zagros fold—thrust belt, Iran. Mar Pet Geol 21:829–843
Sheldon RP (1980) Episodicity of phosphate deposition and deep ocean circulation-a hypothesis. Copyright©2012. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Special Publ 29:239–247
Shemesh A, Kolodny Y, Luz B (1983) Oxygen isotope variation in phosphate of biogenic apatites. II. Phosphorite rocks. Earth Planet Sci Lett 64:405–416
Shemesh A, Kolodny Y, Luz B (1988) Isotopic geochemistry of oxygen and carbon in phosphate and carbonate of Phosphorite francolite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2565–2572
Sherkati S, Letouzey J (2004) Variation of structural style and basin evolution in the central Zagros (Izeh zone and Dezful Embayment), Iran. Mar Pet Geol 21:535–554
Swe SM, Masanori O (2012) Investigation of Cd contents in several phosphate rocks used for the production of fertilizer. Microchem J 104:17–21
Tribovillard N, Algeo T, Lyons T, Riboulleau A (2006) Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies. An update. Chem Geol 232:12–32
Tribovillard N, Recourt P, Trentesaux A (2010) Bacterial Calcification as a possible trigger for francolite precipitation under sulfidic condition. Comptes Rendus Geosci 342:27–35
Vanbuchem FSP, Gerdes KD, Esteban M (2010) (eds) Mesozoic and Cenozoic carbonate systems of the Mediterranean and the middle east: stratigraphic and diagenetic reference models. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, vol 329, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp329.10305-8719/10/$15.00%23. The Geological Society of London
Walter RG, Walker RG (1984) Facies models. Geological Association of Canada Geological Association of Canada, St. John’s
Wrobel-Daveau JC, Ringenbach JC, Tavakoli S, Ruiz GMH, Masse P, de Lamotte DF (2010) Evidence for mantle exhumation along the Arabian margin in the Zagros (Kermanshah area, Iran). Arab J Geosci 3:499–513
Zuza AV, Yin A (2009) Balkatach hypothesis: a new model for the evolution of the Pacific, Tethyan, and Paleo-Asian oceanic domains. Geosphere 13(5):1664–1712
Acknowledgements
This research was generously funded by the Government of the Islamic Republic of Iran to Mr. F. Bolourchifard. The correspondent author is greatly indebted to his Ph.D. A critical review of the original draft and valuable comments by Prof. Adabi, M. H. and Dr. Mossadegh, H. improved the manuscript. Logistics for fieldwork and thin-section preparation were provided by Kharazmi University of Tehran (Faculty of Earth Science) (Obituary: Dr. A. Memar K.: unfortunately unexpectedly and, one of the co-authors passed away, which is a great loss).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolourchifard, F., Fayazi, F., Mehrabi, B. et al. Evidence of high-energy storm and shallow water facies in Pabdeh sedimentary phosphate deposit, Kuhe-Lar-anticline, SW Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 34, 1703–1721 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-019-00520-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-019-00520-4