Abstract
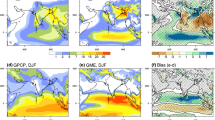
A study of recent climate simulation during the period 1979–2006 is carried out over Bangladesh with Meteorological Research Institute (MRI) global 20 km mesh Atmospheric General Circulation Model (AGCM), called MRI-AGCM. Skills of the model in simulating rainfall and temperature as well as frequency and intensity of extreme events are investigated at various temporal and spatial scales with a focus on mean surface air temperature and rainfall over Bangladesh. Initial and lateral boundary conditions are provided based on the IPCC SRES A1B scenario during the period 1979–2006. The MRI-AGCM shows good performance in simulating meteorological parameters such as rainfall and temperature and exhibits seasonal and inter-annual variations over the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) region including Bangladesh with some persistent biases being present in summer monsoon rainfall. The model successfully simulates temperature over this region with a systematic cold bias due to the East-West temperature gradient. Simulated mean surface air temperature is compared with NCEP/NCAR reanalysis and CRU mean surface air temperature during the period 1979–2006 (28 years) for summer and winter seasons. Outputs from the MRI-AGCM show some fine scale structures that are missed by the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis products due to its coarse resolution. In general, the MRI-AGCM show a predominant cold bias of a few degrees (greater in summer than in winter) throughout the SAARC domain, the MRI-AGCM simulated rainfall shows good agreement with that of CRU and considerable discrepancies are found both with Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) and NCEP rainfall fields in the summer monsoon season. However, model simulated rainfall is relatively in good agreement with NCEP than GPCP. The statistical analysis such as correlation, bias and RMSE are derived between model and all observed data including station data, CRU, NCEP/NCAR and GPCP. Spatial and temporal patterns of summer monsoon rainfall of MRI-AGCM show almost similar pattern with different magnitudes. The high resolution MRI-AGCM rainfall is quantitatively in good agreement with GPCP, NCEP and CRU rainfall.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, R.P., Soden, B.J.: Atmospheric warming and the amplification of precipitation extremes. Science. 321, 1481–1484 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1160787
Allen, M.R., Ingram, W.J.: Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature. 419, 224–231 (2002)
Allen, M.R., Stott, P.A., Mitchell, J.F.B., Schnur, R., Delworth, T.L.: Quantifying the uncertainty in forecasts of anthropogenic climate change. Nature. 407, 617–620 (2000)
Annan, J.D., Hargreaves, J.C.: Reliability of the CMIP3 ensemble. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37, L02703 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL041994
Bates, B.C., Kundzewicz, Z.W., Wu S., Palutikof J.P. (eds.): Climate change and water, technical paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 210 pp., Intergov. Panel on Clim. Change Secr., Geneva (2008)
Christensen, J.H., Christensen, O.B.: Severe summertime flooding in Europe. Nature. 421, 805–806 (2003)
Coppola, E., Giorgi, F.: An assessment of temperature and precipitation change projections over Italy from recent global and regional climate model simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 30, 11–32 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1867.
Coquard, J., Duffy, P., Taylor, K., Iorio, J.: Present and future surface climate in the western USA as simulated by 15 global climate models. Clim. Dyn. 23(5), 455–472 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-004-0437-6
Dai, A., Trenberth, K.E., Karl, T.R.: Global variations in droughts and wet spells:1900-1995. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25(17), 3367–3370 (1998)
Dai, A., Trenberth, K.E., Qian, T.: A global data set of palmer drought severity index for1870-2002: relationship with soil moisture and effects of surface warming. J. Hydrometeorol. 5, 1117–1130 (2004)
Dash, S.K., Kulkarni, M.A., UC Mohanty, K.P.: Changes in the characteristics of rain events in India. J. Geophys. Res. 114, D10109 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010572.
Duan, Q., Phillips, T.J.: Bayesian estimation of local signal and noise in multimodel simulations of climate change. J. Geophys. Res. 115, D18123 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013654
Feng, S.F., Krueger, A.B., Oppenheimer, M.: Linkages among climate change, crop yields and Mexico-US cross-border migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107(32), 14257–14262 (2010)
Gao, X., Pal, J.S., Giorgi, F.: Projected changes in mean and extreme precipitation over the Mediterranean region from latest issue double nested RCM simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L03706 (2006)
Giorgi, F., Mearns, L.O.: Calculation of average, uncertainty range, and reliability of regional climate changes from AOGCM simulations via the “reliability ensemble averaging” (REA) method. J. Clim. 15, 1141–1158 (2002)
Grainger, S., Frederiksen, C.S., Zheng, X.: Modes of interannual variability of southern hemisphere atmospheric circulation in CMIP3 models: assessment and projections. Clim. Dyn. 41, 479–500 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-012-1659-7
Held, I.M., Soden, B.J.: Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 19, 5686–5699 (2006)
Hennessy, K.J., Gregory, J.M., Mitchell, J.F.B.: Changes in daily precipitation under enhanced greenhouse conditions. Clim. Dyn. 13(9), 667–680 (1997)
Hirai, M., Sakashita, T., Kitagawa, H., Tsuyuki, T., Hosaka, M., Oh’izumi, M.: Development and validation of a new land surface model for JMA’s operational global model using the CEOP observation dataset. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 85A, 1–24 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.85A.1
Im, E.-S., Park, E.-H., Kwon, W.-T., Giorgi, F.: Present climate simulation over Korea with a regional climate model using a one-way double-nested system. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 86, 187–200 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00704-005-0215-3
IPCC: Climate Change. The IPCC Scientific Assessment, 1990: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990)
IPCC, 2001: Climate change, 2001: the scientific basis. In: Houghton JT, Ding Y, Griggs DJ, Noguer M, vander Linden PJ, Dai X, Maskell K, Johnson CA (eds) Contribution of working group I to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
IPCC: Climate Change, 2007: the Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Inter-Governmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2007)
Jhun, J.G., Lee, E.G.: A new east Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics of the winter monsoon. J. Clim. 17(4), 711–726 (2004)
Kato, H., Hirakuchi, H., Nishizawa, K., Giorgi, F.: The performance of NCAR RegCM in the simulation of June and January climates over eastern Asia and the high resolution effect of the model. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 6455–6476 (1999)
Kato, H., Nishizawa, K., Hirakuchi, H., Kadokura, S., Oshima, N., Giorgi, F.: Performance of RegCM2.5/NCAR-CSM nested system for the simulation of climate change in East Asia caused by global warming. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 79, 99–121 (2001)
Kim, K.-Y., North, G.: EOFs of harmonizable cyclostionary processes. J. Atmos. Sci. 54, 2416–2427 (1997)
Krishnamurti, T.N., Kishitawal, C.M., Zhang, Z., Larow, T., Bachiochi, D., Williford, E.: Multimodel ensemble forecasts for weather and seasonal climate. J. Clim. 13, 4196–4216 (2000)
Lambert, S.J., Boer, G.J.: CMIP1 evaluation and intercomparison of coupled climate models. Clim. Dyn. 17, 83–106 (2001)
Li, H., Feng, L., Zhou, T.: Multi-model projection of July-august climate extreme changes over China under CO2 doubling. Part I: precipitation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 28, 433–447 (2011)
McAfee, S.A., Russell, J.L., Goodman, P.J.: Evaluating IPCC AR4 cool-season precipitation simulations and projections for impacts assessment over North America. Clim. Dyn. 37, 2271–2287 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-011-1136-8
Mearns, L.O., Giorgi, F., McDaniel, L., Shields, C.: Analysis of variability and diurnal range of daily temperature in a nested regional climate model: comparison with observations and doubled CO2 results. Clim. Dyn. 11, 193–209 (1995)
Meehl, G.A., Arblaster, J.M., Tebaldi, C.: Understanding future patterns of increased precipitation intensity in climate model simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L18719 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL023680
Miao, Y.F., Fang, X.M., Herrmann, M., Wu, F.L., Liu, D.L.: Miocene pollen record of KC-1 core in the Qaidam Basin, NE Tibetan plateau and implications for evolution of the east Asian monsoon. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 299, 30–38 (2011)
Miao, C., Duan, Q., Yang, L., Borthwick, A.G.L.: On the applicability of temperature and precipitation data from CMIP3 for China. PLoS One. 7, e44659 (2012)
Miao, Y., Liu, Y., Dai, Y., Yang, A.: Impact of urbanization on boundary layer structure in Beijing. Clim. Chang. 120, 123–136 (2013)
Mizuta, R., Oouchi, K., Yoshimura, H., Noda, A., Katayama, K., Yukimoto, S., Hosaka, M., Kusunoki, S., Kawai, H., Nakagawa, M.: 20-km-mesh global climate simulations using JMA-GSM model-mean climate states. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 84, 165–185 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.84.165.
Mizuta, R., Adachi, Y., Yukimoto, S., Kusunoki, S.: Estimation of the future distribution of sea surface temperature and sea ice using the CMIP3 multi-model ensemble mean. Technical Report of the Meteorological Research Institute. 56, 28 (2008)
O’Gorman, P.A., Schneider, T.: Scaling of precipitation extremes over a wide range of climates simulated with an idealized GCM. J. Clim. 22, 5676–5685 (2009)
Ou, T., Chen, D., Linderholm, H.W., Jeong, J.H.: Evaluation of global climate models in simulating extreme precipitation in China. Tellus A. 65, 19799 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusa.v65i0.19799
Phillips TJ, Gleckler PJ, 2006: Evaluation of continental precipitation in 20th century climate simulations: The utility of multi-model statistics. Water Resour. Res. 42: https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004313
Rahman MM: A validation of regional climate model simulation with observational data over Bangladesh: M. Phil. thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Library, Dhaka, Bangladesh, (2006)
Rahman, M.M., Nazrul, I.M., Ahmed, A.U., Afroz, R.: Comparison of RegCM3 simulated meteorological parameters in Bangladesh: part I-preliminary result for rainfall. Sri Lankan J. Physics. 8(2007), 1–9 (2007)
Räisänen, J.: How reliable are climatemodels? Tellus A. 59, 2–29 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0870.2006.00211.x
Reichler, T., Kim, J.: How well do coupled models simulate Today's climate? Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 89, 303–311 (2008a)
Reichler, T., Kim, J.: Uncertainties in the climate mean state of global observations, reanalyses, and the GFDL climate model. J. Geophys. Res. 113, D05106 (2008b). https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009278
Scherrer, S.C.: Present-day interannual variability of surface climate in CMIP3 models and its relation to future warming. Int. J. Climatol. 31, 1518–1529 (2011)
Sillmann, J., Kharin, V.V., Zwiers, F.W., Zhang, X., Bronaugh, D.: Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: part 2. Future climate projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118, 2473–2493 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50188
Solomon, S., et al. (eds.): Climate Change, 2007. The Physical Science Basis (Cambridge Univ. Press for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge (2007)
Sugiyama, M., Shiogama, H., Emori, S.: Precipitation extreme changes exceeding moisture content increases in MIROC and IPCC climate models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 571–575 (2010)
Tebaldi, C., Knutti, R.: The use of the multi-model ensemble in probabilistic climate projections. Trans. R. Soc. A. 365(1857), 2053–2075 (2007)
Tebaldi, C., Arblaster, J.M., Hayhoe, K., Meehl, G.A.: Going to the extremes: an intercomparison of model-simulated historical and future changes in extreme events. Clim. Chang. 79, 185–211 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9051-4
Trenberth, K.E.: Atmospheric moisture recycling: role of advection and local evaporation. J. Clim. 12, 1368–1381 (1999)
Trenberth, K.E., Dai, A., Rasmussen, R.M., Parsons, D.B.: The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 84, 1205–1217 (2003)
Wu, T., Li, W., Ji, J., Xin, X., Li, L., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Zhang, F., Wei, M., Shi, X., Wu, F., Zhang, L., Chu, M., Jie, W., Liu, Y., Wang, F., Liu, X., Li, Q., Dong, M., Liang, X., Gao, Y., Zhang, J.: Global carbon budgets simulated by the Beijing climate center climate system model for the last century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 118, 4326–4347 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50320
Xu, Y., Gao, X., Giorgi, F.: Upgrades to the reliability ensemble averaging method for producing probabilistic climate-change projections. Clim. Res. 41, 61–81 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3354/cr00835
Xu, C., Luo, Y., Xu, Y.: Projected changes of precipitation extremes in river basins over China. Quat. Int. 244, 149–158 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2011.01.002
Zhou, T., Yu, R.: Twentieth century surface air temperature over China and the globe simulated by coupled climate models. J. Clim. 19(22), 5843–5858 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The first author is grateful to ICTP, Italy for providing the opportunity for research work at ICTP. The Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD) is acknowledged for providing observational data. We also acknowledge to MRI-Japan to provide high resolution model data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Masahiro Watanabe
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.M., Ferdousi, N., Abdullah, S.M.A. et al. Recent Climate Simulation over SAARC Region Including Bangladesh Using High Resolution AGCM. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 55, 115–134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-018-0077-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-018-0077-0