Abstract
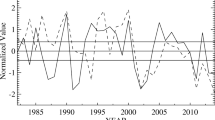
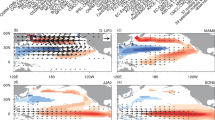
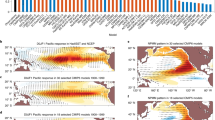
Two leading but independent modes of Northern Pacific atmospheric circulation: the North Pacific Oscillation (NPO) and the Pacific Meridional Mode (PMM), are known external triggers of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) by the sequential migration of sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies into the tropics possibly by means of wind-evaporation-SST (WES) feedbacks. Because of the similar roles of NPO and PMM, most previous studies have explored them with no separation. Here, we investigate their independent and combined effects in triggering ENSO, and find that when the NPO and PMM occur simultaneously during spring, ENSO or ENSO-like SST anomalies are generated during the following winter; whereas when either the NPO or PMM occur alone, ENSO events rarely occur. Furthermore, the relationship between NPO and PMM shows noticeable interdecadal variability, which is related to decadal changes in the mean upper-level jet stream over the North Pacific. Changes in the upper-level jet stream modify the location of the center of the Aleutian Low, which plays a role in bridging the NPO and PMM processes, especially when it migrates to the southwest. The period when NPO and PMM are well correlated coincides somewhat with the active ENSO period, and vice versa, indicating that a more efficient trigger due to combined NPO-PMM processes results in a higher variation of ENSO. Finally, analysis of the coupled model control simulations strongly supports our observational analysis results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M. A., 1992: Midlatitude atmosphere-ocean interaction during El Niño. Part II: the Northern Hemisphere atmosphere. J. Climate, 5, 959–972.
---, I. Bladé, M. Newman, J. R. Lanzante, N.-C. Lau, and J. D. Scott, 2002: The atmospheric bridge: The influence of ENSO teleconnections on air-sea interaction over the global oceans. J. Climate, 15, 2205–2231.
---, and Coauthors, 2006: Extratropical atmosphere-ocean variability in CCSM3. J. Climate, 19, 2496–2525.
---, D. J. Vimont, P. Chang, and J. D. Scott, 2010: The impact of extratropical atmospheric variability on ENSO: Testing the seasonal footprinting mechanism using coupled model experiments. J. Climate, 23, 2885–2901, doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3205.1.
Anderson, B. T., R. C. Perez, and A. Karspeck, 2013: Triggering of El Niño onset through trade wind-induced charging of the equatorial Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, 1212–1216, doi:10.1002/grl.50200.
Ashok, K., S. K. Behera, S. A. Rao, H. Weng, and T. Yamagata, 2007: El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J. Geophys. Res., 112, C11007, doi:10.1029/2006JC003798.
Capotondi, A., 2013: ENSO diversity in the NCAR CCSM4 climate model. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 4755–4770, doi:10.1002/jgrc.20335.
Chang, P., L. Zhang, R. Saravanan, D. J. Vimont, J. C. H. Chiang, L. Ji, H. Seidel, and M. K. Tippett, 2007: Pacific meridional mode and El Niñosouthern oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L16608, doi:10.1029/2007GL030302.
Chiang, J. C. H., and D. J. Vimont, 2004: Analogous Pacific and Atlantic meridional modes of tropical atmosphere-ocean variability. J. Climate, 17, 4143–4158.
---, Y. Fang, and P. Chang, 2009: Pacific climate change and ENSO activity in the mid-Holocene. J. Climate, 22, 923–939.
Compo, G. P., and Coauthors, 2011: The twentieth century reanalysis project. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 1–28, doi:10.1002/qj.776.
Deser, C., A. S. Phillips, R. A. Tomas, Y. M. Okumura, M. A. Alexander, A. Capotondi, J. D. Scott, Y.-O. Kwon, and M. Ohba, 2012: ENSO and pacific decadal variability in Community Climate System Model Version 4. J. Climate, 25, 2622–2651, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00301.1.
Diaz, H. F., and V. Markgraf, 2000: El Niño and the Southern Oscillation: Multiscale Variability and Global and Regional Impacts. Cambridge University Press, 512 pp.
Gent, P. R., and Coauthors, 2011: The community climate system model version 4. J. Climate, 24, 4973–4991, doi:10.1175/2011JCLI4083.1.
Harrison, E. D., and B. S. Giese, 1991: Episodes of surface westerly winds as observed from islands in the western tropical Pacific. J. Geophys. Res., 96, 3221–3237.
Hendon, H. H., M. C. Wheeler, and C. Zhang, 2007: Seasonal dependence of the MJO-ENSO relationship. J. Climate, 20, 531–543.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–471.
Kao, H.-Y., and J.-Y. Yu, 2009: Contrasting eastern-Pacific and central-Pacific types of ENSO. J. Climate, 22, 615–632.
Kerr, R. A., 2000: A North Atlantic climate pacemaker for the centuries. Science, 288, 1984–1986.
Kistler, R., and Coauthors, 2001: The NCEP-NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 82, 247–267.
Kug, J.-S., F.-F. Jin, and S.-I. An, 2009: Two types of El Niño events: Cold tongue El Niño and warm pool El Niño. J. Climate, 22, 1499–1515.
---, M.-S. Ahn, M.-K. Sung, S.-W. Yeh, H.-S. Min, and Y.-H. Kim, 2010: Statistical relationship between two types of El Niño events and climate variation over the Korean Peninsula. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci., 46, 467–474, doi:10.1007/s13143-010-0027-y.
Larkin, N. K., and D. E. Harrison, 2005: On the definition of El Niño and associated seasonal average US weather anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L13705, doi:10.1029/2005GL022738.
Larson, S. M., and B. P. Kirtman, 2014: The Pacific meridional mode as an ENSO precursor and predictor in the North American multimodel ensemble. J. Climate, 27, 7018–7032, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00055.1.
Lau, N.-C., and M. J. Nath, 1996: The role of the “atmospheric bridge” in linking tropical Pacific ENSO events to extratropical SST anomalies. J. Climate, 9, 2036–2057.
Lee, T., and M. J. McPhaden, 2010: Increasing intensity of El Niño in the central-equatorial Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L14603, doi:10.1029/2010GL044007.
Lengaigne, M., E. Guilyardi, J.-P. Boulanger, C. Menkes, P. Delecluse, P. Inness, J. Cole, and J. Slingo, 2004: Triggering of El Niño by westerly wind events in a coupled general circulation model. Climate Dyn., 23, 601–620.
Lin, C.-Y., J.-Y. Yu, and H.-H. Hsu, 2015: CMIP5 model simulations of the Pacific meridional mode and its connection to the two types of ENSO. Int. J. Climatol., 35, 2352–2358, doi:10.1002/joc.4130.
Lindzen, R. S., and S. Nigam, 1987: On the role of sea surface temperature gradients in forcing low-level winds and convergence in the tropics. J. Atmos. Sci., 44, 2418–2436.
Linkin, M. E., and S. Nigam, 2008: The north pacific oscillation-west Pacific teleconnection pattern: Mature-phase structure and winter impacts. J. Climate, 21, 1979–1997.
Mantua, N. J., S. R. Hare, Y. Zhang, J. M. Wallace, and R. C. Francis, 1997: A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 78, 1069–1079.
McPhaden, M. J., S. E. Zebiak, and M. H. Glantz, 2006a: ENSO as an integrating concept in Earth science. Science, 314, 1740–1745.
---, X. Zhang, H. H. Hendon, and M. C. Wheeler, 2006b: Large scale dynamics and MJO forcing of ENSO variability. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, LI6702, doi:10.1029/2006GL026786.
Min, S.-K., and Coauthors, 2015: Changes in weather and climate extremes over Korea and possible causes: A review. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci., 51, 103–121, doi:10.1007/s13143-015-0066-5.
Okajima, H., S.-P. Xie, and A. Numaguti, 2003: Interhemispheric coherence of tropical climate variability: Effect of the climatological ITCZ. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 1371–1386.
Park, J.-Y., J.-G. Jhun, S.-Y. Yim, and W.-M. Kim, 2010: Decadal changes in two types of the western North Pacific subtropical high in boreal summer associated with Asian summer monsoon/El Niño-Southern Oscillation connections. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D21129, doi:10.1029/2009JD013642.
---, S.-W. Yeh, J.-S. Kug, and J. Yoon, 2013: Favorable connections between seasonal footprinting mechanism and El Niño. Climate Dyn., 40, 1169–1181, doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1477-y.
Rogers, J. C., 1981: The North Pacific oscillation. Int. J. Climatol., 1, 39–57.
Smith, T. M., R. W. Reynolds, T. C. Peterson, and J. Lawrimore, 2008: Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land-ocean surface temperature analysis (1880-2006). J. Climate, 21, 2283–2296.
Tang, Y., and B. Yu, 2008: MJO and its relationship to ENSO. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D14, doi:10.1029/2007JD009230.
Taylor, K. E., R. J. Stouffer, and G. A. Meehl, 2012: An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 93, 485–498, doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1.
Vimont, D. J., 2010: Transient growth of thermodynamically coupled variations in the tropics under an equatorially symmetric mean state. J. Climate, 23, 5771–5789, doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3532.1.
---, D. S. Battisti, and A. C. Hirst, 2001: Footprinting: A seasonal connection between the tropics and mid-latitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 3923–3926.
---, ---, and ---, 2003a: The seasonal footprinting mechanism in the CSIRO general circulation models. J. Climate, 16, 2653–2667.
---, J. M. Wallace, and D. S. Battisti, 2003b: The seasonal footprinting mechanism in the Pacific: Implications for ENSO. J. Climate, 16, 2668–2675.
---, M. A. Alexander, and A. Fontaine, 2009: Midlatitude excitation of tropical variability in the Pacific: the role of thermodynamic coupling and seasonality. J. Climate, 22, 518–534.
---, ---, and M. Newman, 2014: Optimal growth of central and East Pacific ENSO events. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 4027–4034, doi:10.1002/2014GL059997.
Walker, G. T., and E. W. Bliss, 1932: World weather V. Mem. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 4, 53–84.
Wang, B., R. Wu, and X. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
Wang, S.-Y., M. L’Heureux, and H.-H. Chia, 2012: ENSO prediction one year in advance using Western North Pacific sea surface temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett., 39, L05702, doi:10.1029/2012GL050909.
---, ---, and J.-H. Yoon, 2013: Are greenhouse gases changing ENSO precursors in the western North Pacific? J. Climate, 26, 6309–6322, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00360.1.
Xie, S.-P., and S. G. H. Philander, 1994: A coupled ocean-atmosphere model of relevance to the ITCZ in the eastern Pacific. Tellus, 46, 340–350.
Yeh, S.-W., J.-S. Kug, and S.-I. An, 2014: Recent progress on two types of El Niño: Observations, dynamics, and future changes. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci., 50, 69–81, doi:10.1007/s13143-014-0028-3.
---, X. Wang, C. Wang, and B. Dewitte, 2015: On the relationship between the North Pacific climate variability and the Central Pacific El Niño. J. Climate, 28, 663–677, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00137.1.
Yu, J.-Y., and H.-Y. Kao, 2007: Decadal changes of ENSO persistence barrier in SST and ocean heat content indices: 1958-2001. J. Geophys. Res., 112, D13106, doi:10.1029/2006JD007654.
---, and S. T. Kim, 2011: Relationships between extratropical sea level pressure variations and the central Pacific and eastern Pacific types of ENSO. J. Climate, 24, 708–720, doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3688.1.
---, H.-Y. Kao, and T. Lee, 2010: Subtropical-related interannual sea surface temperature variability in the central equatorial Pacific. J. Climate, 23, 2869–2884, doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3171.1.
---, M.-M. Lu, and S. T. Kim, 2012: A change in the relationship between tropical central Pacific SST variability and the extratropical atmosphere around 1990. Environ. Res. Lett., 7, 034025, doi:10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/034025.
---, P.-K. Kao, H. Paek, H.-H. Hsu, C.-W. Hung, M.-M. Lu, and S.-I. An, 2015: Linking emergence of the central Pacific El Niño to the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. J. Climate, 28, 651–662, Doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00347.1.
Yuan, X., 2004: ENSO-related impacts on Antarctic sea ice: A synthesis of phenomenon and mechanisms. Antar. Sci., 16, 415–425.
Zhang, L., P. Chang, and L. Ji, 2009: Linking the Pacific meridional mode to ENSO: Coupled model analysis. J. Climate, 22, 3488–3505.
Zhang, Y., J. M. Wallace, and D. S. Battisti, 1997: ENSO-like interdecadal variability: 1900-93. J. Climate, 10, 1004–1020.
Zhou, T., B. Wu, and L. Dong, 2014: Advances in research of ENSO changes and the associated impacts on Asian-Pacific climate. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci., 50, 405–422, doi:10.1007/s13143-014-0043-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, SJ., An, SI. Interdecadal Change in the Relationship Between the North Pacific Oscillation and the Pacific Meridional Mode and Its Impact on ENSO. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 54, 63–76 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-017-0060-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-017-0060-1