Abstract
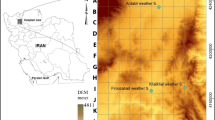
A soil moisture retrieval algorithm using AMSR-E microwave satellite data has been developed by the National Institute of Meteorological Research (NIMR). This algorithm is based on a simple inversion method that does not require a prior soil texture data. In this study, the relationship between soil moisture retrieved from the NIMR algorithm and the occurrence of Asian dust (Hwangsa) is statistically analyzed. The frequency of occurrence of Asian dust events was recorded at 410 sites in China from 2003–2010 in three regions; the Gobi desert, Inner Mongolia and Northeast China. Results showed low soil moisture values of around 0.1 g cm−3 in the Gobi desert and Inner Mongolia-lowest in summer and a little higher in winter. Soil moisture values in Northeast China were marginally higher than in other regions, but lowest in winter and higher in summer. About 55% of Asian dust in the Gobi desert occurred when the monthly mean soil moisture was less than the monthly mean soil moisture for eight years. Approximately 75% of Asian dust in Northeast China occurred when soil moisture was the same as the monthly mean soil moisture for eight years. While soil moisture in the Gobi desert and Inner Mongolia declined in spring, it increased in Northeast of China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albergel, C., and Coauthors, 2010: Cross-evaluation of modelled and remotely sensed surface soil moisture with in situ data in southwestern France. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci, 14, 2177–2191.
De Jeu, R. A. M., and M. Owe, 1994: Microwave vegetation optical depth and signal scattering albedo from larg scale soil moisture and Nimbus/SMMR satellite observations. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 54, 225–239.
Fécan, F., B. Marticorena, and G. Bergametti, 1999: Parameterization of the increase of the aeolian erosion threshold wind friction velocity due to soil moisture for arid and semi-arid areas. Ann. Geophys., 17, 149–157.
Felde, G. W., 1998: The effect of soil moisture on the 37 GHz Microwave Polarization Difference Index (MPDI). Intl. J. Remote Sens., 19, 1055–1078.
Gong, D.-Y., R. Mao, P.-J. Shi, and Y.-D. Fan, 2007: Correlation between East Asian dust storm frequency and PNA. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L14710.
Hong, S.-W., 2009: Retrieval of refractive index over specular surfaces for remote sensing applications. J. Appl. Remote Sens., 3, 033560.
_____, and I. Shin, 2011: A physically-based inversion algorithm for retrieving soil moisture is passive microwave remote sensing. J. Hydrol., 405, 24–30.
Ishizuka, M., M. Mikami, Y. Yamada, F. Zeng, and W. Gao, 2005: An observational study of soil moisture effects on wind erosion at a gobi site in the Taklimakan Desert. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D18S03.
Jackson, T, 1993: Measuring surface soil moisture using passive microwave remote. Hydrol. Process., 7, 139–152.
Jarlan, L, S. Mangiarotti, E. Mougin, P. Mazzega, P. Hiernaux, and V. Le Dantec, 2008: Assimilation of SPOT/VEGETATION NDVI data into a sahelian vegetation dynamics model. Remote Sens. Environ., 112, 1381–1394.
Kurosaki, Y., and M. Mikami, 2002: Seasonal and regional characteristics of dust event in the Taklimakan Desert. J. Arid Land Studies, 11, 245–252.
_____, and ______, 2003: Recent frequent dust events and their relation to surface wind in East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, 1736.
Laurent, B., B. Marticorena, G. Bergametti, P. Chazette, F. Maignan, and C. Schmechtig, 2005: Simulation of the mineral dust emission frequencies from desert areas of China and Mongolia using an aerodynamic roughness length map derived from the POLDER/ADEOS 1 surface products. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D18S04.
Lee, E.-H., and B.-J. Sohn, 2009: Examining the impact of wind and surface vegetation on the Asian dust occurrence over three classified source regions. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D06205.
Lim, J.-Y., and Y. Chun, 2006: The characteristics of Asian dust events in Northeast Asia during the springtime from 1993 to 2004. Global Planet. Change, 53, 231–247.
Marticorena, B., and G. Bergametti, 1995: Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle: 1. Design of a soil-derived dust emission scheme. J. Geophys. Res., 100, 16415–16430.
Mo, T., B. J. Choudhury, J. J. Schmugge, and T. J. Jackson, 1982: A model for microwave emission from vegetation covered fields. J. Geophys. Res., 87, 11229–11237.
Meesters, A. G. C. A., R. A. M. de Jeu, and M. Owe, “Analytical derivation of the vegetation optical depth from the microwave polarization difference index”. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. letter., 2, 121–123, 2005.
Njoku, E. G., J. J. Thomas, L. Venkataraman, T. K. Chan, and S. V. Nghiem, 2003: Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 42, 215–229.
Owe, M., R. A. M. De Jeu, and J. Walker, 2001: A methodology for surface soil moisture and vegetation optical depth retrieval using the microwave polarization difference index. IEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 39, 1643–1654.
Park, H.-S., and B. J. Sohn, 2010: Recent trends in changes of vegetation over East Asia coupled with temperature and rainfall variations. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D14101.
Park, S.-U., A. Choe, E.-L. Lee, M.-S. Park, and X. Song, 2010: The Asian dust aerosol models 2 (ADAM 2) with the use of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) obtained from the Spot4/vegetation data. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 101, 191–209.
Topp, G. C, J. L. Davis, and A. P. Annan, 1980: Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res., 16, 571–582.
Shao, Y., and H. Lu, 2000: A simple expression for wind erosion threshold friction velocity. J. Geophys. Res., 105, 22437–22443.
Sun, J., M. Zhang, and T. Liu, 2001: Spatial and temporal characteristics of dust storms in China and its surrounding regions, 1960–1999: Relations to source area and climate. J. Geophys. Res., 106(D10), 10325–10333.
Wang, S., J. Wang, Z. Zhou, and K. Shang, 2005: Regional characteristics of three kinds of dust storm events in China. Atmos. Environ., 39, 509–520.
Zou, X. K., and P. M. Zhai, 2004: Relationship between vegetation coverage and spring dust storms over northern China. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D03104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Ou, ML., Ryoo, SB. et al. Soil moisture retrieved from microwave satellite data and its relationship with the Asian dust (Hwangsa) frequency in East Asia during the period from 2003 to 2010. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 49, 527–534 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-013-0046-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-013-0046-6